What is Sorbitan Monostearate (E491) in food and yeast? Uses and Safety

Production | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Sorbitan monostearate (abbreviation SMS), or Span 60, is an emulsifier esterified from sorbitol and stearic acid with the European food additive number E491. This ingredient is mostly used in baking yeast by improving the activity of instant dry yeast when the yeast is rehydrated before use.
How is Sorbitan monostearate made?
Generally, sorbitan monostearate can be made from direct esterification of sorbitol and stearic acid. Sorbitan tristearate (E492) would be generated in the production if too much stearic acid is involved.
Sorbitol
Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste and can be used as a sugar replacement and humectant in chewing gum, mints, cookies, bread, and cakes. It is commonly made from starches of corn and potato and follow the hydrogenation process.
Stearic Acid
It is a common saturated fatty acid found in nature both in animal fats/oils and vegetable oils. It can also be used in the production of soaps, cosmetics, and detergents.
The commercial food grade stearic acid may contain 48.7–50.0% palmitic acid.
As sorbitol has six hydroxyl groups and that’s why sorbitan monostearate may also contain palmitic acid esters of sorbitol, sorbitan and isosorbide besides sorbitol, sorbitan, and isosorbide esters of stearic acid.
Properties
Appearance
A white to yellow waxy bead or flake with a slight characteristic smell.
Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB)
With the HLB value 4.7, meaning it is lipophilic and soluble in oil instead of water. It will form W/O (water-in-oil) type emulsion, and it is a strong emulsifying dispersion and has a wetting effect.
Solubility
- Not soluble in cold water, but can be dispersed in hot water.
- Soluble in ethanol, mineral oil, and vegetable oil.
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 1338‐41‐6 |
| Chemical formula | C24H46O6 |
| Molecular weight | 430.62 |
Structure
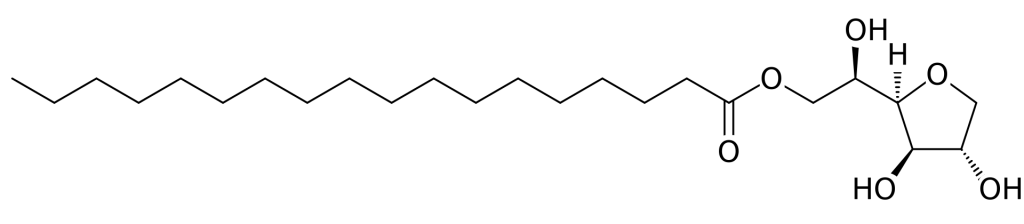
Image Source
What’re the Uses of Sorbitan monostearate?
Sorbitan monostearate is used as an emulsifier, commonly together with polysorbates to keep water and oil mixed in many food products.
It is commonly used in instant dry yeast, fat and oil emulsions, desserts, food supplements, cake, spread, margarine, coffee whiteners, and so on.
The following are its main uses and functions in food:
- Dry yeast: maintain the moisture, increase the shelf life of dry yeast, and help the rehydration of yeast cells before blended with other dough ingredients.
- Ice cream: promote emulsifying of dairy fat, prevent the formation of ice crystals, and improve the mouthfeel.
- Margarine: improve emulsion stability and reduce sandiness.
- Whipping cream: improve foam volume and contribute to a nice and stiff foam.
- Bread & Cake: increase the loaf volume and improve the texture of bread and cake.
- Confections and chocolate: stabilize the emulsion of oils and fats.
Meanwhile, it can be condensed with ethylene oxide to synthesize polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monostearate (polysorbate 60), which is also a food emulsifier.
Is Sorbitan monostearate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects and the safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sorbitan monostearate may be safely used as an emulsifier in the following food, sometimes together with polysorbate (60, 65, 80) (1):
- Whipped edible oil topping
- Cakes and cake mixes, icings and fillings
- Nonstandardized confectionery coatings and standardized cacao products
- Edible vegetable fat-water emulsions in beverage coffee
It can also be used as a rehydration aid in the production of active dry yeast with the maximum usage 1%. It may also be safely used in mineral premixes and dietary supplements for animal feeds. (2)
EFSA
Sorbitan monostearate (E491) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (3).
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
EFSA changed the ADI of 25 mg/kg bw per day set by The Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) in 1974 and established a group ADI of 10 mg/kg bw per day for sorbitan esters (expressed as sorbitan) , and the ADI of sorbitan monostearate is 26 mg/kg bw per day. (4)
Approved uses
Its application is listed together with other sorbitan esters: sorbitan tristearate (E492), sorbitan monolaurate (E493), sorbitan monooleate (E494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E495) and with the maximum use levels “5000-10000 mg/kg” while the use level in dry yeast and yeast for baking is “quantum satis”.
The following food may contain it (5):
- Flavoured fermented milk products
- Beverage whiteners
- Fat and oil emulsions
- sugar confectionery
- Chewing gum
- Decorations, coatings and fillings
- Fine bakery wares
- Emulsified sauces
- Desserts
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents” (6)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 491. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier. (8)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-25 mg/kg bw” set in 1973. (9)
Frequently asked questions
Is SMS Halal?
Yes, it is is a synthetic ester that would be halal complying with the Muslim policy if the fatty acid stearic acid derived from vegetable oils instead of animal origins.
Is SMS Vegan?
Yes, it is corn derivative and vegan if the raw material stearic acid from vegetable oils as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin.
However, some manufacturers may use stearic acid from animal sources. Therefore, vegetarians should avoid it.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the emulsifier – Sorbitan monostearate (E491), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Safety
- FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Thanks for sharing information on Sorbitan Monostearate. My daughter reacts to this ingredient. We keep her off 99% of yeast (there is one yeast in America that does not use this ingredient) and she can only eat fruits/veggies that are typically sold with a waxy coating that are picked straight from the tree/vine and have not gone through the waxing process.
What yeast does not contain Sorbitan Monostearate?
Red Star Yeast doesn’t contain sorbitol monosterate.
But Red Star Quick-Rise yeast does list Sorbitan Monostearate.
@Barbara St Jean, Only the Organic Red Star yeast does not have the Sorbitan Monostearate in it. The other varieties or their yeast do have it
I have found Sorbitan Monostearate listed in grocery store pizza dough.
Is Red Star organic active dried yeast available anywhere in the UK? I wish to avoid using Sorbitan monostearate it in my home baking…no point in baking your own bread if it contains the same ingredients as shop bought bread! It does have adverse effects on people even though it is proclaimed “safe” by the relevant authorities.
Hi. If someone does not do well with sorbitol, sugar alcohols causing digestive upset, should this be avoided as well since it is derived from sorbitol? Or does somehow its binding to the acid change its properties and does not necessarily lead to the same side effects as sugar alcohols on their own? Thanks
In addition to the organic Red Star instant yeast, the Red Star instant dry yeast sold in the small packets does not contain sorbitan monostearate, but the bigger variations do. Molino Rossetto yeast does not contain it either, although it isn’t an instant yeast.