What is Dimethylpolysiloxane (E900) in Food and What are the Uses?

Dimethylpolysiloxane, also known as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), is a form of silicone used as an antifoaming agent in food with the European food additive number E900. This ingredient is commonly used in frying oil due to its good defoaming effectiveness at high temperatures.
Let’s dip into the navigation:
What is Dimethylpolysiloxane?
Definition
It is made of two parts (1):
- (CH3)2 SiO: fully methylated linear siloxane polymers composed of repeating units of the formula (CH3)2 SiO
- (CH3)3 SiO: end-blocking trimethylsiloxy (CH3)3 SiO, with the stabilization function.
Structure
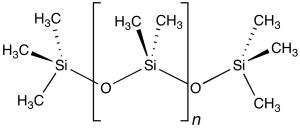
From Wikipedia
Why Mcdonalds Use it in Frying Oil?
From the official website of Mcdonalds’ Gulf region, we can know, dimethylpolysiloxane is a food-grade additive acts as an anti-foaming agent to protect their crew from excessive foaming, splashing or bubbling, which occurs when food is added to very hot oil.
What is it Used for?
PDMS is a silicon-based organic polymer that can be used as an antifoaming agent in fruit and vegetable juices, also it is an anticaking agent in confectionery and flour products, and meanwhile an emulsifier in edible oils essentially free of water.
How is it Made?
PDMS is produced by hydrolysis of a mixture of dimethyldichlorosilane and a small quantity of trimethylchlorosilane.
Properties
Appearance
Clear, colourless, viscous liquid.
Solubility
As its no polarity, it is insoluble in polar substances, such as water and in ethanol while soluble in non-polar materials, like in carbon tetrachloride, benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, toluene and other organic solvents.
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 9006-65-9 |
| Chemical formula | CH3)3-Si-[O-Si(CH3)2]n-O-Si(CH3)3 |
| Molecular weight | 6,800 to 30,000 (average and approximate) |
What’s the Application of Dimethylpolysiloxane?
Its applications are widely such as in aerospace, aviation, food, chemical, metallurgy, medical and healthcare fields as most of the silicone products (such as silicone oil, silicone rubber, silicone resin) are obtained by the reaction of polydimethylsiloxanes with regulators, cross-linking agents, capping agents, etc.
PDMS has many excellent physical and chemical properties, such as high and low-temperature resistance, radiation resistance, oxidation resistance, high air permeability, weather resistance, mold release, hydrophobicity, and physiological inertness.
Here we only talk its brief uses in food and cosmetics.
Food
PDMS is commonly used as an antifoaming agent in cooking oils, processed foods, and fast food as it prevents the formation of foam on the surface of liquids by reducing the surface tension. in m.
Usually, its applied viscosity varies from 300 to 1,050 centistokes at 25 ºC in food.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, it functions as an antifoaming, emollient, skin conditioning and skin protecting agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (2)
We can find it in shampoos, conditioners and skin care products. Its common viscosity is 100 and 350 centistokes at 25 ºC.
Is Dimethylpolysiloxane Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
PDMS is placed as a “secondary direct food additive” for human consumption and it may be safely used in processing foods as a defoaming agent.
The following are some applications and the max level. (3)
| Food Category | Maximum Level |
| Ready-for-consumption Food | 10 mg/kg |
| Milk | 0 |
| dry gelatin dessert mixes | 110 mg/kg |
| ready-to-serve dessert | 16 mg/kg |
| salt for cooking purposes | 250 mg/kg |
| Cooked food | 10 mg/kg |
It can also be used as a lubricant, release agent and surface-active agent. (4)
EFSA
Dimethylpolysiloxane (E 900) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive in the EU as “Additives other than colours and sweeteners”. (5)
Authorised Uses
The following foods may contain it (6):
- Oils and fats for frying
- Chewing gum
- Batters
- Soups and broths
- Pineapple juice
- Flavoured drinks
- Cider and perry
- Fruit or vegetable spreads
- Decorations, coatings and fillings
- Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables
- Food supplements in effervescent tablet form
- Confectionery including breath freshening microsweets
- Jam, jellies and marmalades and sweetened chestnut purée
Also, it can be used:
- as a carrier in glazing agents for fruit
- in all flavourings
- In preparations of beta-carotene and lycopene
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 900a. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, antifoaming agent, anticaking agent. (8)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “0–1.5 mg/kg bw” set in 2011. JECFA withdrew the ADI of 0–0.8 mg/kg bw set in 2008 and re-established the ADI of 0–1.5 mg/kg bw since in 1979.(9)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether PDMS is bad for our health and what are the side effects in the food we eat.
Studies showed that PDMS is almost not absorbed through the skin or from the gastrointestinal tract and excreted unchanged in the faeces in rats. No acute toxicity and allergy but ocular lesions were observed. There were no adverse effects found in the researches of its carcinogenicity, teratogenicity and genetic toxicity. (10)
Therefore, it seems PDMS might have no dangers under proper usage.
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, we can know PDMS is synthetic from the manufacturing process mentioned above.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is recognised as halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free according to FDA that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, PDMS is vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan and vegetarians can eat the food with it.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the antifoaming agent – Dimethylpolysiloxane (E900), from the following aspects:
- Manufacturing process
- Uses and functions in food
- Safety and possible side effects
- FAQs
The antifoaming agents are less common than other categories of food additives, but do you heard of dimethylpolysiloxane before?

Side effect not mentioned.
So proper knowledge need.
Thanks
I developed an allergy to Dimethylpolysiloxane 4 years ago. Because it is almost never identified in ingredient lists I do not know which foods can cause a toxic reaction other than by trial and error. I wish food manufacturers would identify it in their packaging. Life would be easier.
I am VERY allergic to silicone in every form, including dimethylpolysiloxane. Glad rats do so well with it, but this human doesn’t.
They are now saying dimethylpolysiloxane could be linked to CFS/ME!!
Apart from the foods you mention it is in breast implants which because of adverse effects are now a huge cause for concern!!
Because the regulated food body is saying there are no adverse side effects it is commonly used in organic products!!
I’m also severely allergic to all silicon. It’s a struggle and scary that it not listed on all food products that contain it.
Thank you for this valuable information.
I bought some Rico’s nacho cheese and decided to read the ingredients. This was one listed.
It’s scary what they seem safe…
yes almost every edible oil n processed food has this it’s under N900/N900a
is it used in pen cartridges? to seal in the gel ink?