What is Magnesium Stearate (E470b): Uses, Safety, Side effects and More
Composition | Production | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Magnesium stearate, the magnesium salt of stearic acid with the chemical formula Mg(C17H34COO)2. Generally, this salt of fatty acid can be used as an anti-caking agent, lubricant, binder, emulsifier, and mineral (magnesium) supplement in food with the European food additives number E470b.
As stearic acid is commonly sourced from vegetable oils (e.g. soybean oil, palm oil, coconut oil, olive oil and corn oil.), so this ingredient can be vegan.
Magnesium stearate is widely used as a lubricant in the pharmaceutical tablets and capsules due to the properties of strong lubrication, light-weight, and good adhesion. It can also be used in the production of cosmetics, paints and plastics.
What is it Made of?
From the USP definition, magnesium stearate is a mixture of magnesium stearate and magnesium palmitate as the main components. (1)
How is Magnesium Stearate Made?
Since stearic acid is a weak organic acid, it cannot directly react with magnesium sulfate to produce magnesium stearate.
In the commercial manufacturing process of magnesium stearate, stearic acid should first be saponified with sodium hydroxide solution to obtain sodium stearate, and then react with the solution of magnesium sulfate or magnesium chloride to synthesize magnesium stearate.
The following are the brief three above mentioned processes:
- C17H35COOH + NaOH → C17H35COONa + H2O
- 2C17H35COONa + MgSO4 → (C17H35COO)2 Mg + Na2SO4
- 2C17H35COONa + MgCl2 → (C17H35COO)2 Mg + 2NaCl
Specification
| Other names | Magnesium octadecanoate, Magnesium salts of fatty acids, Magnesium distearate |
| CAS number | 557-04-0 |
| Chemical formula | Mg(C18H35O2)2 |
| Molecular weight | 591.27 |
| Melting point | 88.5 °C (191.3 °F; 361.6 K) |
Properties
With both characteristics of metal salt and stearic acid. The lubricity and hydrophobicity are derived from stearic acid.
Stable, but will be decomposed into stearic acid and magnesium salt in case of a strong acid.
A large specific surface area, with strong adsorption and hygroscopicity, a slippery feeling in contact with the skin and is easy to stick to the skin.
Appearance
An off-white to white powder, greasy to the touch.
Solubility
It is an anionic surfactant, unlike with another two metallic stearates (sodium and potassium stearate) but similar with calcium stearate, it is practically insoluble in water with the solubility 0.004 g/100 mL (25 °C).
Partially soluble in ethanol and ether.
Why is it insoluble in water?
The divalent Mg2+ can bind two nonpolar fatty acid molecules while Na+ and K+ as monovalent ions can only combine with one fatty acid.
Two fatty acid molecules protect Mg2+ from interacting with the water molecules and thus make it insoluble in water.
Structure
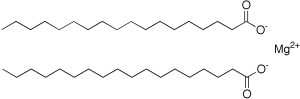
Image Source
It exists as a salt containing two stearate anions and a magnesium cation. Totally there are 36 carbons in length of molecule structure.
What’re the Uses of Magnesium Stearate?
Magnesium stearate is a multifunctional ingredient that has wide uses in food supplements, powdered cosmetics, pharmaceutical tablets & capsules, and plastic products.
Food
Its food grade can be used as a flow agent & anti-caking agent, lubricant, magnesium supplement in dietary food supplement.
Magnesium stearate is often used in the production of vitamin or multivitamin tablets or capsules by serving as a flow agent that binds with other ingredients from sticking and clumping to machine surfaces during production.
The following food may contain this additive:
- Vitamins
- Confectionery
- Chewing gum
- Candies
- Mints
- Baby formulas
- Herbs and spices
- Baking ingredients
Medical tablets and capsules
The major uses of magnesium stearate are as a lubricant, anti-adhesion agent, and glidant in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals tablets and capsules.
Its role is as an excipient (inactive ingredient) and the main function in the formulation of tablets and capsules is to:
- Prevent other ingredients in the formulation from sticking to compress equipment.
- Enable them to flow smoothly during the compression of chemical powders into solid tablets.
- Help improve the consistency and quality control of final products.
What is tablet compressibility?
The compression properties of tablets are also called compressibility, which refers to the compactness and firmness of the raw materials in the compression process.
The compressibility of the tablet is not only related to the properties of the raw material itself, but is also affected by the compression process and the properties of the additional materials, such as lubricants.
A lubricant can reduce the binding force between particles and weaken the hardness of the tablet.
Why are lubricants used?
During the tablet compression process, the friction between the tablet and the tablet press machine will affect the weight and stability of the tablet quality, as well as the wear of the tablet press equipment.
In order to reduce such harmful friction, a certain amount of lubricant is often added to the formulation. The use of lubricants can greatly reduce the ejection force and benefit tablet compression.
Magnesium stearate is the most widely used lubricant. It has the advantages of strong lubricity, good anti-sticking, light weight, large specific surface area, uniform distribution after mixing with other ingredients, and good adhesion.
Lubricating principle
Magnesium stearate will be attached on the surface of the material to form a lubricating film, which blocks the contact and force between ingredients.
Purposes
Lubricant plays an important role in the production of tablets. Commonly with the following three functions:
- Anti-sticking: prevent the adhesion of other ingredients to punches and molds under pressure.
- Free-flowing: reduce the friction between particles and increase their fluidity.
- Lubricity: reduce the friction between particles and the hole of the mold.
Disadvantage
Magnesium stearate is widely used as a lubricant for tablets and capsules with a common amount ranging from 0.25 to 0.50%.
Due to its hydrophobic property, magnesium stearate may lower wettability, delay disintegration of the tablets, and slow down the dissolution rate of the drug from the solid dosage (2). So it may decrease the absorption rates of tablets and capsules in our body.
For your better understanding, here are two simple dissolution time tests of capsule formulations from with or without magnesium stearate.
- Dissolution time of capsule with magnesium stearate
- Dissolution time of capsule without magnesium stearate
That’s why its concentration is generally relatively small in the formulations. However, the usage can be more if formulated in sustained-release dosage forms.
During tablet compression, a large amount of magnesium stearate employed can affect the elastic deformation of the tablet. Therefore, the amount of lubricant should be appropriate to make the tablet have good fluidity and compressibility.
The general usage of it should not exceed 0.5% in the direct compression, otherwise, the tablet will be softened.
When magnesium stearate is premixed with other ingredients before tableting, the longer the mixing time, the more the reduced dissolution rate and tensile strength of the tablet. Therefore, the mixing time should be carefully controlled.
Cosmetics
In the production of powdered cosmetics (e.g. talcum powder makeup), magnesium stearate is often added to improve the adhesion of powders, and make them smooth on the skin surface, and easily adhere to the skin.
In addition, magnesium stearate is often used as a thickener and emollient in cosmetics and personal care products.
Commonly used adhesives are zinc stearate, magnesium stearate, and aluminum stearate. These metal salts of stearic acid are wrapped outside other powder particles after added, making the powdered cosmetics not permeable to water.
Magnesium and zinc stearate are commonly used in this field as aluminum stearate is a little rough, while calcium stearate lacks smoothness.
Plastics
In plastic products, it is a heat stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride, and also a mold release agent and external smoothing agent.
Is Magnesium Stearate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects when used as a food additive. Magnesium stearate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) as a direct human food ingredient by the FDA. (3)
It can be used as a lubricant & release agent, a nutrient supplement, and a processing aid in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice.
In Europe, magnesium salts of fatty acids (E470b) are approved ingredients and their safety as food additives have been re-evaluated together with sodium, potassium and calcium salts of fatty acids by the EFSA in 2018.
The EFSA concluded that no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels of magnesium salts of fatty acids, and no need to establish a numerical acceptable daily intake (ADI) of it. (4)
JECFA classified this additive in the category of anticaking agent, binder, and emulsifier (5). Acceptable daily intake (ADI) “not specific” was set in 2015. (6)
It is also approved in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 470. (7)
What’re the possible Side Effects?
The following small side effects may occur:
- Laxative effect: large uses of magnesium stearate could lead to a laxative effect. (8) Magnesium stearate may be a source of magnesium for constipation. Magnesium citrate and magnesium oxide are common magnesium forms for constipation.
- Allergy may occur. A 28 years old woman affected by an allergic reaction from magnesium stearate with an urticarial manifestation. (9)
- Diarrhea: excessive magnesium intake from magnesium salts for pharmacological/medicinal purposes may also cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal effects. (10)
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, it is not a natural ingredient as it is made from chemical synthesis, though the raw material stearic acid is naturally present in the form of glycerides both in animal fats & oils and vegetable oils.
Is it Halal and Kosher?
Yes, it would be halal and kosher if stearic acid is vegetable based, as that can comply with the policy of Muslims and Jewish dietary regulations.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free that complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is It Vegan?
Yes, plant-based magnesium stearate is considered vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. However, tearic acid also can be produced from animal fats and oils (e.g. mutton tallow, beef tallow, and lard), therefore, vegetarians should avoid this type of magnesium stearate.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the food additive – Magnesium Stearate (E470b), from components, production, properties, uses in food supplement, medical tablets & capsules and cosmetics, safety and possible side effects, and so on.
What do you think of this lubricant? Let me know in the comments.




