What is Calcium Disodium EDTA (E385) in Food: Uses, Safety, Side Effects

What is it | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Calcium disodium EDTA or CaNa2EDTA, a salt of EDTA which can be used as a preservative in food with the European food additive number E385. And you may have encountered this ingredient in the preservation of mayonnaise, salad dressing, pickled fruits, canned soda and other canned food.
What is calcium disodium EDTA?
The abbreviation of calcium disodium ethylene diamine tetra-acetate, a multifunctional food additive commonly used as a preservative, sequestrant, antioxidant, flavouring agent, and colour retention agent in canned food.
Calcium disodium EDTA can combine with free metal ions (such as Zinc, Iron, Copper, Magnesium, Manganese) which are often present in food & beverage and as a result keep the color, flavor and odour of food by preventing these ions reacting with food.
How is it made?
Its food grade can be made from the synthesis of disodium EDTA with calcium carbonate or calcium chloride. (1)
What is it made of?
A mixture of its dihydrate (C10H12O8CaN2Na2·2H2O) and trihydrate (C10H12O8CaN2Na2·3H2O) forms, the dihydrate takes a large part in it.
Properties
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 62-33-9 |
| Chemical formula | C10H12O8CaN2Na2·2H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 410.31 |
Appearance
White, odourless crystalline powder or granular with a faint, salty taste.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol.
Structure
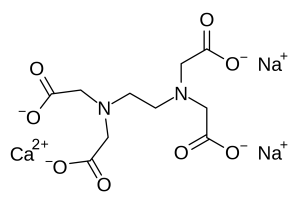
Image Source
What are the Uses?
Food
Calcium disodium EDTA is commonly used as a chelating agent, preservative and antioxidant (to prevent oxidation by chelation) in canned food. It stabilizes food by binding with free polyvalent metal cations.
Canned foods are processed through canning, sealing, heating and sterilization which prolongs the shelf life. Ingredients commonly added in canned foods are mainly preservatives, antioxidants, sweeteners and synthetic colors.
Carbonated beverages
Calcium disodium EDTA promotes flavor retention and reduces discoloration and turbidity in soft drinks.
Coca Cola says it functions as a preservative and protects the freshness and taste in its beverages (2).
In vitamin C fortified beverages, calcium disodium EDTA prevents the reaction from the interference of uncontrolled metal ions, which will deteriorate colors and reduce the shelf life of vitamin beverage. It can also preserve an antioxidant in vitamin A, B, D & E.
Cosmetics
Per the“European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, it functions as a chelating agent in cosmetic and personal care products (3) . Commonly can be found in some lotions, creams, and soaps.
Pharmaceutical
It can be used to treat lead poisoning.
Is calcium disodium EDTA Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Calcium disodium EDTA may be safely used in following food categories for promoting color, flavor, texture retention or other functions with maximum levels ranging from 25 to 800 mg/kg (4):
- Pickled cabbage and cucumbers
- Canned carbonated soft drinks, fermented malt beverages
- Canned white potatoes
- Cooked canned of
- Clams
- Crabmeat
- Dried lima beans
- Legumes
- Pink beans
- Red beans
- Mushrooms
- Shrimp
- French dressing, salad dressing, spreads, sauces
- Mayonnaise, oleomargarine, pecan pie filling, potato salad
- Processed dry pinto beans
- Sandwich spread, artificially Colored and lemon-flavored or orange-flavored
- Hard-cooked egg product
EFSA
Calcium disodium EDTA (E385) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (5)
Authorised Uses And Use Levels
The following foods may contain it with maximum levels ranging from 75 to 250 mg/kg (6):
- Spreadable fats
- Pulses, legumes, mushrooms and artichokes
- Heat–treated meat products: libamáj, libamáj egészben, libamáj tömbben
- Frozen and deep-frozen crustaceans
- canned and bottled fish, crustaceans and molluscs
- emulsified sauces
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (7)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
In Australia and New Zealand with the code number 385. (8)
JECFA
Functional Class: food additives, preservative, sequestrant. (9)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI of 2.5mg/kg was set in 1973. (10)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that consumers have health concerns about whether calcium disodium EDTA is bad for our health and what are the possible health risks. It is generally considered safe but too much consumption may lead to mineral deficiencies.
Large Amount
As it can chelate metal ions such as iron, zinc, copper in the human body, the large dosage may cause vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Frequently asked questions
Is it natural?
No, obviously it is a synthetic preservative.
Is it vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the raw materials disodium EDTA, calcium carbonate or calcium chloride are all from mineral sources instead of animal-derived. So it is vegan and suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Is it dairy free?
Yes, it does not contain dairy as the calcium comes from limestone instead of animal sources. So people who’re lactose intolerance or with milk allergy can eat the food with it.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. E385 has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it gluten free?
Yes, it is typically gluten-free and people with celiacs can eat it. It is an ingredient commonly found in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. The manufacturing process complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Calcium disodium edta vs disodium edta?
Both are chelating agents but are often mistaken for each other as simply referred to EDTA.
Following are the differences:
- Food uses: calcium disodium EDTA is the only EDTA derivative approved in food use by the EU, with the E number E385. However, in the USA, both are authorized with similar applications by the FDA.
- Safety: calcium disodium EDTA seems to be safer than disodium EDTA. Calcium disodium EDTA can be used to treat lead poisoning while disodium EDTA cannot as it will lead to hypocalcemia and possibly fatal tetany, and may also cause nephrotoxicity. (11)
Conclusion
Now you may have a good knowledge of the food additive – calcium disodium EDTA (E385), from its production, uses, approved safety, possible side effects and some FAQs such as is it vegan, gluten free, dairy free, synthetic or natural and the comparison with disodium EDTA.
What kinds of food packaging have you found this ingredient in? Let me know in the comments.



What is the EU limit for E 385 in alcoholic beverages?
Hi Andy,
Its uses in alcoholic beverages are not listed by EU.
You can see here for its approved applications: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2008/1333/2019-10-23
What is global Calcium Disodium EDTA Production Voumes? Can youhelp me? Mr. James. I am Shastry from India.
Thanks for the informative article. I came across it because I was researching the ingredients of my BANG ENERGY drink.
Very helpful and reassuring. Thank you!
I see it in canned red beans (India) I think I will avoid it,,,,
I see it in freshly prepared salads from the butcher
I appreciate learning about this FDA approved additive from this article. Leavin feedbck, however, is difficult with th constant pop-up ads. So, may be why thre areso few and why im just goung to leave the typos. Inglehoffer Creamy dill mustard was the product i had been giveb y a friend. Tastw was off so I lookedbtter at the label. I personally shop organic,and. Possblythee reeaon i pickd up on. Sometijg that stood out