What is Ethyl Maltol in food: Compare with Maltol, Uses and Safety

Vs Maltol | Production | Uses | Safety
Ethyl maltol, a white crystalline powder with the chemical formula C7H8O3, is a commonly used synthetic flavoring agent by providing caramel and cotton candy sweet taste in fruit based foods, confectionery, bakery, beverages, and wines.
Ethyl maltol Vs maltol?
Ethyl maltol is an analogue of maltol (or methyl maltol), which is obtained by replacing the methyl group in maltol molecule with an ethyl group. They’re both flavors with the similar taste of caramelized sugar and are the basic components of some complex flavors and fragrances, and commonly used for the preparation of many fruit flavors, such as the flavors of citrus orange, pear, pineapple, cherry, grape, mango, apple, coconut and etc.
Difference
Ethyl maltol is a synthetic ingredient and is used more widely than maltol, which occurs naturally.
The biggest difference is that the flavor or aroma intensity of the former is about 3 to 4 times stronger than that of the latter and more volatile due to the slight difference in the molecular structure. And thus to reach the same flavor enhancement effect, the dosage of ethyl maltol is only one-third to one-fourth of maltol.
Maltol also has an odor of a burnt caramel, but with little fruity taste. Ethyl maltol has a stronger sweet fruity taste, while less caramel smell. This leads to their different uses. Maltol is especially suitable chocolate and caramel-flavored products, while ethyl maltol is commonly used as a fruity sweet flavor although it is not a real sweetener.
How is Ethyl Maltol Made?
Ethyl maltol can be commercially produced by chemical synthesis, generally with the manufacturing process of Grignard reagent preparation, grignard reaction, hydrolysis, chlorination and rearrangement reaction.
Firstly to obtain Grignard reagent (CH3CH2MgBr) by the reaction of magnesium with CH3CH2Br in the presence of anhydrous ether or tetrahydrofuran solvent.
Then react the Grignard reagent with furfural, and then hydrolyzed to obtain furfuryl alcohol intermediate. Chlorinate the furfuryl alcohol intermediate at low temperature, and then heated to hydrolyze and rearrange to obtain crude maltol in acidic medium, and finally purified by sublimation and recrystallized in ethanol. (1)
Here is the general flow chart:
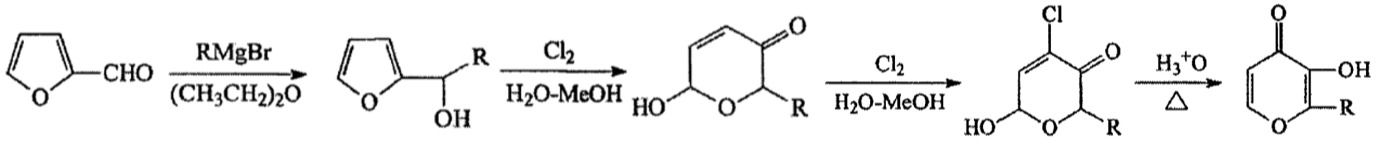
R=CH3CH2-
Properties
| Other names | 2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyrone |
| CAS number | 4940-11-8 |
| Chemical formula | C7H8O3 |
| Molecular weight | 140.14 |
| Melting point | 89-93 ℃ |
| FEMA number | 3487 |
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol and in propylene glycol (can be diluted to 10%).
Structure
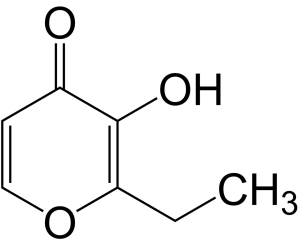
Image Source
What’re the Uses of Ethyl Maltol?
Ethyl maltol is a broad-spectrum synthetic flavoring agent that can improve the flavor of food. It is commonly used in the production of beverages, fruit juices, dairy products, ice creams, fruit wine, sauces, and pickled vegetables to enhance the sweet taste like fruits.
It can also be added to candies, biscuits, cakes, chocolate and meat products (ham and sausage) to impart a caramel aroma.
Only a small amount (0.01%-0.1%) is needed to achieve the desired intensive and long-lasting flavor. Some manufacturers may add other flavors or fragrances into ethyl maltol to make its flavor stronger or purer. In some countries, it is not permitted to be added in edible vegetable oils, such as sesame oil, soybean oil, peanut oil, rapeseed oil, and blended oil.
Yogurt
In yogurt, it improves the flavor, reduces the sourness, increases the sweetness and adds fruity aroma.
Ice cream
It increases the creamy taste of the products in low-fat and low-calorie ice creams.
Beverage
It improves the fruity sweet, reduces the acidity and gives the drink a pleasant aroma.
Bakery
It is an ideal flavoring agent for baked goods due to its sweet and caramel aroma. It can be used in the fillings of baked goods, such as fruit filling, milk cake filling, pudding filling, or cream fillings.
Meat
In meat products, ethyl maltol is not only used to improve the color and delay fat oxidation in cured meat, but also increase the meat flavor.
It enhances the meat color by combining with Fe3 + to form a stable myoglobin complex, therefore preventing the degrading of myoglobin from into iron-free porphyrin-globulin complex, which is easy to be further decomposed to light green porphyrins, which will make the quality and flavor of poultry meat products bad.
The color of pork mainly depends on the pigments in the meat, such as myoglobin (most important), hemoglobin, and cytochrome C.
It can make canned meat pink without the use of nitrite. It can also be used together with other ingredients, such as ferric citrate and zinc gluconate for color development in poultry products.
How to use
Generally, there are two ways for the applications: formulated to a certain concentration of solution (e.g. 0.25%) or dry mix.
It should be added at a lower temperature as much as possible to reduce the volatilization if the end product needs to be heated during the production.
It can also premix with one dry ingredient, and then blend with other ingredients to achieve a uniform mixing effect.
Is Ethyl Maltol Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects and its safety as a food additive has been approved by the FDA, EFSA and JECFA. Ethyl maltol is a synthetic flavoring substance and adjuvant that is Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by the FDA (2).
Ethyl maltol (FL-no: 07.047) is authorised for use as a flavouring agent in the EU according to Annex I to Regulation (EU) No 1334/2008 (3). Its safety used as a favouring agent was re-evaluated by the EFSA in 2010. EFSA established the same conclusion with JECFA that “No safety concern at estimated level of intake as flavouring substance” based on the Maximised Survey-derived Daily Intake (MSDI) approach (4).
An Acceptable daily intake (ADI) of “0-2 mg/kg bw” was set in 1974 by the JECFA. (5)
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the flavor – ethyl maltol, from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Comparison with maltol
- Uses
- Safety
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Hi jems…What caramel colour use for whisky 🥃
Hi Patel,
Maybe Class II (E150b) is better, you can see the article of caramel colour here: https://foodadditives.net/colors/caramel-color/