What is Potassium gluconate (E577) in supplements and VS Potassium citrate and chloride
Uses | Benefits | Safety | FAQs
Potassium gluconate, the potassium salt of gluconic acid, is a multi-functional ingredient that can be used as an acidity regulator and a chelating agent in food with the European food additive number E577. Together with potassium citrate and potassium chloride, this ingredient is commonly used as a nutrient supplement of potassium.
What’re the Uses of Potassium gluconate?
It is mainly used to enrich potassium in dietetic food and thus to prevent potassium deficiency; also it can be applied as a substitute of sodium salts to reduce sodium contents where it is not desired.
Food
A nutritional source of potassium can be used in food fortification, also as a sequestrant in some food applications.
Potassium gluconate is listed in “vitamin formulations and mineral substances which may be added to foods” in EU Regulation (EC) No. 1925/2006 (1) and can be used in the manufacturing of food supplements. (2)
Following products may contain it (3):
- Infant formula
- Processed cereal-based food and baby food
- Food for special medical purposes
- Total diet replacement for weight control
Cosmetics
It functions as a chelating and skin protecting agent in cosmetics and personal care products. (4)
Pharmaceuticals
Potassium gluconate is used for preventing or treating low blood levels of potassium (hypokalemia) in medical uses, also for cats and dogs.
It is commonly sold as in the formulation of tablets or capsules and with various brands and specifications. For example, tablets 595 mg, 550 mg, 500 mg with corresponding 99mg, 92mg and 83mg of potassium.
Other ingredients may contain in such formulations:
- Cellulose gel
- Stearic acid
- Magnesium stearate
- Silicon dioxide
How to calculate potassium content in supplements?
1 mEq potassium is equivalent to 39 mg elemental potassium.
mEq or meq, means milliequivalent, is one thousandth (10−3) of a chemical equivalent, used to express the concentration or strength of certain pharmaceutical products.
So, potassium gluconate 595 mg is around 2.5meq potassium.
Industrial
It can be used as a sequestering agent in textiles.
Specification
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 299-27-4 |
| Chemical formula |
|
| Molecular weight |
|
Structure
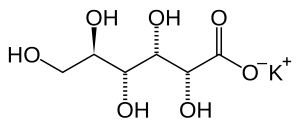
Image Source
A six carbon chain with five hydroxyl groups (-OH) and a carboxylic acid group.
Properties
Appearance
An odourless, free flowing white to yellowish white powder or granular with a slightly mild saline taste.
Stability
Stable in air.
Solubility
- It is a 1:1 salt of gluconic acid that dissociates potassium cation and gluconate anion in water. Freely soluble in water with the solubility around 900 g/L at 20°C.
- Practically insoluble in ether, benzene.
PH
Between 7.0 and 8.3 (10 % solution) (5)
What are the Benefits of Potassium gluconate?
Potassium plays an important role in our body as we need it to maintain nerve impulses, stimulate muscles and with other functions. Potassium gluconate is a supplement of potassium, which is also good for people with diabetes and high blood pressure.
1. Reduce risk of diabetes
A study in 2011 found that lower levels of potassium may be linked to a higher risk of diabetes. (6)
2. Prevent muscle cramps
Too little potassium, and other minerals, like calcium or magnesium in our diet can cause muscle cramps, like leg cramps. (7)
3. Low blood pressure
Dietary supplementation of potassium can lower blood pressure by losing sodium through urine and easing tension in blood vessel walls. (8)
Is Potassium gluconate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Potassium gluconate can be used as a nutrient supplement and sequestrant in food. (9)
EFSA
Potassium gluconate (E577) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (10).
Approved uses
Its food applications are listed in “Group I” with the maximum use levels “quantum satis”. The following food may contain with it (11):
- Dairy products
- Fats and oils and fat and oil emulsions
- Fruit and vegetables
- Confectionery
- Bakery wares
- Meat
- Fish and fisheries products
- Eggs and egg products
- Sugars, syrups, honey and table-top sweeteners
- Salts, spices, soups, sauces, salads and protein products
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (12)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 577. (13)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, acidity regulator, nutrient supplement, yeast food. (14)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specified” set in 1997. (15)
Frequently asked questions
How is it made?
The manufacturing process is similar with that of producing other gluconates, by fermentation of glucose to obtain gluconic acid and then neutralized with a potassium carbonate.
Potassium gluconate vs potassium citrate vs potassium chloride?
All of them can be used as a source of potassium to formulate low sodium foods and treat or prevent low potassium level. The differences among them are mainly the potassium assay, taste, function, absorption and so on. Generally, tripotassium citrate and potassium gluconate may be the preferred potassium sources for supplements.
Potassium assay
- Potassium citrate: with the highest molecular weight 306.4 g/mol, formula C6H5K3O7.
- Potassium chloride: molecular weight 74.6 g/mol, formula KCl.
- Potassium gluconate: molecular weight 234.3 g/mol, formula C6H11KO7.
We can calculate that potassium chloride contains the highest level of potassium over potassium citrate and potassium gluconate, the latter is the least.
Taste
Like sodium chloride, the table salt, potassium chloride has a salty taste; the taste of potassium citrate is sour and slightly salty; potassium gluconate with a slightly mild saline taste.
Function
Potassium citrate is commonly used as a buffer agent in carbonated beverages to adjust the PH level, and for medical purposes, it is used to prevent the formation of kidney stones by combining with calcium to inhibit crystals in the urine. Potassium gluconate can prevent muscle cramps and lower blood pressure.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the nutrient – potassium gluconate (E577), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses in food supplement
- Safety as a food additive and a nutrient
- FAQs: compare with another two potassium sources: potassium citrate and potassium chloride
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.

