What is Calcium Chloride (E509) in food and its common uses?

Production | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Calcium chloride (CaCl2), an inorganic ingredient made of calcium and chloride elements. We can find its uses in everyday life, the food grade can be used as a firming agent (not only this purpose) in food with the European food additive number E509.
The industrial grade is commonly used in roads de-icing, dust control, brine refrigeration, dehumidification due to its characteristics of releasing heat after dissolved in water, lowering the freezing point of water, strong hygroscopicity and deliquescent.
How is Calcium chloride made?
Commercial calcium chloride is mainly synthesized with three manufacturing processes as follows:
Ammonia-soda process
CaCl2 is a by-product in the production of sodium carbonate. The process is also called Solvay process in which the reaction between sodium chloride (salt brine) with calcium carbonate (limestone), and ammonia as a catalyst (1):
2 NaCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + Na2CO3
Limestone-hydrochloric acid Process
React hydrochloric acid with calcium carbonate (limestone).
2HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Natural brine process
Purification of naturally-occurring brines (such as salt lakes) by removing magnesium with adding Ca(OH)2, and precipitating sodium chloride by increasing the concentration of CaCl2.
Specification
Two types
According to the different amount of crystalline water, calcium chloride can be divided into two types:
- Dihydrate: the main type in the market for deicing and dust control.
- Anhydrous: commonly as a drying agent for gases and liquids. It can attract 6 times moisture: CaCl2 + 6H2O → CaCl2 · 6H2O
Also with hexahydrate form, but seldom in the market.
CaCl2 can also be classified into food and industrial grades based on the different uses.
| Other names |
|
| CAS number |
|
| Chemical formula |
|
| Molecular weight |
|
Properties
Appearance
White, odourless, both hygroscopic and deliquescent (converts to a liquid brine after absorbing enough moisture). It is supplied in the form of powder/pellet/flake/granular or solution depending on the requirements of the application.
Solubility
Highly soluble in water with the solubility 1g/1.5ml at 25°C and soluble in ethanol. It dissociates calcium ion and chloride ion when dissolved in water with the following equation: CaCl2 (aq) → Ca2+ (aq) + 2Cl– (aq)
Reactions
CaCl2 is commonly reacts with the below ingredients and with the chemical reactions:
- Sodium carbonate: CaCl2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2NaCl
- Sodium bicarbonate : CaCl2 + 2NaHCO3 → CaCO3 + 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
- Potassium carbonate: CaCl2 + K2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2KCl
- Sodium phosphate : CaCl2 + Na3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2 + NaCl
- Sodium hydroxide: CaCl2 + 2NaOH → Ca(OH)2 + 2NaCl
Structure
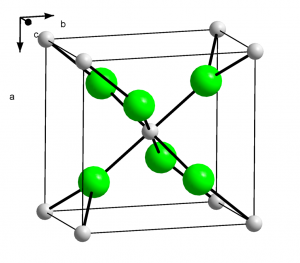
Image Source
What’re the Uses of Calcium chloride?
Food
Generally, food grade calcium chloride is mainly used as a firming agent, anti-caking agent, pickling agent, preservative, stabilizer, texturizer, moisture absorber, and low sodium salt in food processing. Its main applications are in bottled water, cheese making, beer brewing, gel with sodium alginate, canned fruits & vegetables and so on.
Bottled water
Bottled water companies add calcium chloride and other minerals & salts (e.g. magnesium chloride or sulfate, sodium or potassium bicarbonate) in bottled drinking water mainly for the following two purposes:
- Impart a taste of clean, sweet and salty to purified water which tastes flat after distilled.
- Balance electrolytes in your body after sweat or urinate and therefore avoid overhydrate.
Cheese
Calcium chloride is often added to milk for cheese making. It increases rennet activity, accelerates coagulation and increases curd firmness by slightly raising milk acidity and reacting with protein to hold together.
Beer
Calcium chloride or sulfate is commonly used in beer brewing. The function of calcium ions as follows:
- Reduce the pH
- Preserve mash enzymes
- Avoid mineral deficiencies and improve the hardness of beer water
- Remove phosphate and oxalate
- Promote yeast growth and flocculation
- Bind with the cell wall proteins after absorbed by the growing yeast cells
Chlorine ions can promote the activity of alpha-amylase, improve the activity of yeast, make the beer taste soft, increase the malt flavor, clarify the beer, and stabilize the colloid.
Pickles
Calcium chloride can be used to replace sodium chloride in pickling brine. It adds a salty taste to pickles without increasing sodium intake, helps the cucumbers look nice and maintain firmness, and also speeds up fermentation during the pickling process. Meanwhile, it is environment friendly (2).
Desiccant
With the function of strong water absorption rate, anhydrous calcium chloride is an efficient dehumidifier which absorbs moisture from the surrounding environment and thus reduces the humidity in the sealed packaging, and therefore protects food from moisture during storage.
Fresh vegetables
Preserving the freshness of fruits and vegetables by sprayed or dipped in calcium chloride solution after harvesting is an effective method, which
- Slows physiological disorders
- Reduces the respiratory strength
- Maintains firmness by reacting with the pectin
- Delays the loss of Vitamin C
- Enhance nutritional calcium level
- Used together with calcium propionate and calcium ascorbate to the surface of apples and lemons as an antibrowning agent (3)
- Reduces decay
And therefore extend the shelf life of fresh fruits and vegetables.
Low sodium food
CaCl2 is similar to table salt, but it contains calcium instead of sodium. It can be used in food where low sodium is desired.
Other food uses
- As a coagulant in tofu making.
- gel or spherification with sodium alginate.
- For meat tenderization.
- Improve protein stability and kneading resistance in wheat flour and as a calcium fortification.
- Calcium supplement in dairy products.
- As a refrigerant for ice cream and frozen dessert products manufacturing.
- Preserve color and texture, retain firmness in canned fruit and vegetables, e.g. processed tomatoes.
- Reduce the formation of acrylamide in the production of potato chips and sticks in high-temperature cooking (4) which caused cancer in animals at very high doses. (5)
Industrial
Industrial grade calcium chloride is commonly used in roads snowmelt and de-icing; as antifreeze for construction which accelerates the hardening of concrete and increases the cold resistance of construction mortar; an aqueous solution can be used in oil drilling; the ability of adsorption and desorption of ammonia can be used for refrigeration.
Let’s see the details.
Ice melt
Calcium chloride is usually used for snow melting and de-icing in winter on roads, highways, parking lots, docks, and airports to improve the safety for drivers and pedestrians. It is more workable than sodium chloride at lower temperatures as low as −52 °C (close to its freezing point) (6).
Its function as a deicer is mainly for the following three characteristics:
- Gives off a lot of heat while dissolved in water as an exothermic reaction. Such property promotes the melting of snow and ice.
- The formed brine lowers the freezing point of water, making water hard to produce snow and ice on contact of the road again.
- Accelerates the formation of such brine by attracting the moisture from its surroundings.
Concrete
Calcium chloride is used to accelerate cement hydration, reduce set time and improve the strength for concrete in colder weather.
Road dust control
The strong ability of water absorption or deliquescence makes it a dust control on the surface of gravel roads (especially on unpaved roads) by absorbing moisture from air & added in the construction with gravel particles. This property also ensures safety for humans by removing dust from the air we breathe.
Pool
CaCl2 is used to adjust the calcium hardness in the pool. It prevents pools from freezing in the winter, and alleviates the corrosivity of pool water and metal equipment (e.g. heaters, ladders, and handrails.) caused by low levels of calcium hardness.
Fertilizer
Source of both calcium and chloride for the plant, also adjust the level of sodium in the soil.
Is Calcium chloride Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects and the safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Calcium chloride is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) that can be used as a firming agent, nutrient supplement, pH control agent, anticaking agent, humectant and others in the following food categories and with the maximum usage:(7):
- Baked goods, dairy product analogs 0.3%
- Beverage 0.22%
- Cheese, processed fruit and fruit juices 0.2%
- Coffee and tea 0.32%
- Condiments and relishes 0.4%
- Gravies and sauces 0.2%
- Jams and jellies 0.1%
- Meat products 0.25%
- Plant protein products 2.0%
- Processed vegetables and vegetable juices 0.4%
- Other food categories 0.05%
EFSA
Calcium chloride (E509) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (8).
Safety re-evaluation in 2019
EFSA concluded no safety concern when calcium chloride (together with hydrochloric acid (E507), potassium chloride (E 508) and magnesium chloride (E 511)) used as a food additive after the studies on genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and other researches. (9)
Approved uses
Its application is listed in “Group I” with the maximum level “quantum satis”. Meanwhile, its separate use levels are also “not limited” in the following products are also (10):
- Dehydrated milk
- Ripened cheese
- Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables
- Fruit compote other than apple
- Jam, jellies and marmalades
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (11)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 509. (12)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, firming agent. (13)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1973. (14)
Frequently asked questions
Is CaCl2 Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as a naturally occurring mineral and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is suitable added to the diet of vegetarians.
Is CaCl2 acid or base?
It’s neither acid or base, it is a salt.
Is CaCl2 polar?
Yes, it is polar. It is an ionic molecule which dissociates to calcium ion and chloride ion in water.
Calcium chloride vs calcium lactate vs calcium gluconate?
Calcium chloride, calcium lactate, calcium lactate gluconate are three commonly calcium salts used in spherification. They all contribute to calcium ions and the main difference is calcium chloride has the highest level of calcium, but it has a bitter taste while the other two don’t have a flavor.
Is CaCl2 natural?
Yes, it is natural if made from the brine process, otherwise it is synthetic.
Is CaCl2 gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free or without gluten as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains, therefore can be used for people with celiac disease.
Is CaCl2 dairy free?
Yes, it is dairy free as calcium is derived from limestone instead of milk.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the firming agent – Calcium chloride (E509), from the following aspects:
- Three manufacturing processes.
- Two types: anhydrous and dihydrate forms.
- Food grade uses: bottled water, cheese, beer, pickles, desiccant, vegetables & fruits and so on.
- Industrial grade applications: ice melt, road dust control, pool water and etc.
- Safety
- FAQs
What kinds of food or industrial product labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.
Featured image source

Hello.
Thank you for a very informative and detailed analysis on Calcium Chloride.
However I would like to know if Calcium Chloride with CAS No. 10035-04-8 safe to use as a food additive. I am wanting to use it in home pickling process and eventually making pickles for commercial processing and selling.
You response would be highly appreciated.
Hi Gosai,
Calcium Chloride can be used in pickles, you can see here: https://www.ars.usda.gov/news-events/news/research-news/2014/calcium-makes-for-an-environmentally-friendly-pickle/
It is safe to use, here is the reference from FDA: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=184.1193
The comment section ‘is it vegan’ is a convoluted way of trying to explain this. Also confusing as it says at the end ‘it is vegetarian’ These comments are not the same. Vegan is different from vegetarian
Thanks for your comment, Ken!
Dear James, very interesting and informative your summary. Allow me to add something that is the outcome of recent research that might cause a different view on calcium chloride, at least what refers to intake of Calcium supplements, that may increase risk of death in older people with aortic valve stenosis. Calcium and in the same way calcium chloride together with vitamin D seems to be the culprits as regards formation of stenosis. It would be interesting in hearing your opinion. Best regards, Johann