What Is Sodium Benzoate (E211) In Food & Why People Afraid It With Vitamin C?

If you’ve ever seen sodium benzoate in the ingredients list, then you’ve already known it is a preservative to prolong the food shelf life.
But what is it? How is it made? How does it work? What’re the common uses? What’s the difference with benzoic acid and potassium sorbate? Does it really cause cancer in soda with vitamin c?…
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- What is Sodium Benzoate
- How it is made
- Its mechanism of preservation
- Common uses in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
- Approved safety
- Possible side effects
- FAQs: including comparison with benzoic acid and potassium sorbate
What is Sodium Benzoate?
Sodium benzoate, the sodium salt of benzoic acid, is a large-scale used food preservative with the European food additive number E211.
China is the biggest manufacturer of sodium benzoate and its export quantity of benzoic acid, its salts and esters reached 90,500 MT and the corresponding amount of 120 million USD in 2019.
If calculated by its max usage with 0.1% in food, the total food with it would be around 1 billion MT. Wow…so big market.
How is Sodium Benzoate Made?
It can be chemically synthesized by the reaction between benzoic acid with sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, or sodium hydroxide.
Here is the brief manufacturing process came up by the China top manufacturer Tianjin Dongda (1):
- Obtaining crude sodium benzoate by the neutral reaction between benzoic acid and sodium hydroxide at pH 7.5-8.0
- Decolorizing, filtering, palletizing and drying
Here is the reaction equation:
C6H5COOH + NaOH = C6H5COONa + H2O
By the way, benzoic acid can be produced by the reaction between sodium benzoate and hydrochloric.
Powder and Granular
Powder and granular are two common forms of sodium benzoate, but the powdered form is easy to caking in storage and transportation due to its hygroscopicity and poor fluidity.
How does Sodium Benzoate work?
Sodium benzoate is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial preservative that is most active against yeast and bacteria, also but less effective on mold.
Suitable PH
Primarily used in acidic food and drink with the PH value at or lower 4.0-4.5 (2). The effectiveness goes up with a decreasing pH.
Mechanism of Preservation
When sodium benzoate dissolves in water, it dissociates into benzoate ion and sodium ion.
Then benzoate ion combines with proton forming benzoic acid. It is the undissociated benzoic acid that has the inhibiting activity.
The undissociated benzoic acid can easily enter the cell of microorganisms through the cell membrane, interferes with the permeability of microbial cell membranes and disrupts its normal metabolism.
Properties
A white or colorless crystalline powder or granular, with an astringent sweet taste, odorless or with a faint odor.
Other Names
- Benzoate of Soda
- Sodium salt of benzenecarboxylic acid
- Sodium salt of phenylcarboxylic acid
CAS Number
532-32-1
Chemical formula
C7H5NaO2 or C6H5COONa
Molar Mass
144.105 g·mol−1
Boiling Point
248.00 to 249.00 °C
Melting Point
410 °C (770 °F; 683 K)
Structure
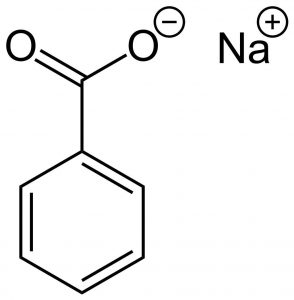
Image Source
Functional Group
Ester group and aromatic benzene ring. The ester group is easy to react with other groups.
Solubility
In water: very soluble in water, with solubility 53.0 g/100 mL at 25 °C.
In organic solvents: sparingly soluble in ethanol (solubility 2.3 g/100 g at 25 °C), methanol, and ethylene glycol; does not soluble in ether as it is a very polar molecule due to the negative charge while ether is a non-polar solvent.
PH
The pKa of benzoic acid is 4.2. In order to generate a good inhibiting effect, the pH value needs to be lower than its pKa. That’s to say, a low PH level can converts sodium benzoate to benzoic acid.
Following is the equilibrium of the benzoate anion with benzoic acid in water solutions.
C6H5COOH→C6H5COO– + H+
What’re the Uses of Sodium Benzoate?
Sodium benzoate has been used in a wide variety of food products for its antimicrobial and flavor properties. Apart from its use in foods and beverages, it is also added to cosmetics and pharmaceutical products.
Let’s have a closer look at its various uses.
Food
In the food industry, sodium benzoate food grade is mainly used to:
- prevent spoilage from harmful bacteria, yeasts, and molds
- maintain freshness by slowing or prevent changes in color, flavor, or texture
- adjust flavor
- control PH
In all of its food applications, its major use is as a preservative in the soft drink to increase the acidity flavor and as a preservative to extend the shelf life.
Coca Cola
Sodium benzoate, potassium benzoate and potassium sorbate are the three common preservatives in Coca Cola’s drink (3). Sodium benzoate is used as an antimicrobial agent and to protect taste (4). And we can commonly find it in the ingredient lists of Sprite and Fanta.
Pepsico
Sodium benzoate can also be found in the ingredients list of Pepsi carbonated soft drinks which is used to preserve freshness. However, it is used less than potassium benzoate in Pspsico’s popular soda, such as in Diet Pepsi and Pepsi, which are using potassium benzoate as the preservative. (5)
Other food may with it:
- Salad dressings
- Pickles
- Sauces
- Condiments
- Fruit juices
- Wines
- Snack foods
Cosmetics
Like food and drink products, cosmetics also need preservatives to prevent the growth of bacteria. Preservative-free, natural products cannot be stored for a long time.
Sodium benzoate can be used as an anti-corrosive, masking and preservative (6) in a large variety of cosmetics and personal care products, including:
- Mouthwash & toothpaste
- Hair products such as shampoo
- Skincare products such as sunscreen, moisturizers, creams, serums
- Baby wipes
Sometimes, it blends with gluconolactone for uses in cosmetics.
Safety & usage
The function of benzoic acid and sodium benzoate are both as a preservative or non-preservative purposes in following cosmetic products with the maximum concentrations (7):
- rinse-off products: 2.5 %
- oral-care products: 1.7 %
- leave-on products: 0.5%
In Toothpaste
To inhibit the growth of microorganisms in toothpaste, producers usually add a certain amount of preservatives. When considering the antimicrobial effect, safety and the price, sodium benzoate may be the better choice compared with other commonly used preservatives in toothpaste, such as methyl paraben and ethyl paraben.
You can see this ingredient in the toothpaste of Colgate and also in its mouthwash and dental rinse.
Pharmaceuticals
Sodium benzoate can also be used in pharmaceutical products for its antimicrobial properties, such as in the formulation of tablets, capsule and cough syrup.
Also, it can be used as an active ingredient to treat urea cycle disorders by reducing the levels of ammonia in children. (8)
Is Sodium Benzoate Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sodium benzoate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and can be used as an antimicrobial agent and flavoring agent in food with the maximum usage of 0.1% (9). It is also GRAS when used as a preservative in feed. (10)
EFSA
Sodium benzoate (E211) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (11).
Safety re-evaluation in 2016
Base on the studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity and other researches, EFSA considered that the use of sodium benzoate does not raise a health concern and derived an acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 5 mg/kg bw per day (expressed as benzoic acid) in 2016. (12)
Approved uses
In Food
It can be found in a lot of food labels with its name or E211. The approved food uses are listed in the same categories with benzoic acid, sodium and calcium benzoate (E210-E213) with the maximum used levels range from 150 to 6,000 mg/kg. It can also be combined with sorbic acid-sorbates (E 200–202) and p-hydroxybenzoates (E 214–219). (13)
Silage Additive
EFSA concluded that sodium benzoate was safe for the consumer when used as a silage additive in pigs, poultry, bovines, ovines, goats, rabbits and horses. Meanwhile, it reduces pH and increases the preservation of dry matter and therefore improve silage production. (14)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (15)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 211. (16)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, antimicrobial preservative. (17)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “5 mg/kg bw” expressed as benzoic acid was set in 1996. (18)
What are the possible Side Effects of Sodium Benzoate?
Preservatives are the categories of food additives that have more concerns from customers, especially for sodium benzoate as people always think it is bad for health and will bring several side effects. The most talked possible side effect is whether it could cause cancer.
Let’s see the details.
Why does Sodium Benzoate cause cancer?
If present with ascorbic acid (vitamin c) or erythorbic acid, it can be converted to benzene (low ppb level) in the beverage which is a carcinogen that can cause cancer in humans. Light and heat processes will accelerate the formation of benzene.
Consumers are confused about whether citric acid can also turn sodium benzoate into benzene, currently, there is no solid proof.
What is the truth?
The FDA considers the maximum allowable level for benzene in drinking water is 5 ppb. Almost all beverage products are under this number that will not pose a threat to our health. (19)
Is Sodium Benzoate Safe to Pregnant?
It is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but better consult with your doctor for the use of condition.
A study in 2001 found that mother rats receiving high doses of sodium benzoate had significantly high ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) values and decreased serum bilirubin and increased serum urea. The study demonstrated that high doses of sodium benzoate may be dangerous to pregnant women. (20)
What’re the Allergies of Sodium Benzoate?
A small percentage of people may be hypersensitive to is and may have the following allergic symptoms:
- Epidemiologically relevant: A study found that epidemiologically relevant increases noted with sodium benzoate in patients. (21)
- Perioral contact urticaria: an early study found toothpaste with it may cause perioral contact urticaria. (22)
- Pruritus: it may cause pruritus symptoms. (23)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Sodium Benzoate natural?
No, it is a synthetic preservative although benzoic acid is found naturally (also commercially obtained by chemical synthesis). The salt is not found to occur naturally and the manufacturing process is through chemical synthesis, so it is natural.
Is Sodium Benzoate halal?
Yes, it is halal. Comply with the Muslim policy and we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is Sodium Benzoate kosher?
Yes, it is kosher. E211 meets Jewish religious dietary law.
Is Sodium Benzoate gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Is Sodium Benzoate vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin.
Is Sodium Benzoate Acid or Base?
The conjugate base is benzoate ion. As benzoic acid is a weak acid, so its conjugate base is strong, and can get protons from water.
How much Sodium Benzoate to Use?
Suitable to use in acid foods with the level of 0.05–-0.1%.
Potassium Benzoate Vs Sodium Benzoate?
Together with potassium benzoate (E212) and calcium benzoate (E213), they’re three salts of benzoate. The use of potassium benzoate can reduce the level of sodium, maybe it is the reason the Pepsico use it to replace sodium benzoate in its Pepsi drink as mentioned above.
Is Sodium Benzoate the same as MSG?
No, totally different, it does not contain MSG which is a flavor enhancer to impart an umami taste.
What are Sodium Benzoate Alternative?
Potassium sorbate is a novel preservative substitute for the traditional preservative- sodium benzoate. Also biopreservatives such as natamycin, nisin and polylysine can replace it in some food applications.
There are a lot of issues to consider, such as PH value and what kinds of microorganisms intended to inhibit.
Sodium Benzoate Vs Benzoic Acid?
Although it is the benzoic acid that has the antimicrobial ability, it is used less than sodium benzoate for food preservation purposes for its much less soluble (0.34g/100ml, 25 °C) in water.
Potassium Sorbate (E202) Vs Sodium Benzoate?
The combination of these two preservatives are commonly seen in food, they’re used together to provide synergism against a wider variety of microorganisms.
The following are their difference:
- Microorganisms: potassium sorbate is the inhibitor of molds and yeasts while sodium benzoate is mostly active in yeasts and bacteria.
- Uses level: the maximum levels of potassium sorbate are bigger such as in cheeses with the number below 0.3%, some are less than 0.1% which is the same level as sodium benzoate.
- Working PH range: the former is suitable at PH value 3.0-6.5 while the latter is suitable in 2.5-4.0.
- Safety: Consumers are afraid of the safety of sodium benzoate in food with vitamin c under heat process, so some food manufacturers prefer potassium sorbate if only one preservative is utilized.
Conclusion
Now you may have a good knowledge of the preservative – sodium benzoate (E211), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Safety
- Possible side effects
- Comparison with benzoic acid and potassium sorbate
- FAQs
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Hi James
Thank you for a brilliant blog .
We have been using Potassium Sorbet & Sodium Benzoate successfully to make tamarind sauce. Lately we are finding the The sauce starts to ferment and some of the bottles have exploded.
Our manufacturing process has not changed and we are still using the same equipment.
Can the preservatives become ineffective and if so what would cause it.
Your comments would be greatly appreciated.
Thank You
Hi Patel,
This is a big question to answer, better to ask your QA and QC.
Hope you can solve this problem soon.
Hello James:
I just bought Dabur Chyawanprash 2x to boost immunity to get rid of prolonged cough as an ayurvedic supplement. While I was trying to learn how to consume it, I came across about its ingredients that it has natural vitmin c foods and sodium benzoate is used for preservation. Combination of vitamin c and sodium benezoate is known to cause cancer. Is it really true and can that happen even if the ingredients are real food like avla and 39 more items. When it says combination of vitamin c and benzoate combination does it mean chemical form of vitamin c or food that contain vitamin c also can cause cancer if combined? Thanks in advance for your help.
Hi Alison,
Take it easy. You can see what FDA said about it: https://www.fda.gov/food/chemicals/questions-and-answers-occurrence-benzene-soft-drinks-and-other-beverages
Hello Mr Han,
Your blog really helped me to understand Sodium Benzonate.
I am working at food manufacuter as R&D.
Thank you very much.