What is Potassium Sorbate (E202) in Food & Why Add it in Wine?

Production | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Potassium sorbate, the potassium salt of sorbic acid, is a commonly used preservative in food with the European food additive number E202. Generally, it is synthetic, vegan and gluten-free.
This ingredient is used to protect food from spoilage and therefore prolong the food shelf life by slowing the growth of molds and yeasts. You may have seen it in the label of wines, cheeses, cider, mead, soft drinks, and baked goods.
How is Potassium Sorbate made?
It can be commercially synthesized by neutralizing sorbic acid (E200, also a food preservative, can be naturally found in berries, but the commercial one is made from chemical synthesis) with potassium hydroxide. (1)
Here is the brief four steps manufacturing process:
- Condensation reaction: obtain polymeric ester of 3-hydroxy-4-hexenoic acid by the condensation between ketene and crotonaldehyde. The following is the reaction equation: H2C=C=O + CH3–CH=CH–CHO = CH3CH=CH−CH=CH−COOH
- Decomposition: decompose the polyester to produce sorbic acid.
- Purification: through activated carbon, distillation, recrystallization or other processes.
- neutralization with potassium hydroxide.
How does Potassium Sorbate work as a Preservative?
Potassium sorbate is an inhibitor of both yeasts and moulds, also active for several bacteria (2) but less effective. It is the sorbic acid (active form) that has the inhibitory activity which is generated after the ionization of potassium sorbate in water.
It inhibits microbial growth by changing the cell membrane morphology, integrity and function and then disrupting the transport functions and metabolic activity. (3)
This mechanism of preservation is similar to sodium benzoate, but different with that of nisin and natamycin.
Specification
| Other names |
|
| Chemical formula | C6H7KO2 |
| CAS No. | 24634-61-5 |
| Molar mass | 150.22 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 270 °C |
Properties
Appearance
A crystal white powder, granular or spherical/pellets with neutral taste and odor. It is easy to absorb water and expired if exposed to humid air.
Structure
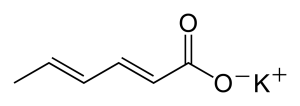
Image Source
Solubility
Freely soluble in water and soluble in ethanol. As the solubility of sorbic acid is very low in water (0.16g/100ml at 20 °C), as this result, it is usually made into its soluble potassium salt – potassium sorbate (solubility 67.6g/100ml at 20 °C to as a preservative in food.
PH
Its antimicrobial effectiveness is in a wide pH range from 3.0 to 6.5), and better under acidic conditions with pH value less than 5-6. The activity increases as the pH decreases.
Potassium sorbate is still effective at higher pH ranges, for example, PH 6.5, while sodium benzoate and potassium benzoate almost lost its antimicrobial activity which are effective to only below PH 4.5. However, potassium sorbate will also ineffective if pH above 7.0.
What’re the Uses of Potassium Sorbate?
Sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate are often synergized (combined used) in acidic food to protect against a wider variety of microorganisms. Potassium sorbate inhibits the growth of mold, yeast and other microorganisms and thus increasing the preservation time of food products.
The common preservation dosage ranges from 250 ppm to 1000 ppm levels, depending on PH, microbial types and other conditions.
It can be used by direct adding, spraying, in packing material or in other methods.
Soft Drink
Food grade potassium sorbate is commonly added to diet soft drinks as a preservative.
Coca Cola
Like sodium and potassium benzoate, potassium sorbate is the common preservative Coca Cola put in some non-carbonated and juice-containing drinks to protect taste. (4) (5). We can find it in the ingredient lists of Sprite lymonade and Fanta Orange.
Pepsico
Potassium sorbate is used to preserve freshness and flavors in some Pepsico drinks (6). You’ll find this ingredient in its Fountain Drinks, such as Mtn Dew Kickstar – Black Cherry or Orange Citrus. (7)
Wine
Potassium sorbate is an ingredient for winemaking and some winemakers think that adding it can stop the wine fermentation process. But is it true?
Potassium sorbate functions as a wine stabilizer which isn’t added until the fermentation process is complete. Its purpose is not to prevent the fermenting but to keep wines from starting to ferment again by inhibiting yeast reproducing.
That is to say, existing yeast will die and new cells of yeast cannot be generated. The yeast will multiply several generations during a fermentation process, it ensures the current generation of yeast is the last generation by adding potassium sorbate.
In this way, it stabilizes wine and is always combined with potassium metabisulfite in sweet wines before bottling.
Other food may with it:
- Cheese
- Wine
- Mead
- Hard cider
- Dried meats and dried fruit
- Yogurt
- Pet foods
- Soft drinks
- Baked goods
Cosmetics
Potassium sorbate is used as a preservative (8) in cosmetics and personal care products. It is a mild preservative that extends shelf life by inhibiting yeasts and molds, also it can replace parabens.
The common cosmetics including:
- Sunscreen
- Moisturizers
- Creams
- Shampoos
- Skin care and hair products
Feed
It can also be safely used as a preservative in feed, such as in animal food for pigs, poultry, cat and dog food. (9)
Is Potassium Sorbate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
Metabolism
Potassium sorbate is the salt of unsaturated fatty acids that participate in fat metabolism and finally metabolized into water and CO2 in the human body. (10)
FDA
It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) as a chemical preservative when used in accordance with good manufacturing practice. (11)
How much to use
Approved with the following concentration (12):
- Cheeses < 0.3%
- Fruit Butter & Art Sw Jelly & Preserves < 0.1%
- Margarine & Oleomargarine < 0.1% or 0.2% total in combination w/other preservatives
EFSA
Potassium sorbate (E202) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (13).
Approved uses
The following food list may contain with potassium sorbate at the maximum use levels ranging from 20 to 6,000 mg/kg (14):
- Cheese of unripened ripened, whey or processed
- Spreads, beverage whiteners
- Jam, jellies and marmalades
- potato dough and pre-fried potato slices
- Chewing gum
- Toppings
- Pre-cooked or processed cereals
- Bread, fine bakery wares
- Meat products
- Seasonings and condiments
- Fruit juices, beer Cider and perry
- Aromatised wines
Safety re-evaluation in 2015
Due to the reproductive and developmental toxicity, EFSA established a new temporary ADI of 3 mg sorbic acid/kg bw/day in 2015 which was revised from the ADI of 25 mg/kg bw/day set in 1996. (15)
Safety re-evaluation in 2019
EFSA changed the temporary group ADI from 3 mg /kg bw per day to a new group ADI of 11 mg /kg bw per day. (16)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (17)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 202. (18)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, preservative. (19)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “25 mg/kg bw” in 1973. (20)
What are the possible Side Effects of Potassium Sorbate?
Although Potassium sorbate is approved safe by the FDA and EFSA, there may be some possible side effects, and the controversy focus on that it may cause some health problems, such as:
- allergy symptoms
- genotoxicity
- lead to cancer
- DNA breakage
- migraine
Allergy
Allergy symptoms like skin and eye irritation in some people who’re allergic to potassium sorbate especially from cosmetics and personal products.
Genotoxicity
There is no solid proof that potassium sorbate is genotoxicity but a study in 2012 found that another sorbate salt – sodium sorbate may be genotoxic to human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro at the highest concentrations. (21)
Does Potassium Sorbate cause Cancer?
No, it is not a carcinogen. But the above study said that sodium sorbate may also cause cancer because of its mutagenic and genotoxic effects.
Too much Potassium sorbate
In the book of Trends in Food Science & Technology (published in 2018) says too much intake of potassium sorbate (>25 mg/kg) may lead to DNA breakage and other adverse effects. (22)
Is it safe for Pregnancy?
It is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but better consult with your doctor for the use of the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Potassium Sorbate Natural or Synthetic?
It is synthetic. Potassium sorbate is a salt of sorbic acid which is naturally found in some fruits, like berries. However, both sorbic acid and potassium sorbate sold in market are almost both manufactured through chemical synthesis, so they’re not natural.
Is Potassium Sorbate Halal?
Yes. It is halal complies with the Muslim policy and we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is Potassium sorbate Kosher?
Yes, It is kosher. E202 meets Jewish religious dietary law.
Is Potassium sorbate Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Is Potassium sorbate Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as it is not made from animal matter or products derived from animal origin. It is suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Potassium Sorbate vs Sodium Benzoate?
See the details in that of sodium benzoate.
Conclusion
Now you may have a good knowledge of the preservative – Potassium sorbate (E202), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses: in soft drinks, wine and other foods
- Safety
- Possible side effects
- Comparison with sodium benzoate
- FAQs
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



What year was E202 first used in food.
Hi James!
I have been a migraine sufferer for a number of years.
For me potassium sorbate is a trigger. I study the ingredients lists of everything i buy – food, shampoo, cosmetics. Everything.
I had an inkling that Potassium Sorbate has other names and related chemicals but was unable to identify them.
Your website, stumbled on by accident, is a revelation. Thank you so much for helping me identify this trigger.
Regards,
Teena.
Many of the side effects I experience are in parallel to those described by people who have been diagnosed with coeliac disease, or think that it may be their problem. I was diagnosed with IBS over 40 years ago and have wondered in recent years if it was in fact coeliac disease. I stick to a gluten free diet, and have done so for many years, as well as removing other items which have caused me to be hospitalised several times – no cause found by medical professionals and tests. Recently I consumed a supermarket brand Ginger Ale and suffered the intense pain, diarrhoea, bloating and extreme flatulence that are also my IBS symptoms, for around 12 hours. So, when I have such an intense and painful reaction I naturally want to know what may be the cause. The following day I consumed another branded Ginger Ale that does not contain potassium sorbate and I’m absolutely fine. I certainly knew a few decades ago that I could not tolerate sorbitol, but this recent episode is making me research and try to understand the additives in what I might have consumed. It seems pretty clear to me now that I am highly intolerant to this ingredient/additive and I’m really surprised that there is so little scientific study on it when it is so widely used as a preservative.
Hi please I will like to how much quantity I will need in 1 litter of yogurt.
If potassium sorbate (*E202) and Natamycin (E235) are in yoghurt, so they not kill the probiotics present?