What is Sodium Stearate (E470a) in Food and its Uses in Soap?

Composition | Production | Properties | Uses | Safety
Sodium stearate, the sodium salt of stearic acid (a naturally occurring saturated fatty acid) with the chemical formula C17H35CO2Na. You may be with familiar with this ingredient as it can be commonly found in soap.
It can be used as a binder, emulsifier, and anticaking agent in food. Also, as a major component (an emulsifier) of soap bar, a gelling agent in deodorant, an anionic surfactant in pharmaceuticals and so on.
What is Sodium Stearate Made of?
According to the USP definition, sodium stearate is a mixture composed of (1):
- Sodium stearate: not less than 40.0%
- Sodium palmitate (C16H31NaO2): it’s content plus sodium stearate, not less than 90.0%
- Small amounts of the sodium salts of other fatty acids
How is Sodium Stearate Made?
Generally, there are two manufacturing processes that can be used to obtain this ingredient.
1. Direct process
In this method, purified sodium stearate is synthesized by the chemical reaction between stearic acid and sodium hydroxide. Reaction equation as follows:
C17H35COOH+NaOH=C17H35COONa+H2O
This process is also suitable to produce potassium stearate (with another base KOH) and other salts of fatty acids.
2. Triglyceride hydrolysis
It can also be made from a saponification or basic hydrolysis reaction between NaOH with triglyceride. Reaction equation as follows (2):
(C18H35O2)3C3H5 + 3 NaOH → C3H5(OH)3 + 3 C18H35O2Na
Triglyceride is glycerine molecules attached to long hydrocarbon chains – stearic acid. It is the common form that stearic acid presents in natural sources: animal oils & fats and vegetable oils.
Where is Stearic acid comes from?
It can be derived either from edible fats and oils or from distilled food fatty acids.
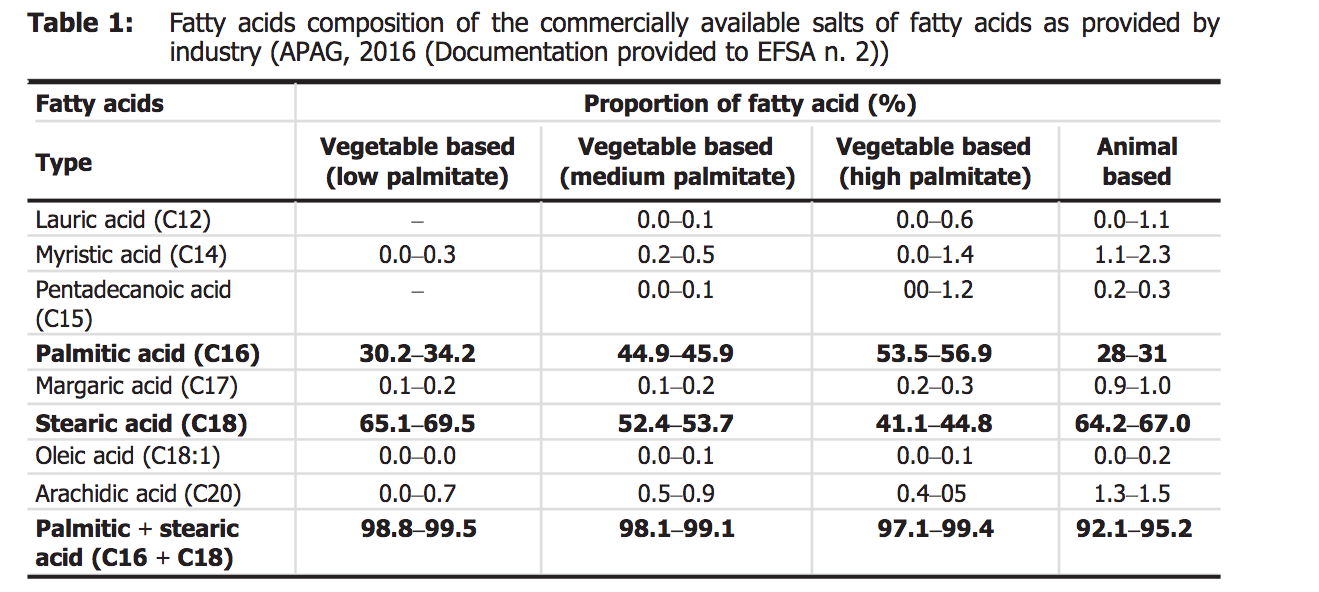
Image Source
Above are the datas provided by the EFSA, we can see that:
- Palmitic acid and stearic acid together take a large part in all fatty acids, no matter in vegetable-based oils or animal-based fats & oils.
- Animal sourced fats & oils (e.g. lard and tallow) have a higher percentage of stearic acid than vegetable sources (e.g. rapeseed oil, soybean oil, palm oil, coconut oil, and sunflower oil).
Properties
Appearance
White or creamy powder, flake or semi-solid. With an odor of fat when smelt and a feeling of greasy when touched.
Solubility
Among all alkali metal stearates, only sodium and potassium stearate are soluble in water and dissociate sodium/potassium and stearate ions after dissolved in water, while stearic acid does not.
Stearate ions react with water to form fatty acids and hydroxyl ions, so the aqueous solution is alkaline and it forms an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsifier with the HLB value around 16. However, sodium and potassium stearate are soluble only in water at a temperature about 70°C. (3)
Another two metallic stearates, calcium stearate and magnesium stearate are practically insoluble in water.
| Other names | Sodium octadecanoate
Sodium salts of fatty acids |
| CAS number | 822-16-2 |
| Chemical formula | C17H35COONa |
| Molecular weight | 306.466 |
| Melting point | 245 to 255 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol |
Structure
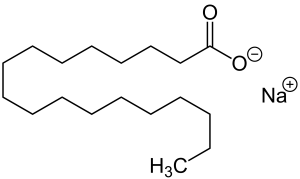
Image Source
There are 18 carbons in the structure of sodium stearate. It has both hydrophilic (the carboxylate, polar end) and hydrophobic parts (the long non-polar hydrocarbon chain).
The structure explains the characteristics of soap as the non-polar tail dissolves in non-polar substances while the polar head will not. And the polar, ionic head is hydrophilic and does dissolve in polar solvents such as water.
This property is utilized in making soap.
What’re the Uses of Sodium Stearate?
We can find the uses of sodium stearate in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Let’s dip into details.
Food
Sodium stearate can be used as a binder, emulsifier, and anticaking agent in food. This ingredient is listed in “Group I” in Europe, where the application fields are wide and the approved usages are “not limited”. Following food may contain it (4):
- Table-top sweeteners in tablets
- Dried herbs and spices
- Fruit (as a glazing agent)
- Nutrient (as a carrier)
Cosmetics
For its lubricating properties and ability to keep emulsions from separating, sodium stearate can be used as a stabilizer and a thickener in the following products:
- Deodorants and air fresheners: its gelling ability can help form a structure with other materials like propylene glycol, glycerin, and propanediol to form a solid stick shape.
- Cosmetics & personal care products: skincare products, body wash products, toothpaste and so on.
Industrial
A major component in soap.
Is Sodium Stearate Safe to Eat?
It almost has no side effects, and its safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Sodium salts of fatty acids may be safely in food and in the manufacture of food components for use as a binder, emulsifier, and anticaking agent in accordance with good manufacturing practice (5). It can also be safely used in the manufacture of chewing gum. (6)
Feed-grade sodium stearate may be safely used as anticaking agents in animal feed. (7)
Approved fatty acids includes stearic acid (C18), palmitic acid (C16), oleic acid (C18:1), lauric acid (C12), myristic acid (C14), capric acid (C8), and caprylic acid (C10). (8)
EFSA
Sodium stearate (E470a) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners”.
Safety re-evaluation in 2018
The EFSA pointed out there was no need to established an acceptable daily intake (ADI) of sodium salts of fatty acids (E 470a) when used as food additives and there was no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels in 2018. (9)
UK Food Standards Agency
It is listed in the category of “Emulsifiers, Stabilisers, Thickeners and Gelling Agents” (10)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 470. (11)
JECFA
Function class: food additive, anticaking agent, emulsifier. (12)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1985. (13)
Frequently asked questions
Is sodium stearate the same as baking soda?
No, they’re totally different. Baking soda is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), which is used commonly used with leavening acids to release CO2 in bakery.
Is it Natural?
It is a chemical synthesized ingredient and not natural, but derived from the natural ingredient stearic acid, which is a saturated fatty acid can be made from vegetable sources, such as rapeseed oil, palm oil and sunflower oil.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is halal if stearic acid is from vegetable based, which can comply with the halal policy.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve if made from vegetable oils. And you’ll find several suppliers following with different grades with pareve and passover.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free and can be used as a binder, emulsifier, and anti-caking agent in gluten free food.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, plant based sodium stearate is considered vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin.
Conclusion
Now you may have an understanding of the salts of fatty acids – Sodium Stearate (E470a), from its components; production; properties; uses in food, cosmetics and soap; safety and so on.
What do you think of this additive? Let me know in the comments.