What is Fumaric Acid (E297) in Food? Uses, Safety, Side Effects

What Is Fumaric acid | Benefits | Uses | Safety | Side Effects | FAQs
Fumaric acid, the strongest organic food acid commonly used as a flavoring agent and pH control agent. It provides more sourness than other acidulants, e.g. citric acid (E330) and malic acid (E296) in food. The European food additive number for it is E297.
What is Fumaric Acid?
It is a weak organic acid (a dicarboxylic acid) commercially made from maleic acid and with chemical formula C4H4O4. It is a precursor for the production of other acids, like L-aspartic acid and L-malic acid.
Fumarate, citrate and malate are all the intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle or KREBS cycle to produce energy in the form of ATP in our humans and most living cells.
What are the Natural Sources?
It can be naturally found in fumitory, bolete mushrooms, lichen, and Iceland moss. (1) Also, it presents in fruits such as apple and watermelon. Generally, it is less found in most fruits than another two acidulants, citric acid and malic acid. (2)
How is it Made?
Fumaric acid can be produced by the isomerization of maleic acid or glucose fermentation. The following are the two manufacturing processes:
1. Isomerization of Maleic Acid
Commonly the production is chemically synthesized from isomerization of maleic acid which is the hydrolysis of maleic anhydride. (3)
Maleic anhydride is the cis-counterpart of fumaric acid. It is manufactured from butane, butene, or benzene from petroleum are the starting materials. (4)
2. Sugar fermentation
Fermentation by Rhizopus species using glucose or other carbohydrate substrates. (5)
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 110-17-8 |
| Chemical formula | C4H4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 116.072 |
| Melting Point | 287 °C |
| Boiling Point | 156 °C |
Structure
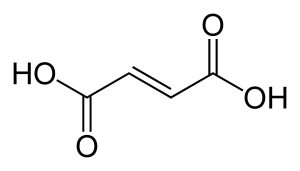
Image Source
Properties
Appearance
It is a white or nearly white crystalline powder or granular with a clean, persistent sourness with dryness. The sourness is around 1.5 times that of citric acid.
PKa
Fumaric acid is a weak organic acid containing two carboxylic acid functional groups and as a result it has two PKa values, PKa1 = 3.03 and PKa2 = 4.44. Its PKa1 and PKa2 value is higher than that of citrate acid and malic acid.
PH
Fumaric acid is an unsaturated di-carbonic acid and it has 2 dissociation equilibrium equations. Its PH value is 2.03 in the concentration of 100 mM (0.1mol/L). (6)
How to Calculate the PH Value?
The method to calculate its PH is the same way with that of malic acid.
It is a relatively strong acid and has a strong buffering property to maintain the pH of the aqueous solution at around 3.0, which is important for preservatives that function around pH 3.0.
Fumaric acid helps stabilize the pH of a fruit juice drink, which in turn makes colour and flavour stable. Therefore, it is often used together with preservatives, such as sodium benzoate (E211).
Solubility
In water
It has a solubility of 0.5% (0.5g/100ml) at 20°C in water while citric, malic and tartaric acid are all very soluble in water.
The hydrophobic of fumaric acid makes it an effective antimicrobial agent because it can disrupt microbial activity by interacting with lipid materials on the microbial cell wall.
In organic solvents
Soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in oils. Slightly soluble in acetone with solubility 1.29g/100g at 20°C. (7)
What are the Benefits?
Treatment of Psoriasis
Due to its poor absorption after oral intake, fumaric acid esters, such as monoethyl fumarate (MEF) and dimethyl fumarate (DMF) are used for the treatment of psoriasis. However, several side effects occurred in the studies from the year 1990-1998. Including (8):
- Flushing
- Diarrhoea
- Kidney retention
- A reversible elevation of transaminases, lymphocytopenia and eosinophilia.
- Gastrointestinal complaints, mild stomach upsets, increased frequency of defecation and tenesmus, to stomach cramps, tympanites and diarrhoea.
What are the Uses?
Fumaric acid is the strongest organic food acid. It is used as a flavoring agent for its sourness taste, and an antimicrobial agent for its hydrophobic characteristic. Generally, it is used in food, beverage, animal nutrition, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industry.
Food
When compared to other acidulants like citric acid, fumaric acid can be used in dry mix products as it is non-hygroscopic and will not absorb moisture. This advantage makes dry mix products do not cake or harden during storage.
In beverage, fumaric acid functions as a PH control agent and enhancing flavor.
Besides this beverage application, we can also find the following food products containing it and its other functions (9):
- Bakery and tortillas: as a leavening acid in the leavening agent and also acts as a flavoring agent for savory baked goods.
- Confectionaries and desserts: non-hygroscopic agent.
- Chewing gum: slow dissolution and hydrophobicity property, prolongs the sourness in the mouth so that it enhances the flavor of chewing gum.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, it acts as a buffering in cosmetic and personal care products. (10)
Is Fumaric Acid Safe to eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Safety
Fumaric acid and its calcium, ferrous, magnesium, potassium, and sodium salts may be safely used in food. (11)
Uses
It can be used for antimicrobial agent, curing or pickling agent, flavoring agent or adjuvant, leavening agent and a PH control agent in food. (12)
EFSA
In food
Fumaric acid (E297) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (13)
Uses
The following foods may contain with E297 and its maximum level (14):
| Food Category | Maximum Level |
| Fruit-flavoured desserts | 4000 |
| Sugar confectionery | 1000 |
| Chewing gum | 2000 |
| Decorations, coatings and fillings | 1000 |
| Fillings and toppings for fine bakery ware | 2500 |
| Instant products for preparation of flavoured tea and herbal infusions | 1000 |
| Gel-like desserts, fruit-flavoured desserts, dry powdered dessert mixes | 1000 |
In feed
Fumaric acid is currently authorised as a preservative in feedingstuffs for all animal species. It is considered safe for pigs and poultry provided that an expected use level of 20 000 mg/kg in complete diets for pigs and poultry is not exceeded. (15)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (16)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient with the code number 297 in Australia and New Zealand. (17)
JECFA
Function class: food additive, flavouring agent, acidity regulator. (18)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1989 and no safety concern at current levels of intake when used as a flavouring agent in the safety re-valuation in 1999. (19)
What are the Possible Side Effects of Fumaric acid?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether fumaric acid is bad for our health and what are the possible health risks. We understand that consumers prefer natural ingredients and have concerns about the synthesized acidity regulators in the foods we eat. It is generally considered safe but some people may be allergic or sensitive to it.
Allergy
There were little reports regarding its side effects, but it may trigger some allergy symptoms such as headaches, diarrhea, nausea, and other reactions to people who are allergic to it.
Is it Safe for Pregnant?
It is generally safe, but better consult with your doctor.
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, as usually it is the synthetic one sold in the market, so it is not nature as it is from a chemical synthesis – isomerization of maleic acid. However, it could be natural if made by fermentation as the production method mentioned above.
Also, it naturally exists in some fruits and vegetables and also occurs in human skin when exposed to sunlight.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as ingredients involved in the production without referring to any animal product, by-product or derivative. So it is considered vegan and vegetarians can eat the food with it.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher and we can find several suppliers with synthesized or natural fumaric acid certificated with pareve. It may also with passover.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is typically gluten-free and people with celiacs can eat it. It is an ingredient commonly found in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. Its production complying with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
What is Fumarate?
The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C4H2O2−4 ion (in solution).
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the acidity regulator – Fumaric acid (E297), from the following aspects:
- Two types and both brief manufacturing processes, either by fermentation or chemical synthesis
- Uses in food
- Benefits
- Safety
- Common FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



From where , you get this information?
Is it according to CODEX or some random experiment?
Thank you.
Hi Patole,
it is based on my experience and some reference.
Hi James,
Thank you. What are the units for maximum permitted levels listed in the table please?
i found it in food and search it and now i have understood
thanks for this!
Hi Branaghan,
You can see here: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02008R1333-20191023
Given what I now know about the EFSA and FDA etc, can any of them be trusted ?
They say a substance is or is not safe, and or, they disapprove of a substance yet, they don’t ban it, or it was banned but now it’s “safe” ?
Brominated Vegetable Oil is a good example, authorities said they “did not encourage its use” because they knew it had health issues, they did not want to ban it outright. The “UK Food Safety Agency” in Britain does the same with a known toxic red food dye in glazed cherries. It is banned in everything but the cherries.
The recent US baby food that was passed as safe by the government when it was not safe.
Leaded drinking water in Flint, Michigan.
The “GMO Free” butterfly logo on products that actually contained GMO ingredients, I’m referring to a certain brand of green colored “health” drink, sued in court.
Recently we had court cases over “nonstick coatings are safe”, turns out they lied about that for 40 years. All this can be looked up as its all on public records.
Who are you going to believe about what is safe or not when corrupt government or scientists are not beyond corruption for corporate money ?
Bottom line is, they don’t care, they have no ethics. Our food could be the cleanest it’s ever been but no, it’s iften toxic junk.