What are Gluconic acid (E574) and Gluconates in Food and Uses?

Production | Gluconates | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Gluconic acid, a mild organic acid derived from sugar, mainly used as an acidity regulator and chelating agent in food with the European food additive number E574. This ingredient is also used to produce gluconates (E576, 577, 578, 579, 585) and glucono delta-lactone (E575) to be used in different food applications and other fields.
Natural sources
It is naturally present in fruit, wine, honey (1), rice, meat (2) and in kombucha fermentation.
How is Gluconic Acid made?
Generally, gluconic acid is produced by oxidation of D-glucose (derived from starch hydrolysis) with different manufacturing processes (3):
- Bromine water
- Microorganisms, such as Aspergillus niger and Acetobactor suboxydans (4)
- Enzymes derived from microorganisms
What are Gluconates?
Gluconates usually refer to the salts of gluconic acid that are commonly made from the reaction between gluconic acid and the corresponding metal carbonate salts. The following are six common types of gluconates and their uses/functions in food:
- Calcium gluconate: functions as a firming agent, formulation aid, sequestrant, stabilizer or thickener and texturizer that can be used in baked goods, dairy products, gelatins, puddings and sugar substitutes. (5)
- Sodium gluconate: a sequestrant (6). Learn more about this ingredient
- Copper gluconate: works as a nutrient supplement and a synergist, may be used in infant formula. (7)
- Ferrous gluconate: a nutrient supplement that may be used in infant formula (8), also can be acted as a food color (9). Learn more about this ingredient
- Manganese gluconate: a nutrient supplement that can be used in baked goods, dairy and meat products, poultry products, and infant formulas. (10)
- Zinc gluconate: nutrient. (11)
What are the Health Benefits of Gluconic Acid?
- Urinary stones prevention: an early study showed that it can prevent urinary stones. (12)
- Intestinal microflora activity promotion: a study in piglets exhibited that gluconic acid had a positive effect on the intestinal microflora and may improve piglets growth. (13)
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 526-95-4 |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 196.155 |
| Melting Point | 131 °C |
Structure
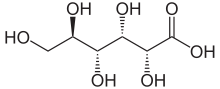
Image Source
Five hydroxyl groups and a carboxylic acid group in the chemical structure.
Properties
Its food grade is commonly 50% solution in water with colourless to light yellow color, and contains about 5% glucono delta-lactone at room temperature. As in aqueous solution, gluconic acid exists in a stable equilibrium with the cyclic ester – GDL (glucono delta-lactone).
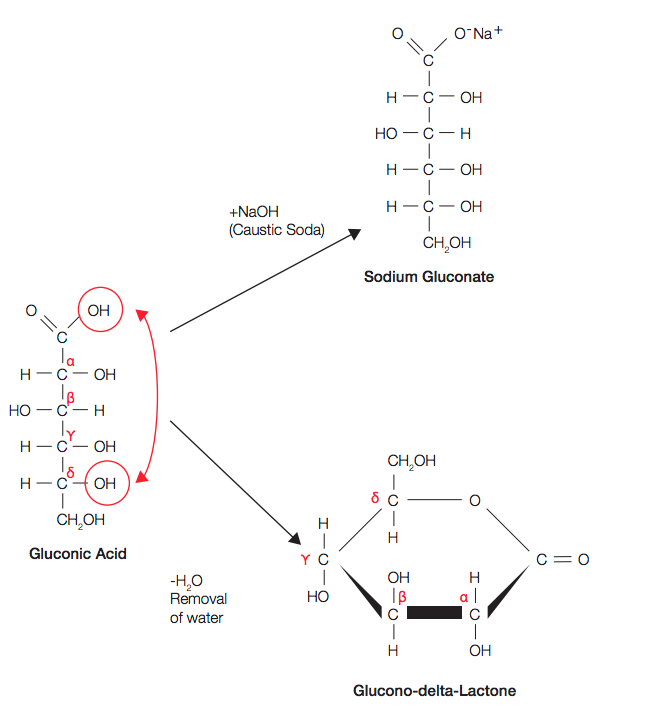
Image Source
Solubility
In water
Freely soluble in water with the solubility 100g/100ml at 25°C. (14)
In organic solvents
Slightly soluble in alcohol, insoluble in ether and most other organic solvents.
PKa & PH
Gluconic acid is a weak carboxylic acid with a dissociation constant pKa 3.6. It dissociates a proton and a gluconate ion (conjugation). Its aqueous solution has a neutral pH. (15)
What’re the Uses of Gluconic Acid?
Mainly used for its leavening and acidity properties in food; chelating and perfuming agents in cosmetics products; also it can be used in industrial uses for chelating heavy metals.
Food
The following food may contain with gluconic acid:
- Bakery goods: as a leavening acid in leavening agent to increase dough volume by producing gas by the reaction with baking soda.
- Dairy products: as a chelating agent and prevent milkstone.
- Some food and beverage: as an acidity regulator to impart a mild organic acid and adjust pH level and also as a preservative and an antifungal agent. Also, it can be used to clean aluminium cans.
Animal Nutrition
Gluconic acid functions as a weak acid in piglet feed, poultry feed and aquaculture to comfort digestive and promote growth, also to increase the production of butyric acid and SCFA (Short-chain fatty acid). (16)
Cosmetics
It can be used as a chelating and perfuming agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (17)
Industrial uses
The power of chelating heavy metals is stronger than that of EDTA, such as the chelation of calcium, iron, copper, and aluminium in alkaline conditions. This property can be utilized in detergents, electroplating, textiles and so on.
Is Gluconic Acid Safe to Eat?
Yes, this acid has been approved safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
D-gluconic acid can be added to food as a nutrient supplement. (18)
EFSA
Gluconic acid (E574) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (19).
Approved uses
The food application of gluconic acid is classified in “Group I”, which means the usage is “quantum satis”, also the same use levels in nutrients. (22)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 574. (23)
Frequently asked questions of Gluconic Acid
What is it made of?
Generally, it is a mixed aqueous solution of gluconic acid and glucono-delta-lactone. (24)
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the raw material is from the plant sources and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So that it is suitable to be added in the diet of vegetarians.
Is it Natural?
Yes, it is natural if obtained by microbial oxidation of glucose.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free or without gluten as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains, therefore can be used for people with celiac disease.
Is it the same with Glucuronic acid?
No, it is different with Glucuronic acid (C6H10O7), which is also a derivative of glucose.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the acidulant – gluconic acid (E574), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Gluconates
- Uses in food, animal and others
- Safety
- FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



It is one of the 3 ingredients (water, rice, gluconic acid) in “bibigo ” (brand name) Korean cooked sticky white rice (medium grain rice) sold at Costco. Microwable in plastic bowls (210g) for 1min 30 sec.
Thank you for the very helpful info.