What are Sucrose esters of fatty acids (E473) in Food and its Uses?

Production | Components | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Sucrose esters of fatty acids or sucrose esters, also known as sugar esters, is an emulsifier different with other emulsifiers as it can be used almost in all kinds of emulsions due to its wide range of HLB values formed by 1-8 fatty acids molecules attached with the hydroxyl groups in the sucrose molecule. The European food additive number for it is E473.
How are Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids made?
Sucrose esters can be synthesized by the direct esterification of sucrose with a fatty acid, or transesterification reaction of sucrose with a fatty acid ester. The same processes produce mono and diglycerides (E471).
The above latter method is commonly used in commercial production and there are generally three food fatty acid esters that can be used as the raw materials: methyl, ethyl and vinyl esters of fatty acids.
The following are the brief manufacturing processes the manufacturers Sisterna and Compass foods uses:
Sisterna
Sisterna is reacting methyl esters of food fatty acid with sucrose (1):
- Obtaining methyl esters of food fatty acid by reacting a fatty acid with methanol and then purified.
- Then reaction between methyl esters of food fatty acid with sucrose.
Compass Foods
It can also be produced by inter-esterification (same as transesterification) of sucrose with the vinyl esters of fatty acids. The supplier, Compass Foods is using this method (2). EFSA approved the safety of this method in 2010. (3)
Fatty acids source
Edible fatty acids can be derived from tallow/hydrogenated edible tallow or vegetable oils (4).
Here is the common fatty acids that can be derived from palm and coconut oils:
- Stearic acid
- Palmitic acid
- Lauric acid
- Oleic acid
- Myristic acid
Sucroglycerides are obtained by reacting sucrose with an edible fat or oil.
What are Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids made of?
Based on the sources (palm and coconut oils) of the fatty acids, stearic acid and palmitic acid always present together and commonly used, so the common food grade of sugar esters is mainly composed of:
- Sucrose monostearate
- Sucrose monopalmitate
- Sucrose distearate
- Sucrose dipalmitate
Also with triesters, and may also contain minor levels of higher esters, such as tetra, hepta or octa-esters.
It is different with sucroglycerides (E474) which also contain mono-, di- and triglycerides originally from edible fat or oil.
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 977019-37-6 |
| Mono- to tri-esters | ≥ 80% (Assay) |
| Chemical formula | Variable |
| Molecular Weight | Variable |
Properties
Appearance
The appearance depends on the type of fatty acid used in the production and the degree of esterification. It can be colorless to slightly yellow thick gel, soft solid or greyish-white powder. (5)
Hydrophilic – Lipophilic Balance (HLB)
It has a good emulsification effect both on oil and water. Compared with other emulsifiers like mono and diglycerides and sorbitol esters, sugar esters have the highest hydrophilicity.
Its HLB value varies from 1 to 16, the more monoesters content, the higher the HLB value. Generally, the HLB value of monoesters are from 10~16, the diesters is 7~10, and triesters is 3~7.
It can be both used as emulsifiers for water-in-oil and oil-in-water formulations depending on the HLB value.
Solubility
The solubility of sucrose esters various according to the HLB value, generally, the higher the HLB value, the better soluble in water, the less soluble in oils/fats. For example:
- High HLB value (11-16) soluble in water.
- Medium HLB value (6) partly soluble in water and oils/fats.
- Low HLB value (2) sparingly soluble in water, soluble in oils/fats.
Structure
- Hydrophilic group: hydroxyl group on sucrose molecule
- Lipophilic group: the carbon chain with the fatty acid molecule.
Since there are 8 hydroxyl groups on sucrose molecules, therefore it can react with 1 to 8 fatty acids molecule.
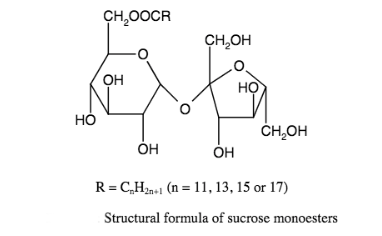
Image Source
It is powder form if sugar reacts with higher fatty acids, such as stearic acid, palmitic acid, and oleic acid. This ingredient will be viscous liquid if esterified with lower fatty acids, such as – sucrose acetate isobutyrate (SAIB, E444), produced by esterification of sucrose with acetic acid anhydride and isobutyric anhydride.
What’s the Uses of Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids?
Sugar esters are used widely than other food emulsifiers in food, cosmetics, pharmaceutical and other industrial applications for its HLB value can vary from 1 to 16.
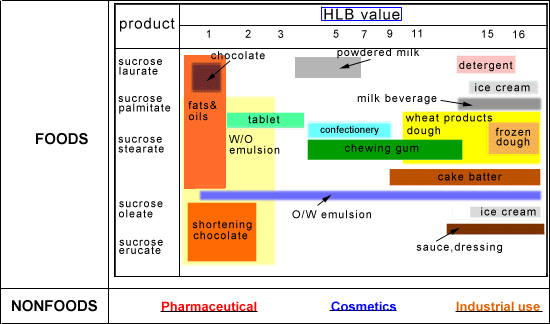
Image Source
Food
Sugar esters are commonly used in oil-in-water emulsions. This property is based on its main content – sucrose mono- and diesters which have higher HLB values.
And the common foods with it are like in beverage, bakery, dairy, confectionery, cereals, and ice cream.
Let’s see its various functions in food.
Beverages
Stabilize the emulsion and prevent precipitation and delamination; provide a creamy mouth feel.
Formulated milk
Interact with proteins to prevent protein flocculation and also improve the taste of the milk.
Bakery products
Interact with proteins in the flour and react with the amylose molecule, resulting in an increased volume and soft crumb; retard starch retrogradation and oil leakage, and therefore extend shelf life.
Light cream
Prevent oil and water from separating.
Chocolate and cocoa products
Prevent oil separation, sugar crystallization and fat oxidation. Also, reduce chocolate products from being damaged and deformed by moisture and heat. Reduce the viscosity of the chocolate mass, similar to the function of lecithin.
Candy
Help mix the raw materials thoroughly and to prevent oil separation and reduce stickiness to teeth and wrappers. In hard candy, it can replace titanium dioxide to impart a white appearance and also can substitute gum arabic; in soft candy, it enhances a soft texture.
Chewing gum
Reduce the viscosity in the gum base, making it easier for ingredients to mix together.
Meat products
Improve the water retention of sausages and hams and prevent the separation of oils and fats from meat products with high fat.
Condiment
Improve emulsification and dispersion, prevent caking of moisture-absorbing powder, and improve fluidity.
Cereal bars
Act as a release agent by reducing stickiness during the production of cereal bars.
Jelly
Improve the shape retention and prevent syneresis of jelly products.
Surface-treated fresh fruit
Keep the fruits fresh and extend the storage period.
Cosmetics
A type of sugar esters – sucrose stearate can function as an emollient, emulsifying, skin conditioning and surfactant in cosmetic and personal care products. (6)
Is Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sucrose fatty acid esters may be safely used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, or texturizer in food in accordance with current good manufacturing practice.
Following food may contain with it Sucrose fatty acid esters (7):
- Baked goods and baking mixes
- Chewing gum
- Coffee and tea beverages
- Confections and frostings
- Dairy products
- Frozen dairy desserts and mixes
- Surimi-based fabricated seafood products
- Fresh fruits
EFSA
Sucrose esters (E 473) (and sucroglycerides, E 474) are listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (8).
Approved uses
The application of sucrose esters and sucroglycerides are listed together. The following food may contain it and generally the usage varies from 1 to 20 g/kg(9):
- Flavoured fermented milk products
- Sterilised cream
- Beverage whiteners
- Fat emulsions for baking
- Edible ices
- Sugar confectionery
- Chewing gum
- Decorations, coatings and fillings
- Fine bakery wares
- Infant formulae
Safety re-evaluation in 2004
In 2004, after evaluated the safety and toxicity, the EFSA changed the acceptable daily intake (ADI) of both sucrose esters of fatty acids (E473) and sucroglycerides (E474) from 0-20 mg/kg bw (expressed as sucrose monostearate, set in 1992 by SCF) to 40 mg/kg bw/day. The fatty acids here are stearic acid, palmitic acid and myristic acid. (10)
Safety re-evaluation in 2010
EFSA also confirmed the safety of sucrose esters made from stearic acid, palmitic acid, lauric acid, and myristic acid. (11)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (12)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
They’re approved ingredients in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 473 and 474, respectively. (13)
JECFA
Sucrose esters of fatty acids
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier. (14)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-30 mg/kg bw” set in 1997. (15)
JECFA further classify INS473 into INS473a (Type I, high-esterified) and INS473b (Type II) according to the esterification degree.
Sucroglycerides
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier. (16)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-30 mg/kg bw” set in 1997. (17)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Sucrose esters sugar?
No, it is a sugar derivative, made from the chemical synthesis from sugar and food grade fatty acid esters.
How to dissolve Sucrose esters before use?
- Its high HLB types (5 to 16) can be dispersed in water first then heated until dissolved.
- Dissolve the low HLB types (0 to 3) in oil.
Is Sucrose esters Vegan?
Yes, commonly it is vegan as produced from vegetable sources of food fatty acids (palm oil and coconut oils), and sugar is also plant-based, therefore the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is suitable for vegetarians.
However, it may not be vegan as the food fatty acids that can be derived from edible tallow or hydrogenated edible tallow.
Is Sucrose esters Halal?
Yes, it is halal if produced from plant sources, or otherwise it is not, similar as mentioned in vegan.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the emulsifier – Sucrose esters of fatty acids (E473), from the following aspects:
- Production process: inter-esterification of sucrose with a fatty acid ester
- Made of: the main components mono- and sisters of sucrose
- Uses and functions in various food
- Safety
- FAQs: how to use, is it vegan
I’m probably forgetting some information of sucrose esters, and if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Would this ingredient be considered an Artificial ingredient? Thanks
Hi Bri,
Yes, of course, it is an artificial ingredient as you can see synthesized from the chemical reaction of sucrose with a fatty acid.
Hello James how I Can check that fatty acids
Is made from plant sources .
Hi Zaman,
Maybe it indicates in the food label, or otherwise, you need to check with the food manufacturer
Thanks for your detailed information. I pretty sure from reading this article that sucrose ester does not have an impact on blood sugar levels but as an insulin resistant person on a low carb and sugar free diet, I would like to make sure. So I’m asking if this additive is 0 on the glycemic index. I have recently come across it’s ingredient in a magnesium product called magnesium breakthrough that claims to have seven types of magnesium in it and therefore better than the magnesium citrate, 750mg from Les Labs that I am currently taking. Thank you again, I will definitely be looking at your site for detailed information.
Is Sucrose Esters of Fatty Acids safe as an ingredient in a supplement for a dog?
Hi Han,
Sucrose Esters can be made from palm and/or coconut.
Do you know a producer that only uses Coconut?
Kind Regards
Joram