What are Mono and Diglycerides (E471) in Food? Does it contain Trans Fatty Acids?

Types | Components | Production | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Mono and diglycerides, also called mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids, saturated or unsaturated, are a mixture of monoglycerides (commonly with 40-90%) and diglycerides, and also includes minor amounts of triglycerides. It is the most used emulsifier in the food and with the European food additive number E471.
Types of Mono and Diglycerides
Mono and diglycerides is a group of emulsifiers and the following are the common types (with the only difference in fatty acids):
- Glycerol monostearate
- Glycerol monopalmitate
- Glycerol monooleate
- Glycerol monolaurate
- Glycerol monoricinoleate
Although these products only have one fatty acid that starts with “mono” before a fatty acid in the names, actually they’re the mixture of mono and diglycerides and may also contain triesters.
Esters Of Mono and Diglycerides
Mono and diglycerides can be esterified with other food grade acidulants (acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid or tartaric acid) to produce another category of emulsifiers – E472 as follows and ethoxylated mono-and diglycerides:
- Acetic acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472a, ACETEM)
- Lactic acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472b, LACTEM)
- Citric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472c, CITREM)
- tartaric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472d, TATEM)
- Mono- and diacetyl tartaric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472e, DATEM)
- Mixed acetic and tartaric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E472f, MATEM)
What are Mono and Diglycerides made of?
As mentioned above, it mainly consists following three compositions:
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
It may also contain small percentages of free fatty acids and glycerol.
The difference between monoglycerides and diglycerides is that monoglycerides are obtained by glycerol (E422) esterification with one fatty acid (E570) while diglycerides is derived from glycerol reaction with two fatty acids.
Monoglycerides
In the below example of monoglycerides, glycerol is esterified with a saturated fatty acid, palmitic acid.
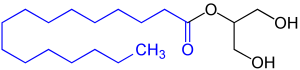
Image Source
Diglycerides
Following is an example of diglycerides obtained by esterified glycerol with a saturated fatty acid – palmitic acid (blue color), and an unsaturated fatty acid – elaidic acid (green color).
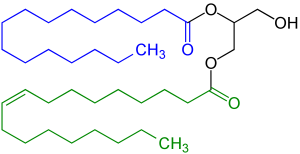
Image Source
Monoglycerides and Diglycerides Percentages
The common content of monoglycerides in commercial food grades of mono- and diglycerides are 40%, 60% or 90%.
Following is a table from the EFSA regarding the composition (% by weight) of monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides and others in different food grades of mono and diglycerides of fatty acids in the market.
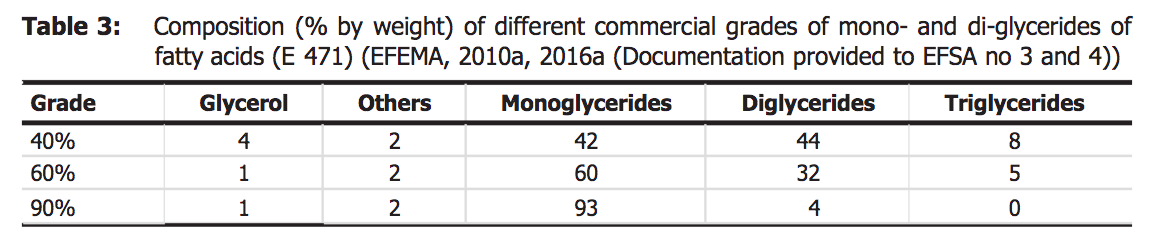
Image Source
How are Mono and Diglycerides made?
The main raw materials involved in the production of mono and diglycerides are fatty acids and glycerol, both are naturally present in edible fats/oils of animals (e.g. cow, pig) and vegetable (various plant seeds).
Generally, mono and diglycerides can be made from two manufacturing processes, transesterification process or direct esterification process.
Transesterification process
Transesterification means a reaction between an ester and an alcohol.
Mono- and diglycerides can be obtained by the glycerolysis reaction between fats /oils with glycerol, for example between methyl ester and glycerol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst (e.g. NaOH, KOH).
Diglycerides and triglycerides can also be produced in the reaction. (1)
The following is the equilibrium reactions:
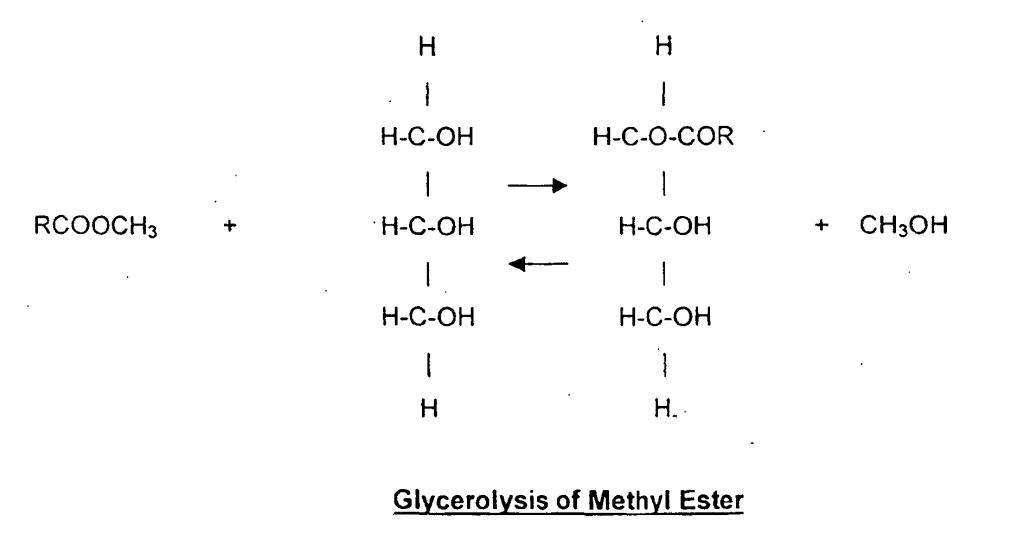
Image Source
Further distillation and other processes can be done to separate/refine monoglycerides and diglycerides, such as to produce distilled monoglycerides.
Direct esterification process
It can also be synthesized by the esterification between glycerol and fatty acids.
Below is the reaction equation:
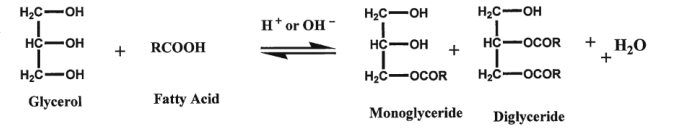
Image Source
Source
The common vegetable sources of fatty acids and glycerol are as follows:
- Palm oil
- Coconut oil
- Soybean oil
- Rapeseed oil
- Sunflower oil
- Cottonseed oil
Fatty acids
The common fatty acids including:
- Stearic acid
- Palmitic acid
- Lauric acid
- Linoleic acid
- Myristic acid
- Oleic acid
Glycerol
Glycerol is also called glycerine or glycerin, it has three hydroxyl groups, which can be esterified with one, two, or three fatty acids to form monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides.
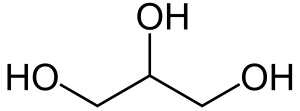
Image Source
It is a multi-functional ingredient that can be used as a sweetener, humectant, and thickener in the food and pharmaceutical industry.
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | Variable |
| Chemical formula | Variable |
| Molecular Weight | Variable |
Properties
Appearance
It is available both in liquid and solid form:
- Liquid: a pale yellow to pale brown oily liquid
- Solid: white flake, powder or beads
Solubility Structure
Soluble in fat, not soluble in water.
Structure
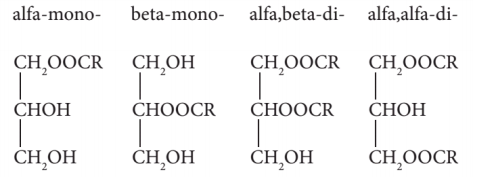
Image Source
Hydrophilic – Lipophilic Balance (HLB)
The lower the HLB value of an emulsifier indicates that it is more soluble in oil and can form W/O (water in oil) emulsions, or otherwise it is more soluble in water and forms O/W (oil in water) emulsions.
In the molecule of mono and diglycerides, glycerol is hydrophilic while the fatty acid long chain is lipophilic.
It forms W/O (water in oil) emulsion and generally, the HLB value ranges from 3 to 6.
What’re the Uses of Mono and Diglycerides?
Mono- and diglycerides is a multi-functional ingredient that primarily used as emulsifiers in the following food and for the purpose of:
- Bread: function as a dough softener, also improves loaf volume and the texture, and therefore prolongs bread freshness and shelf life.
- Cake mix: improve cake volume and texture, also improve crumb structure and tenderness.
- Margarine: stabilize the emulsion.
- Cream & Creamers: enhance the stability of the emulsion system such as in coffee mate.
- Ice cream: improve the creamy mouthfeel, stabilize the air in ice, create a stable structure and reduce freezing time.
- Spreads & Butter: improve the emulsion stabilization and spreadability, reduce stickiness, improve flavour.
- Cheese: to obtain a smooth texture, such as in peanut butter.
- Desserts: benefit aeration and foam stability.
Are Mono and Diglycerides Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Mono and diglycerides are a multi-functional ingredient which are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) that can be used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener, texturizer, dough strengthener, surface-active agent (and so on) in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (2)
It is also generally recognized as safe when used as an emulsifying agent in feed. (3)
EFSA
Mono- and Diglycerides of fatty acids (E471) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (4).
Approved uses
Its application is listed in Group I with the usage “not limited”and separately. The following food may contain it (5):
- Unflavoured pasteurised cream
- Fats and oils (free from water)
- Bread and rolls
- Processed potato products
- processed eggs and egg products
- Jam, jellies and marmalades and sweetened chestnut purée
- Cocoa and Chocolate products
- Pasta
- Quick-cook rice
- Table-top sweeteners in tablets
- Infant formulae
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
After the studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity and other researches, EFSA concluded there were no safety concerns when mono- and di-glycerides of fatty acids used as a food additive and no need for a numerical acceptable daily intake (ADI). (6)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (7)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 471. (8)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier. (9)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1973. (10)
What are the possible Side Effects of Mono and Diglycerides?
Generally, there are no observed adverse effects of monoglycerides and diglycerides when used as an emulsifier. However, sometimes consumers are worried that it may do bad to our health due to the trans fatty acids that may in it.
Do Mono and Diglycerides really contain Trans fatty acids?
EFSA pointed out during the safety re-evaluation of mono and diglycerides of fatty acids in 2017, that it may increase the amounts of trans fatty acids in final products if it is manufactured by glycerolysis (transesterification process) of hydrogenated fats and/or oils.
Furthermore, the European Commission is considering putting the item of “maximum limits for trans fatty acids” in its specifications for mono- and diglycerides.
How does Trans fatty acids occur?
It is also called trans-unsaturated fatty acids, which are produced during the partial hydrogenation process of naturally occurring vegetable oils as physical properties of parts of the unsaturated fatty acids (exist in the vegetable oils ) may be altered, changed from cis-unsaturated fatty acids to trans-unsaturated fatty acids in such process.
Trans fatty acids health risk
Human studies show that intake of trans fatty acids may increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease. (11)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it Natural?
No. Mono and diglycerides is a synthetic emulsifier which is made from chemical synthesis, the direct esterification between glycerin and fatty acids or the transesterification of glycerin with fats/oils (triglycerides).
Is it Halal, Kosher and Vegan?
Yes, mono and diglycerides are halal, kosher and vegan if fatty acids and glycerol come from vegetable oils. As the starting raw materials derived in these ways, complies with:
- The diet policy of Muslims, so it is Halal.
- Jewish religious dietary law, so it is Kosher.
- Vegetarians diet as the production without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin, therefore it is vegan.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And can be used for people with celiac disease.
Is it a Fat?
Monoglycerides and diglycerides are not fat, but triglycerides are. A fat is formed when three hydroxyl groups on glycerol combine with three fatty acids.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the emulsifier – Mono and diglycerides (E471), from the following aspects:
- Several types of mono and diglycerides based on different assay of monoglycerides and diglycerides, and various kinds of fatty acids linked to glycerol.
- Two production processes: from transesterification process and direct esterification process.
- Uses in food
- Safety
- Possible side effects: due to the existence of trans fatty acids
- FAQs: is it natural, halal, vegan, gluten free, fat.
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Is there any way to read the ingredients and know if it is vegetable based?
If only read from the food label, most people cannot well understand unless it is marked from vegetable sources.
Just to clarify, if it says, “Mono- and diacetyl tartaric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids,” does that mean it’s vegan and halal? (because with DATEM the raw materials don’t use any animal matter or products)
Hi, this was very interesting to read! With the Internets recent obsession with Mochi I have been doing a bit of research in order to understand if it is suitable for the Muslim diet. This article was very interesting but I was wondering if all mono and diglycerides are halal?
Hi Iram,
Halal or not depends on where the raw materials sourcing from, some are not halal mainly as the fatty acids are from animals.
Hi Mateen,
fatty acids can be sourced from animal, so whether it is vegan and halal depends on the source of fatty acids.
If the manufacturer only mentions in the ingredients:mono and diglycerides (vegetable source) or ( animal source) it would become so easy for vegan , halal, kosher people.
Hi,
If the manufacturer mentions in the ingredients for e.g.mono and diglyceride ( vegetable source) ,mono and diglyceride ( animal source) it would be easy for muslim , vegan and kosher people. I myself being a muslim struggle with when i want to buy something bcoz I don’t know which source it comes from.
Is there a way to tell if a product containing E471 contains high levels of trans fats or not? Given that the UK only has a voluntary restrictions on trans fats I’m not sure how best to avoid these additives in the diet when they are related to increased risk of heart disease.
How can you know whether the source of the fatty acids and glycerols is from animal or vegetable?
Maybe it is written, but may not.
Thank you James, this was an extremely thorough and informative article. Excellent work