What is TBHQ (E319) in food: Uses, Mechanism and Safety

Production | Uses | Mechanism | Safety | FAQs
TBHQ, which stands for “tertiary-butyl hydroquinone”, is both used as a preservative and antioxidant in fats and oils to protect against oxidative deterioration or rancidity, and therefore extend storage stability. This ingredient is fat-soluble and especially effective for unsaturated vegetable oils with the European food additive number E319.
How is TBHQ made?
Commercial TBHQ is produced by reacting hydroquinone with tert-butanol or isobutylene. Here is a detailed manufacturing process between hydroquinone and tert-butanol from a China manufacturer (1).
The following is the brief reaction equation:
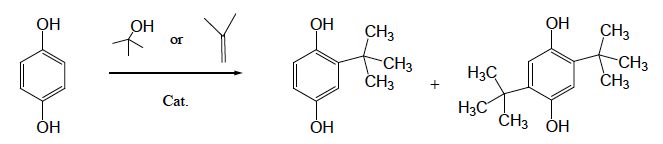
Specification
| Appearance | White or tan powder with a light characteristic odour. |
| Other names | Tert-butylhydroquinone, tert-butyl-1,4-benzenediol |
| CAS number | 1948-33-0 |
| Chemical formula | C10H14O2 |
| Molecular weight | 166.220 |
| Stability | With high thermal stability, no discoloration in the presence of metal ions (e.g. iron, copper). |
| Solubility | practically insoluble in water, easy to dissolve in oils & fats and organic solvents |
What’re the Uses of TBHQ?
Fats and oils are important nutrients in our food. However, under normal conditions, they’re easily oxidized and will gradually deteriorate due to unsaturated fatty acids in it during storage.
Food grade TBHQ is a powerful synthetic phenolic antioxidant mainly used for preserving freshness by preventing unsaturated fatty acids in oils and fats from being oxidized & deteriorated.
It is commonly used alone or with other phenolic antioxidants, such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), and propyl gallate (PG) to produce highly effective antioxidant combinations.
Vegetable oils and animal fats in the following processed food may be preserved with TBHQ:
- Fried foods: chicken nuggets, potato chips, McDonald’s Mighty Wings (2)
- Nuts
- Candy
- Crackers
- Butter
- Chocolate
- Instant noodles, ramen noodles
- Microwave popcorn
Vegetable oils
TBHQ is the best oil antioxidant, especially in vegetable oils, such as in peanut oil, blending oil of peanut and soybean. The antioxidant effect is stronger than the commonly used antioxidant, BHA, BHT and PG in palm oil and walnut oil. The antioxidative effect will be better if in combination with citric acid or ascorbic acid.
Animal fats
The shelf life of fish oil can be extended after the addition of TBHQ. The antioxidant effect of 0.02% TBHQ is almost equivalent to that of 0.1% Vitamin E. It is an ideal oil antioxidant not only with good oil solubility, but also does not affect the color of the fish oil.
How does TBHQ work?
Fats and oil-rich foods often suffer from spoilage during processing, storage, and transportation. Free radicals are generated from unsaturated fatty acids after oils & fats exposed to light, oxygen, metal ions and bacteria.
And following several reactions, unsaturated fatty acids convert to hydroxides and secondary oxidation products which can change the physical and chemical properties of oils and fats (e.g. color, flavor, smell and nutritional value), and finally shorten the shelf life and make the oils & fats or the foods deteriorate or even make foods become toxic.
The oxidation mechanism is generally as follows:

TBHQ provides hydrogen free radicals which terminate the above free radical chain transfer reaction of unsaturated fatty acids. This is the mechanism of how TBHQ works as an antioxidant.

Is TBHQ Safe to Eat?
Yes, although it may cause side effects such as stomach tumors at very high doses (3), the safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
TBHQ may be safely used as an antioxidant alone or in combination with BHA and/or BHT and with the maximum use level 0.02% of oil or fat content in food. (4)
EFSA
Tertiary-butylhydroquinone (E319) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (5).
Safety re-evaluation
EFSA stated TBHQ was not carcinogenic in its safety evaluation in 2004. (6)
An ADI (acceptable daily intake) of 0.7 mg/kg body weight (bw) was confirmed in 2004, which was established by the JECFA in 1998. (7)
Approved uses
Its application is listed together with BHA and propyl gallate, with the maximum level “25-400mg/kg”. The following are some of its uses (8):
- Milk powder for vending machines
- Fats and oils for heat-treated foods
- Frying oil and frying fat (excluding olive pomace oil) and lard, fish oil, beef, poultry and sheep fat
- Processed nuts
- Dehydrated products: potatoes, meat and soups & broths
- Chewing gum
- Cake mixes
- Seasonings and condiments, sauces
- Precooked cereals, cereal-based snack foods
- Solid/liquid form of food supplements (not for infants and young children)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Antioxidants” (9)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 319. (10)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, antioxidants. (11)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-0.7 mg/kg bw” set in 1997.(12)
Frequently asked questions
Is TBHQ halal?
Yes, it is halal complying with the Muslim policy.
Is TBHQ Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
TBHQ vs BHA vs BHT?
They’re all antioxidants widely used in edible oils and fats for preserving freshness. The advantages of TBHQ over others are as follows:
- Better antioxidative properties.
- More stable in heat and maintains its antioxidant activity.
- Better solubility in oils.
- Also acts as a preservative to inhibit the growth of bacteria and molds.
Is TBHQ vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the main raw material – hydroquinone is made from the reaction of benzene with hydrogen peroxide; tert-butanol or isobutylene are also derived from chemical synthesis; and the animal-derived products are not involved in the manufacturing process of TBHQ, so it is suitable to the diet of vegetarians.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the preservative & antioxidant – TBHQ (E319), from the following aspects:
- Manufacturing process
- Property
- Uses
- Antioxidative mechanism
- Safety
- FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



A. I wld like to know if the doses of tbhq found in sunflower oil could be harmful to ones health? (Long term / short term)
B. Are the sunflower oil without tbhq less stable? (shorter shelf life?)
C. I need to use oil as preservative in my pesto products… any suggestions other than sunflower oil?
D. Is Apple cider vinegar really better than the normal vinegars for use in pickled foods? Any suggestions..
Hi Gideon,
My answers for your reference:
A: the safety of TBHQ (with the limited doses) has been recognised by authorities, such as FDA and EFSA. You can see such information in this article.
B: Yes, the purpose of TBHQ is to make sunflower oil stable and therefore extend the shelf life, and other antioxidants can be as alternatives.
C: use oil as preservative? sorry i didn’t got your idea.
D. It depends.
A. Is it safe to use expired TBHQ antioxidant? Why?
B. What are the dangers in using expired TBHQ antioxidant?
Better no use expired TBHQ
Hi, how can I use (scale) TBHQ properly in peanut oil.. e.g 1000ltr Of peanut oil required how many gram of TBHQ?
Thanks for your help.
Thank you for your article, it gave me a lot of interesting information.Can you be more specific (about the mechanism or about the survey results) to prove that TBHQ is better than BHA, BHA? Thank you very much. Hope to hear from you soon
Latest research shows TBHQ is an immunosuppressant. It can cause dangerous allergies (can vouch for that personally). Kidney and thyroid damage has been documented and Japan smartly banned it (not much food allergies reported there). It’s not safe at all
It causes shock and collapse in humans just at 1gm. Instantaneously lethal start just at 5 gm. It’s like cyanide. Never should’ve been allowed in food. The food mafia corrupts the licensing authorities and the result is innocent people suffering
thank you suma I knew this was true what you say.
it’s amazing how this has been allowed but information us getting out
What is recommanded level in Lysolecithin feed grade as such and in combination with BHT&BHA