What is Sorbic Acid (E200) in Food & the difference with Potassium Sorbate?

Source | Production | Mechanism | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Sorbic acid, an unsaturated six-carbon fatty acid, is a naturally occurring preservative that is used less in food compared to its potassium salt – potassium sorbate (E202) due to the slight solubility in water. This ingredient can be used in low water content food such as baked goods, cheese, dried fruits, meat and fatty media.
It is generally used to inhibit the growth of molds (also mycotoxin-forming molds), yeast and some bacteria. The European food additive number for it is E200.
Natural source
It can be naturally found in berries species, such as mountain ash, rowan and magnolia vine. (1)
How is Sorbic Acid made?
It is commercially synthesized from the condensation between ketene and crotonaldehyde instead of extracted from berries. The manufacturing process is described in the first three steps of production of potassium sorbate.
How Sorbic Acid works as a Preservative?
The bacteriostatic or bactericidal mechanism of sorbic acid are the same as that of potassium sorbate. When added to water, potassium sorbate dissociates into sorbic acid and potassium ions. It is the sorbic acid that is active as an antimicrobial preservative.
Like benzoic acid, sorbic acid is a lipid-soluble weak acid that:
- enters into the cell of microbial through the cell membrane
- then accumulates and finally influences the internal PH of microbial
- eventually disrupts its transport functions and metabolic activity
- result in the death of the microbial
Specification
| Other names |
|
| Chemical formula | C6H8O2 |
| CAS No. | 110-44-1 |
| Molecular weight | 112.128 |
| Boiling point | 270 °C |
Properties
Colorless needles or white free-flowing powder with a slight faint characteristic odor.
Structure
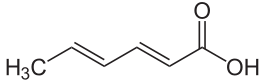
Image Source
Solubility
In water
Slightly soluble in water (solubility 0.16 g/100 mL at 20 °C) so it is not suitable to use it in food with much water content. Generally, it is made into salts form, potassium sorbate, which is the commonly utilized form.
In organic solvent
Soluble in ethanol, ether, propylene glycol, peanut oil, glycerin and glacial acetic acid.
PH
The antimicrobial activity of sorbic acid generates when it is in the form of a molecule, the condition of undissociated.
The PKa of sorbic acid is 4.76. That’s to say, its inhibitory activity rises as pH value (below 4.76) decreases as the percentage of the undissociated sorbic acid goes up, this leads to the enhanced antimicrobial activity.
The optimal pH for the antimicrobial activity is from 3.0 to 6.5.
What’re the Uses of Sorbic Acid?
Sorbic acid and potassium sorbate have become the primary preservatives in food application due to its good antimicrobial activity & effectiveness in the weak acid pH range and their safety over benzoic acid and sodium benzoate.
Mostly, it protects food from yeast and mold spoilage and commonly added with usage from 0.025% to 0.10%.
Sodium sorbate and Calcium sorbate
Another two sorbates, sodium sorbate and calcium sorbate which were also used as food additives in Europe. However, in other countries, they are permitted, for example, in the US.
Sodium sorbate (previously had the E number E201) is not an approved food additive in the EU for its genotoxicity.
Calcium sorbate (previously had the E number E203) was no longer allowed to be used in the European Union since Jan, 2018 as the EFSA was not able to evaluate its safety due to the lack of data, such as genotoxicity data, also, it was unable to set an ADI. Therefore this ingredient was deleted in the list of food additives. (2)
Food
Sorbic acid can prevent the spoilage of yeast, mold, and some bacteria in food and therefore prolong food shelf life. It can be used to preserve foods with low water content and the following food may contain it:
- cheese
- dried fruit
- yogurt
- pet foods
- dried meats
- baked goods.
While in liquid form/aqueous systems for preservation, potassium sorbate is preferred.
How to use it?
Sorbic acid can be added in food with several methods (3):
- directly used
- dusted in powder form
- sprayed onto the food surface
- dipped into sorbate solutions to prepare a certain concentrations
- packaging materials
Cosmetics
Sorbic acid can also be used as a preservative (4) in cosmetics and personal care products to inhibit the growth of yeast and mold.
Is Sorbic Acid Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) that can be used as a chemical preservative in accordance with good manufacturing practice for human consumption. (5)
Uses limit
It is authorized in the following food (6)
- Cheeses and cheese related products < 0.2%
- cheeses and cheese related products, used alone or combined with potassium or sodium sorbate < 0.3%
- Art sw fruit jellies, pres, and jams < 0.1%
- Concentrated orange juice < 0.2%
- Margarine <0.1% alone or <0.2% in combination with other preservatives
EFSA
Sorbic acid (E200) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (7).
Approved uses
The same with that of potassium sorbate, at the maximum dosage from 20 to 6,000 mg/kg (10) (11)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (12)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 200. (13)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, preservative. (14)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “25 mg/kg bw” in 1973. (15)
What are the possible Side Effects of Sorbic acid?
Although sorbic acid is approved safe by FDA and EFSA, there may be some mild possible side effects, like allergy symptoms in skin or scalp irritation or dermatitis from skin care products; digestive problems such as diarrhea. It is almost no toxicity and not linked to cancer.
Allergy
Allergy symptoms like skin and eye irritation, from some people who’re sensitive to sorbic acid especially from cosmetics and personal products.
A report in 2008 showed that sorbic acid may cause allergic reactions, such as dermatitis. (16)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it Natural or Synthetic?
It is natural if it comes from the fruits, however, mostly sorbic acid in the market is synthetic as made from chemical production.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan and manufactured without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it can be used in the food for vegetarians.
Sorbic acid vs Ascorbic acid?
Some people may be mistaken these two different categories of food additives, sorbic acid is a preservative while ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an antioxidant and also a vitamin c supplement.
Conclusion
Now you may have a good knowledge of the preservative – sorbic acid (E200), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Comparison with potassium sorbate
- Safety
- Possible side effects
- FAQs
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



You have made some decent points there. I looked on the net to find out more about the issue and found most individuals will go along with your views on this web site.
Hello! I’m investigating different preservatives. I was wondering if you could suggest to me a way I could compare different preservatives e.g comparing sodium propionate to sorbic acid.
What exactly should I look at?
Hi Hanaaz,
You can find some information about many preservatives here: https://foodadditives.net/preservatives/
hope it can help you.