What is Sodium Metabisulfite (E223) in food? Uses and Safety

Production | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Sodium metabisulfite (SMBS), one of the sulfites that can be used as a preservative, antioxidant and bleaching agent in food with the European food additive number E223. It is a reducing agent that commonly used for the preservation of fresh & dried fruits, vegetables and wines.
How is Sodium Metabisulfite made?
Sodium metabisulfite can be made from the reaction between sulfur dioxide with sodium carbonate. The following is the reaction equation: SO2 + Na2SO3 → Na2S2O5
Here is the manufacturing process came up by Solvay (1): Reaction between sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) solution to form the mixed solution of sodium bisulfite and sodium sulfite (Na2SO3). Reaction equation: Na2CO3+2NaHSO3 = Na2SO3+H2O+CO2
Add excess sulfur dioxide (SO2) to the above solution to convert sodium sulfite to sodium bisulfite and also obtain the dissolved sulfur dioxide. Reaction equation: Na2SO3+H2O+SO2=2NaHSO3
Convert the dissolved sulfur dioxide to sodium bisulfite by adding an alkali ingredient, e,g, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, or sodium sulfite, or the mixtures. Reaction equation: Na2CO3+H2O+SO2=2NaHSO3+CO2
Obtaining sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5) through two sodium bisulfite molecules reacts itself by cooling the above sodium bisulfite solution, and follows purification and drying processes to produce crystals or powder. Reaction equation: 2NaHSO3 = Na2S2O5+H2O
Specification
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 7681-57-4 |
| Chemical formula | Na2S2O5 |
| Molecular weight | 190.11 |
Properties
Appearance
White crystals or crystalline powder. Slowly oxidized to Na2SO4 (sodium sulfate) and release sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas if exposed to air and moisture. SO2 is also released by the reaction with acid.
Solubility
Soluble in water and its water solubility increases with temperature, 54g/100ml at 20°C and 81.7g/100ml at 100°C. It produces sodium bisulfite (HSO3−) when dissolved in water and the aqueous solution is acidic with the PH 4.0-5.5 (10 % aqueous solution).
Na2S2O5 + H2O = 2 NaHSO3
Soluble in glycerin, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in benzene.
Structure
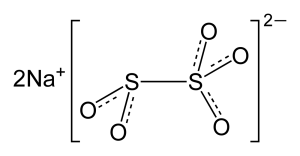
Image Source
What’re the Uses of Sodium Metabisulfite?
Sodium metabisulfite is a strong reducing agent that can react with oxidizing agents as the sulfur atom in it with a positive valence of 4, the maximum valence of which is 6. That is the mechanism why sodium metabisulfite is a multifunctional ingredient that can be used as a preservative, antioxidant and bleaching agent in agricultural food products, wine and other applications.
Preservative
SMBS is a sulfur-containing preservative that inhibits the oxidase in the food, and also can block the normal physiological oxidation process of microorganisms and thus inhibit the reproduction of microorganisms in food preservation.
Antioxidant
Since sulfite is a strong reducing agent, it reacts with oxygen from fruits and vegetables and also inhibits oxidase activity, so it prevents food spoilage caused by oxidation and protects vitamin C in them.
Bleaching agent
Reduce the colored material to a bright and fresh color or prevent/slow oxidative browning.
The following are its main purposes in food:
Wine
You may have seen sulfur dioxide in the ingredients list of wine, but not like other ingredients you notice in the label, sulfur dioxide is not directly added to wine, it is formed by the adding of sodium metabisulfite or potassium metabisulfite. The following are the reaction equation of Na2S2O5 in wine:
- Na2S2O5 + H2O <===> 2Na+ + 2(HSO3)-
- HSO3- + H+ <===> H2O + SO2
Sulfur dioxide plays an important role in almost every manufacturing process of winemaking, from grape picking to bottling. It is mainly to inhibit the growth of yeast and bacteria, and therefore preserve the wine fresh and extend the shelf life.
Sodium metabisulfite or potassium metabisulfite is commonly added to wines, ciders, or maybe beers as an antioxidant, preservative and stabilizer. Also, it can be used to clean and sanitize wine equipment and wine bottles.
Bakery
Like L-cysteine, sodium metabisulfite functions as a reducing agent in biscuit/pastry dough which loosens the dough, reduces the rest time and accelerates the kneading process by reacting with disulfide bonds and generating thiolsulfate esters in gluten protein after hydrolyzed to bisulfite (HSO3−) in water.
Processed fruit products
Like other sulfites (e.g. sodium sulfite, sulfur dioxide), sodium metabisulfite can be used as both a preservative and antioxidant in processed fruit products to slow browning reactions, as well as inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms.
Industrial
Industrial grade sodium metabisulfite is used in a wide range of applications:
- Pharmaceuticals: used for the purification of chloroform, phenyl propyl sulfone and benzaldehyde.
- Rubber: a coagulant.
- Printing and dyeing: as a dechlorination agent for bleached cotton.
- Leather: impart leather the properties of soft, waterproof, folding resistance in leather treatment.
- Surfactants and polymerization: as a sulfonating agent and reducing agent.
- Gold refining: as a reducing agent to precipitate gold out of an aqua regia solution by reducing the Au³⁺ to Au.
Is Sodium Metabisulfite Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects and the safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sodium metabisulfite is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used as a preservative except in meats, foods recognized as a source of vitamin B1 and fresh fruits or vegetables. (2)
EFSA
Sodium metabisulfite (E223) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ additives other than colours and sweeteners” (3).
Safety re-evaluation in 2016
EFSA concluded that the current group ADI of 0.7 mg expressed as SO2 equivalent/kg bw per day for E220-E228 was temporary and would be re-evaluated due to the uncertainties and limitations in the database (4)
Approved uses
Its application is listed together with sulfur dioxide (E220), sodium sulfite (E221), sodium bisulfite (E222), potassium metabisulfite (E 224), calcium sulfite (E226), calcium bisulfite (E227) and potassium bisulfite (E228) and with the maximum use levels “10-2000 mg/kg”.
The following food may contain it (5):
- Fresh, Peeled, cut and shredded, Frozen, Dried fruit and vegetables: such as table grapes, peeled potatoes, frozen and deep-frozen potatoes, dried coconut, dried mushrooms, dried ginger, dried tomatoes, dried apples, pears and bananas
- Jams, jellies and mermelades
- Dry biscuits
- Beer and malt beverages
- Cider and perry
- Fruit wine and made wine
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Preservatives” (6)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 223. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, antioxidant, flour treatment agent, preservative. (8)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-0.7 mg/kg bw” set in 1998. (9)
Frequently asked questions
Sodium metabisulfite vs potassium metabisulfite?
Both are wine making ingredients and add sulfites to wines. The main difference between them is sodium metabisulfite will add sodium ions in the wine while potassium metabisulfite will leave potassium ions.
The latter is usually preferred for the following three reasons:
- not bringing any dietary intake of sodium which will raise the blood pressure.
- potassium ions stabilize and promote the release of tartaric acid.
- sodium metabisulfite gives the wine a salty taste.
Sodium metabisulfite vs sodium bisulfite?
Both are sulfites but totally different. Chemical formula of sodium bisulfite is NaHSO3, and with the E number E222. Sodium bisulfite is commonly a mixture of sodium bisulfite and sodium metabisulphite, while the latter is a pure product. And it is convenient and cheaper to replace bisulfite with metabisulphite.
From the above manufacturing process of sodium metabisulfite, we can know, it is hard to produce the pure form of crystal sodium bisulfite as it crystallizes to sodium metabisulphite.
That’s why the European food additive number E222 specifies “NaHSO3 in aqueous solution” instead of its power or granular.
What’re the possible Side Effects of Sodium Metabisulfite?
Sodium metabisulphite may cause asthma-like allergy and may have adverse effects as follows (10):
- Skin, eyes, and respiratory tract irritation
- Headaches
- Breathing difficulties
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Its residue, sulfur dioxide, which may produce sulfite, sulphuric acid and sulfate on moist mucous membranes, enhances the stimulating effect and inducing various respiratory tract inflammatory diseases.
Sulfur dioxide can destroy the activity of enzymes, prevents the metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins. In addition, sulfur dioxide decomposes vitamin B.
Is SMBS Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as the raw materials and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the preservative – sodium metabisulfite (E223), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Safety
- Side effects
- FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



People have died from ingesting sulfites either from asthmatic attacks or allergic reactions. It should be considered safe for most people but there are those that should not have anything to do with it. It has been reported that one lady inhaled the vapors from a passing platter of steamed shrimp treated with sulfites and died from it. Many others have explosive diarrhea or severe headaches.
Is 223 SAFE when added in “Chatka” Crab food??
The total kind of additives in one package of Russian Crab food which I am hesitating to consume, are as follows: E385, E621, E223, E331, & E330. If possible, Please let me know how safe could this combination of Additives could be..!! Thank you for your attention.!
The FDA link goes to a page for the wrong chemical. Without references to proper sources, this article is not a reliable reference on these topics.
Hi Jordan,
Thanks for pointing out the mistake. The FDA reference has been updated and please check it. You can also see it here: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=182.3766
Having allergy symptoms after drinking cordial containing sodium metabisulphite
How many grams of sodium metabisulfite to put cane vinegar for 3.2 liters ..
I am allergic to sodium metabisulphite, potassium disulphite, sodium hydrogen sulphite i sodium sulphite, expoxy resin.
Why is it in raw meat for animals? It doesn’t mention in this article that it can be used in meat products.
Pure poison
I grow a lot of apple trees and I am trying to keep them as fresh as possible. What and how can I use E223.
It is in MasterFoods Horseradish Cream, Condiment.
I recently learned that this chemical is used in salad and guacamole (to keep them green) in a restaurant at which a friend works. But it looks like the FDA classifies this chemical as GRAS EXCEPT in “meat, foods recognized as a source of vitamin B1 and fresh fruits or vegetables.” Can you explain why there are these exceptions? And should this restaurant be using it for these purposes? Thanks.
You can see here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=niRBlcZWOo0
It cannot be used in some food (especially fresh food, like fruits and vegetables). Of course, restaurants should obey to FDA’s regulations.
Hello, My brother took my 4 Gallon bottle of water mixed with 3 tbsp Sodium Metabisulphite that I was using to sterilize my wine bottles, “he thought it was just water” and poured all this mix on my garden herbs and squash. Is it still safe to keep growing these items or do I have to discard them now. Please let me know and thank you for your help to this matter.
Got diarrhea after eating a jar of pickled peppers with sodium metabisulfite
I just purchased a jar of Frank’s Quality Sauerkraut and noticed that along with the normal ingredients of cabbage, water and salt, it has Benzoate of Soda and Sodium Metabisulfite. I don’t understand why a fermented food needs additional chemicals to preserve it. So I looked it up and found your article. I have asthma and don’t think I’ll be eating this now.
I was wondering about what had changed in the recipe of my Orange Squash to make it so much yummier than it was in the past and had noticed the recipe has now contained E223 being a brexiteer I was cautious of such a substance being added. But if this is what they can do to my orange juice you may as well call me a rejoiner already!!!!
It’s now common to find it in sausages and many fruit squash. I started with a touch allergy to this but now can’t eat or drink anything that has the smallest amount in. It seems that more and more companies are switching to this preservative, maybe as it’s a cheaper option. However when going to restaurants and such they list their allergens as sulphites, this doesn’t help when they aren’t specific and I’m worried I’ll get to a point where I have to avoid anything it lists with just sulphites.
Sodium metabisulphite in sausages gives me asthmatic symptoms