What is Succinic Acid (E363) in Food? Uses, Safety, Side Effects

Natural Source | Production | Uses | Health benefits | Safety | FAQs
Succinic acid or butanedioic acid, a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid that can be used as an acidulant and flavouring agent in food with the European food additive number E363. This ingredient is commonly used in industrial applications instead of in food. Generally, when used in food, it is safe, natural or synthetic, vegan, halal, kosher and gluten-free.
Natural Source
The natural source of succinic acid is mainly from amber (a famous one is baltic amber), which is formed from pinus resin after being buried in the ground for a long time. The content of succinic acid is around 3-8% in amber.
It can also be naturally found in broccoli, rhubarb, beets, asparagus, fresh meat extracts, sauerkraut and cheese (1).
It is naturally present in almost all plant and animal tissues. Like citric acid and fumaric acid, it plays an important role in metabolic processes and may be involved in the net synthesis of glucose, other sugars and fatty acids in the Citric Acid Cycle in the human body (2).
How is Succinic Acid Made?
Succinic acid was first obtained from amber by distillation, so it is also known as amber acid. Currently, there are two common manufacturing processes, one is the traditional chemical synthesis from petroleum-derived raw materials, another is biological-based fermentation from carbohydrates.
Chemical Synthesis
It is mainly commercially produced from maleic anhydride, obtained by oxidation of n-butane or butadiene. There are mainly two steps in the process, maleic anhydride is catalytic hydrogenated to succinic anhydride and then reacted with water to form succinic acid.
The following is the flow chart:
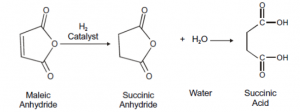
Succinic acid can also be made by hydrogenation of fumaric acid.
Bio-based Fermentation
There was a brief fermentation-based manufacturing process used by the manufacturer BioAmber in 2014. A gene-modified Pichia sp. strain of Saccharomycetaceae yeast (Pichia sp.) was utilized and biomass as the substrate for the production of succinic acid. (3)
European Commission mentioned that bacteria strains isolated from the rumen and industrial microorganisms (such as Escherichia coli or Saccharomyces cervisiae) can be used in the fermentation of glucose from starch, sugar crops and lignocellulosic materials. (4)
Specification
|
Appearance |
Colourless or white, odourless crystalline powder or granular with a sour taste. |
|
Other names |
|
|
CAS number |
110-15-6 |
|
Chemical formula |
C4H6O4 |
|
Molecular weight |
118.09 |
|
Melting point |
185.0-190.0 °C |
Structure
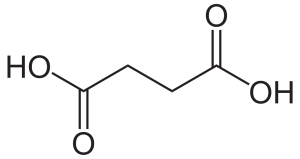
Image Source
Properties
Solubility
In water: it is polar and freely soluble in water, with the solubility, 1g/13ml at 25°C.
In organic solvents: soluble in Ethanol (5.4g/100ml) and glycerol (5.0g/100ml), not soluble in ether and petroleum ether.
PKa
It is a weak diprotic acid that has undergoes two dissociations and so follows two PKa, PKa1 4.2 and PKa2 5.6, respectively.
PH
PH value 3.65 with a concentration of 1 mmol/L at 25°C and 3.12 with a concentration of 10 mmol/L. (5)
What are the Uses of Succinic acid?
Food
Food grade succinic acid can be used as an acidulant and flavoring agent in food and beverage to regulate acidity. However, it is not commonly used in food compared with other acidulants, such as citric acid and malic acid.
It can be used as a raw material to synthesis following ingredients:
- Starch Sodium octenyl succinate (E1450)
- Starch aluminum Octenyl succinate (E1452)
- Disodium succinate
- Vitamin E calcium succinate
- Ferrous succinate
- Succinate monoglyceride
Supplement
The main reason succinic acid can be used as a supplement is that it participates in the citric acid cycle or krebs cycle that helps to restore a healthy metabolism. Succinic acid can be used for symptoms caused by menopause such as hot flashes and irritability. It can also help reduce fatigue and improve brain performance. (6)
Industrial Applications
Its main commercial applications are as an intermediate for the manufacturing of several chemicals, such as 1,4-butanediol (BDO), tetrahydrofuran (THF), γ-butyrolactone (GBL), and polybutylene succinate (PBS) which are used to make polyurethanes, biodegradable polyesters, and other special products that are used in plastics, nylons, paints, solvents, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, dyes, rubber, pesticides, and other industries.
Succinic acid is a dibasic acid and contains two active methylene groups that can be used to produce a lot of complex organic compounds for its reaction characteristics of halogenation, dehydration, esterification, sulfonation, acylation, oxidation, reduction, etc.
The following are its derivatives.
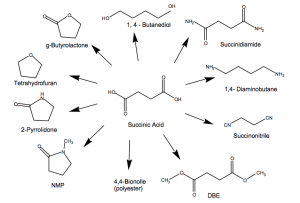
Image Source
Cosmetics
This diacid functions as a buffering, and masking agent in cosmetic and personal care products (7). Bio-succinic acid has the functions of antimicrobial property, anti-acne treatment, antioxidant activity and others when used in cosmetics, which is said by the supplier, Roquette. (8)
What’s the Health Benefits of Succinic Acid?
When it comes to its benefits, apart from its functions in participating in the citric acid cycle in our body, we always turn to baltic amber teething necklaces which are popular as it is thought to relieve teething pain and have anti-inflammatory functions in medical uses.
However, a study in 2019 found that succinic acid could not be released from the baltic amber beads into human skin, and also no approved anti-inflammatory properties. (9)
Is Succinic Acid Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Succinic acid is generally recognised as safe (GRAS) and can be used as a flavor enhancer and pH control agent in food at levels not to exceed good manufacturing practice, the approved applications are in condiments & relishes with the maximum usage 0.084% and 0.0061% in meat products. (10)
EFSA
Succinic acid (E363) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (11).
Approved uses
The following food may contain E363 with the maximum uses range from 3000-6000mg/kg:
- Flavoured fermented milk
- Soups and broths
- Flavoured drinks in powder form for home preparation of drinks
- Desserts
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (12)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 363. (13)
What are the Possible Side Effects of Succinic acid?
After the studies on oral toxicity, carcinogenicity, genotoxicity and other, the manufacturer Bioamber concluded that the food grade had no adverse effect and safe under the conditions of its intended uses, which is approved by the FDA in 2015.
Frequently Asked Questions
Succinic Acid vs Citric Acid?
Both are acidulants, used as PH regulator and flavor agent in food. The former is a weak acid and used less than the latter in food.
Is Succinic acid Vegan?
Yes, both the chemical derived and bio-based succinic acid are vegan as animal products are not involved in the manufacturing process. So it is suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Is Succinic Acid Soluble in Hexane?
No, as hexane is nonpolar while succinic acid is polar.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a good knowledge of the acidulant – succinic acid (E363), from following aspects:
- Two production processes
- Uses in food, supplement, cosmetics and industrial
- Approved safety
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Let me know in the comments.
Featured image Source


