What is Sodium Citrate (E331) in food? Types, Uses and Safety

Three Types | Production | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Sodium citrate, the sodium salts of citric acid with the European food additive number E331. This ingredient is usually added together with citric acid to enhance flavor or reduce the PH level in food and drinks, also it can act as an emulsifier in cheese making. It commonly refers to trisodium citrate (E331iii) when we talk about sodium citrate.
3 Types of sodium citrate
As there are three carboxyl groups in the molecule of citric acid, so there can be three types of sodium citrates (mono, di and trisodium citrate) based on the partial or total neutralization of citric acid. Among them, trisodium citrate is the most used one in food, while disodium citrate is seldom to see in food.
Monosodium citrate
Also known as sodium dihydrogen citrate, is a monobasic salt of citric acid with a slightly salty and acidulous taste.
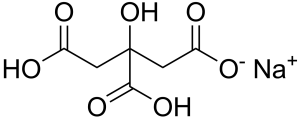
Image Source
| Chemical formula | C6H7NaO7 (anhydrous) |
| CAS number | 18996-35-5 |
| E number | E331(i) |
Less prone to caking than citric acid and can be used as an acidulant (PH 3.5 to 3.8 of 1 % aqueous solution) or buffering agent in combination with free acidulants in dry blends, jellies and beverages, also can be used as a tablet disintegrant.
Disodium citrate
Also known as disodium hydrogen citrate with the PH from 4.9 to 5,2 (1 % aqueous solution), used less as a direct food additive.
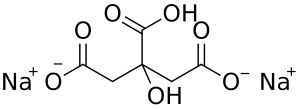
Image Source
| Chemical formula | Na₂C₆H₆O₇ |
| CAS number | 144-33-2 |
| E number | E331(ii) |
Trisodium citrate
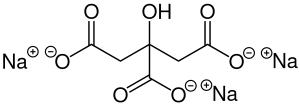
Image Source
It has two forms, trisodium citrate dihydrate and anhydrous. It commonly refers to the dihydrate type when used as a flavoring agent, buffer, chelating agent, emulsifier, stabilizer, and preservative in food.
With the capability of absorbing water and free-flowing, trisodium citrate anhydrous can be used as a carrier in moisture-sensitive formulations by providing a longer shelf life for its low water content.
How is sodium citrate made?
It can be directly synthesized by the neutralization of sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide with citric acid, but several disadvantages may occur, such as the speed of reaction and quality of the final product.
The following manufacturing process was came up by a China manufacturer with better output (1):
- Obtain calcium citrate by reacting calcium carbonate and/or calcium hydroxide with citric acid.
- Calcium citrate reacts with citric acid further to produce calcium hydrogen citrate and/or calcium dihydrogen citrate.
- Then neutralize with the sodium carbonate and/or the sodium hydroxide to produce sodium citrate.
Specification
| Other names |
|
| CAS number |
|
| Chemical formula |
|
| Molecular weight |
|
Properties
Appearance
Crystalline white powder or crystals.
Solubility
Soluble in water (1g/1.5ml, 25°C), insoluble in ethanol.
PKa
Sodium citrate is the base of citric acid, which is a weak organic acid with three carboxylic acid groups and as a result it dissociates three H+, and with three PKa values, PKa1 = 3.14, PKa2 = 4.77 and PKa3 = 6.39.
PH
7.5 to 9.0 (5 % aqueous solution) (2)
What’re the Uses of Sodium citrate?
Sodium citrate is a multi-functional ingredient that is commonly used in carbonated drinks, powdered drinks, jams, jellies, ice cream, yogurts, processed cheeses, meat, sausage, and ham.
It is mainly used for the following purposes:
- Flavoring agent: enhance taste by imparting both a salty and a tart flavor in beverages.
- Buffer: commonly used together with citric acid to adjust the PH by reducing the acidity of foods.
- Chelating agent: the power of chelating metal ions, e.g. Ca2+, Mg 2+, and Fe2+ in dishwashing and laundry detergents.
- Emulsifier: prevent the separation of oil and protein in the cheesemaking process.
- Preservative: prevent food spoilage.
- Anticoagulant: used as an anticoagulant and prevent blood from clotting by combining calcium ion.
Yogurt
Citric acid adds sour taste to dairy products, but its sour taste is strong, and the sour taste can be eased with the combination of sodium citrate, so these two ingredients are often used together in yogurt to adjust and improve the sour taste.
Cheese
Cheese is an emulsion of dairy fat, protein and water, and it tends to break down at high temperatures.
While it is melting, sodium citrate works as an emulsifier to prevent cheese curdling or the separation of fat and protein by keeping fat and protein together and binding calcium ions in the cheese. The usage in cheese is around 3%, depending on your recipes.
Cheese with sodium citrate can melt evenly and produce a smooth & creamy sauce. This property makes it possible to obtain portable and sliceable cheese (in mold, can take everywhere) in home cooking.
Following cheese products may contain with it:
- Cheese sauce
- Nacho cheese
- Macaroni and Cheese
Beverage
Sodium Citrate is used to adjust the tartness in Coca Cola’s beverages (3). And you can find it in the ingredient lists of Sprite (4), Vitamin water (5) and other drinks. It is also added in sports and energy drinks for such purposes, such as in the products of Redbull and Monster.
Is Sodium citrate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sodium citrate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (6)
It can be used in following products (7):
- Milk and cream
- Cheeses and related cheese products
- Artificial sweet fruit jelly, jam, and preserves
EFSA
Monosodium citrate E331(i), disodium citrate E331(ii) and trisodium citrate E331(iii) are listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (8).
Approved uses
Sodium citrates are classified into “Group I” with the maximum use levels “quantum satis”, and also listed in its separate uses. The following food may contain it (9):
- UHT goat milk, dehydrated milk
- Edible caseinates
- Cheese
- Frozen fruit and vegetables
- Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables
- Jam, jellies and marmalades
- Meat preparations, unprocessed fish
- Table-top sweeteners in liquid, powder or tablet form
- Infant formulae
- Processed cereal-based foods and baby foods
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (10)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 331. (11)
JECFA
Trisodium citrate
Function Class: food additives, acidity regulator, sequestrant, stabilizer. (12)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1973. (13)
Sodium dihydrogen citrate
Function Class: food additives, acidity regulator, sequestrant. (14)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1979. (15)
Frequently asked questions
Sodium citrate vs citric acid?
Sodium citrate is made from citric acid, generally, they’re different in acidity, taste and uses. For the details, please visit Citric acid Vs sodium citrate
Sodium citrate vs sodium chloride?
Both maintain electrolyte (Sodium) balance after dehydration during exercise or sweat. Sodium citrate may have the following two advantages over sodium chloride (known as salt) for such supplement:
- Involved in Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb’s Cycle) which converts sugar and fat into energy.
- A buffer to keep the balance of acid-base.
Potassium citrate vs sodium citrate?
Potassium citrate can be used in food with the lower sodium desired.
Is it natural?
No, commercial sodium citrate is synthetic although it is also naturally found in citrus fruits.
Is it vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the raw material used and manufacturing process without the use of animal product, so it can be added in the food for vegetarians.
Is it gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free or without gluten as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains, therefore can be used for people with celiac disease.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the acidity regulator– sodium citrate (E331), from the following aspects:
- 3 types: E331(i, ii, iii) according to the neutralization levels
- Two manufacturing process
- Main food uses in beverage and cheeses
- Safety
- FAQs: compare with citric acid, sodium chloride and potassium citrate
What kinds of food labels have you found it in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.


What is best to use in fruit juices and concentrates, sodium citrate, sodium ascorbate or potassium ascorbate? Thank you.
Hi Balan,
It depends on your intention to use which of them.
The latter two are antioxidants, although they can also be used as acidity regulator (to increase PH) and adjust the taste.
Potassium ascorbate can be as a sodium free source.
Found in Walmart’s Great Value half and half.
I found it in Safeway Signature Select Club Soda. Is it a preservative, a flavoring agent or used for something else?
I found it in cultured buttermilk. I’m in the process of making sourdough starter and the YouTuber suggested to use buttermilk as the liquid (watered down of course) to ensure and accelerate the process. She insisted on using cultured buttermilk. I thought all buttermilk was cultured while not knowing what cultured meant. When I checked the label the last ingredient was sodium citrate. The other ingredients were starches and salt. Which left me still to wonder what ‘cultured’ means. If one doesn’t have buttermilk on hand an acceptable alternative is lemon juice or vinegar. Lemon juice and a pinch of salt seem to be related to sodium citrate. Now I don’t know why I go buy a quart of buttermilk for the recipe and push the half empty carton around the refrigerator for the next three months.