What is Glucono Delta Lactone (E575) in Food? Uses, Safety, Side Effects

Production | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs | Conclusion
Glucono delta-lactone (abbreviation GDL) or gluconolactone, an inner ester of gluconic acid, is a naturally occurring ingredient commonly used as a coagulant in tofu making, a leavening acid in bakery, a mild acidulant in cheese and meat products, and a sequestrant in some food applications. The European food additive number for it is E575. It is kosher, halal, vegan and GMO free.
In aqueous solution, GDL rapidly dissolves and the lactone ring opens up and slowly hydrolyzes to gluconic acid, thus producing mild acidification. And there is an equilibrium between D-gluconic acid (55% – 66%) and the delta and gamma lactones.
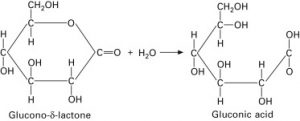
Image Source
How is it made?
Glucono delta-lactone is produced by direct crystallization from the aqueous solution of gluconic acid which can be produced by the oxidation of D -glucose with bromine water or with microorganisms or with enzymes derived from these microorganisms (1). Corn starch is the major source of glucose.
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 90-80-2 |
| Chemical formula | C6H10O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 178.140 |
| Melting Point | 150–153 °C |
Properties
GDL is the less commonly used than other food acidity regulators, such as citric acid, malic acid and fumaric acid.
It has two major differentiating properties:
- A slow-release acidulant: it provides a progressive and continuous decrease of pH due to the slow hydrolysis to gluconic acid.
- Less tart than other common acidulants: the initial slightly sweet taste making the final flavour of an aqueous solution of GDL Less tart.
Appearance
A white, odourless crystalline powder or granular.
Solubility
In water: freely soluble in water, 59g/100 mL (water) at 25°C.
In organic solvents: sparingly soluble in alcohol.
What’re the uses of Glucono delta-lactone?
GDL is a multifunctional ingredient that can be used as a coagulant in tofu, a leavening acid in the bakery (e.g. bread, cakes & pastries), controlled release acidulant & curing accelerator in processed meat & seafood, mild acidulant, chelating agent, and buffering agent in food.
Coagulant in Tofu
Glucono delta-lactone can be used as a coagulant in tofu for its gradual acidification initiates the curdling of the protein. It can replace the function of nigari or in combination uses with nigari in tofu. The following steps are how to make silken tofu with GDL.
Step 1: Select beans
It is recommended to pick light white soybeans with good color and high protein content.
Step 2: Soaking beans
The time and temperature of soaking beans should be appropriate. Beans are easy to ferment and protein is easy to lose if soaking time is too long. The quality & yield of tofu will be decreased if with a short soaking time, along with less soy milk.
Quantity: for example, soak 500 g of dry soybeans to obtain 1000 g – 1100 g of wet soybeans.
Temperature and time: Soak 6 – 7 hours at 15 °C, or 5 hours at 20 °C, and 10 hours or more if in winter.
Water & PH: it is better to use soft water, such as surface water or tap water to soak beans. It is also recommended to add baking soda, about one-thousandth of the weight of the bean to adjust the pH value of the water to promote protein leach. The amount of water used should make sure to submerge soybeans completely.
Step 3: Refining
It can be used with stone grinding or refining machine. It is required to grind the wet beans twice and adding water while grinding. 1500 grams added at the first refining, and 750 g for the second refining.
Step 4: Discharge Air Out
Put 20-30 grams of edible oil in the heated pot until the oil is boiling, then add a small amount of warm water (about 50 °C), and pour into the soy milk and stir for 5 minutes.
This step is mainly to discharge the air out of the soy milk and reduce the viscosity to make sure soy milk can filter quickly and filter thoroughly.
Step 5: Filter
Cloth or gauze can be used as a filter to separate the soy dregs and soy milk. 60°C water is used several times, and stir the filter residue while adding water. Totally, around 1750 grams of water is used in this process and finally get the pure soy milk.
This step is to filter soy dregs and get soy milk or obtain protein completely.
Step 6: Cooking
Cooking pure soy milk with a fierce fire.
Step 7: Making Tofu
There are two ways to make soft tofu, Cold process or thermal process.
Cold process: cool the soy milk down below 30 °C, then add 9 (can be less if with nigari) grams of GDL and stir it. Then put soy milk in a smooth box or in a food bag, steam it for 25 minutes or directly place the box or bag in boiling water for 25 minutes and wait it cools to form tofu.
Thermal process: cool the soy milk down to 90 °C, then put GDL and stir it. Soon put soy milk into the box for 15 minutes.
Leavening acid in bakery
The combination of Glucono delta-lactone and baking soda would be a good choice to form a baking powder as a leavening agent in baked food.
When the baking powder in contact with water, GDL reverts to gluconic acid that reacts with sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide, which increases dough volume and the bread to rise.
The following are the preparation steps to make the bakery with GDL.
- Step 1: Mix GDL with baking soda to form a quick-acting leavening agent with a ratio of 2:1.
- Step 2: 1. Weight 500 grams of flour. 2. Weight 10.25g the mixture of GDL with baking soda which prepared in step 1. 2.5% of the weight of the flour. 3 Put the mixture in flour and stir.
- Step 3: Add 300 grams of cold water into the mixture prepared in step 2.
- Step 4: Knead the dough to be soft and there is no need to add any fermented material.
- Step 5: Steam it and you can get a soft bakery product.
Acidifier in meat products
Glucono delta-lactone can be used as an acidity regulator and a color enhancer in meat products, especially for dry-cured sausages, where a slow release of acid is required. It also function as a preservative as it inhibits the growth of bacteria by lowering the pH.
GDL can enhance meat preservation by reducing the level of nitrite, accelerate the curing process and produce a more stable product with an extended shelf life.
Color stabilizer
GDL can provide a bright color and make the color unchanged/stable in meat products. Also, it can keep the meat products fresh & tender, at the same time offer a good preservative effect, and reduce the residual amount of nitrosamines by lowering the usage of nitrites.
Acidifier
Acidification is essential for the coagulation of meat proteins in the production of raw sausages. The ripening and curing process of sausages will be efficient if added with GDL. And the sensory is easy to mask as the acidification of GDL is mild compared with other food acidulants, a third of the sourness of citric acid.
Other food
Cheese, dairy products, canned food, desserts, salads, sauces, soups, mayonnaise and so on.
Cosmetics
GDL is commonly called gluconolactone when used in cosmetics and personal care products. It is generally used for its chelating and skin conditioning properties which are suggested by the European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients. (2)
We may find products that contain gluconolactone:
- Skin care products
- Hair products
- toothpaste
- deodorant
- Cream
- lotions
Is Glucono delta lactone safe to eat?
Yes, GDL has been approved as a safe preservative by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
FDA has affirmed glucono delta lactone is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) as a direct human food ingredient. And it can be used as a curing and pickling agent, leavening agent, pH control agent; and sequestrant in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (3)
EFSA
Glucono-delta-lactone (E575) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (4).
Approved uses and usage
GDL is classified in class I with the use level “quantum satis”, which means there is no specific limit in its uses.
The following food may contain it (5):
- Mozzarella
- Ripened cheese (products), whey cheese
- Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables
- Fresh (pre-cooked) pasta
- Biscuits and rusks for infants and young children
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (6)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 575. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, acidity regulator, raising agent, sequestrant. (8)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1998, also for sodium, calcium, magnesium, potassium salts of gluconate. (9)
What’re the possible side effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have health concerns if Glucono delta lactone is bad for our health and what are the dangers. It is generally considered safe as it is a natural ingredient made from the fermentation and there were no toxicity and few side effects reported in studies (10).
However, some populations may be sensitive to it and may cause following allergic symptoms (11):
- rash
- itching
- swallowing
- others
Is GDL safe for pregnant?
Yes, it is generally safe, better consult your doctor for the uses under conditions.
Frequently asked questions
Is Glucono delta-lactone dairy origin?
No, GDL is made from the fermentation of plant-derived sources and is not originate from dairy so without casein and lactose, safe for people with lactose intolerance.
Is Glucono delta-lactone vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as synthesized from the raw material – gluconic acid, which is a vegetable ingredient, animal matter or animal-derived products are not involved in the manufacturing process. Therefore, it is suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Is Glucono delta-lactone natural?
Yes, it is a natural food acid which can be found in honey, fruit juices, and wine (12).
Is Glucono delta-lactone Halal?
Yes, GDL is halal complying with the diet policy of Muslims.
Is Glucono delta-lactone Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. E575 meets all the “kashruth” requirements and has been certified as kosher.
Is Glucono delta-lactone Gluten free?
Yes, GDL is gluten free or without gluten as comply with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a knowledge of the acidity regulator – Glucono delta-lactone (E575), from the following aspects:
- The relationship with gluconic acid.
- Manufacturing process starts from corn.
- Food uses: a coagulant in tofu, a leavening acid in the bakery, color stabilizer & acidifier in processed meat and so on.
- Approved safety.
- Possible side effects.
- Common FAQs: is it gluten free, vegan and natural.
What kinds of food packaging have you found this additive in? Let me know in the comments.



I have found GDL in „ Greek white Block“ by Violife (violifefoods.com)
It’s in a precooked bowl of quinoa made by O Organics. The bowl has a more than one year shelf life. I haven’t tried eating it yet because I didn’t know if it was safe. Sounds like it basically is, and I’ll watch for any side effects.
Does Glocono Delta lactone powder has a shelf life ? If it’s expired 10 months is it safe to use?
Organic cooked Quinoa bowls from Costco. Been eating it for several years with no ill effects.
Hi Mia,
Every ingredient has its shelf life. Better no use if expired.
So…I am allergic to corn. Corn Starch the major source of glucose for manufacturing. Corn is not a vegetable, it is a grain. So how then is Gluconic Acid a vegetable ingredient? Just curious? As someone allergic to corn deciphering food labels is extremely frustrating. Kind of like Citric Acid isn’t made from citrus….
I had a major allergic reaction to this in a cauliflower noodle, and didn’t realize this was corn derived until reading this. Just getting over it. I blew up like a balloon and went up over 7lbs overnight. I knew I was allergic to corn, so maybe that was it or this preservative is my new allergy.
Bumble Bee brand tuna salad kit purchased from Rouse’s Market. No negative reaction.
Oyeter sauce
Dude! We must be distantly related as we share the same last name. HAH! Thanks for the thorough explanation. It was helpful. I found this ingredient in the three little pig brand’s pâté.
I found that it was the reason that for over a year I have had a wheezing cough. It was in one of my stables – Tofu, that is shelf safe, but not safe for my respiratory system. Beware!
found in a bag of hostess donettes. Specifically the Old Fashioned mini donuts. After checking all the other Hostess brand minis, this was the only style of donut with glucono delta lactone. in it. This is weird to me.
3.0 oz (86g) Brunswick chicken salad with crackers. I came here to find out what the heck GDL is.
oops. also in the same size of Brunswick lemon pepper tuna salad with crackers. It may be in all varieties.
Teatulia cold brew iced tea.
Sams Club chicken salad. Delicious. Side affect was good sleep