What is EthylCellulose (E462) in Food and Why also Used in Coating Formulation?
What is it | Property | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Ethyl cellulose, or ethylcellulose, also known as its abbreviation EC. It is made from cellulose and commonly used as a coating in pharmaceutical formulations. The European food additive number for it is E462.
What is EthylCellulose?
It is an ether of cellulose Or it is a water insoluble polymer derived from cellulose where some of the hydroxyl groups are replaced by ethyl ether groups.
Structure
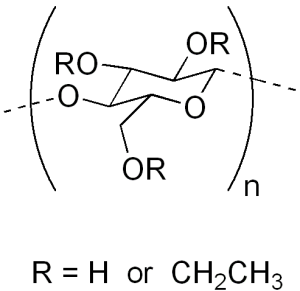
Image Source
How is EthylCellulose Made?
EC is a naturally occurring polymer produced from wood pulp or cotton by treatment with alkali and then ethylation of the alkali cellulose with ethyl chloride.
Following are the simple manufacturing process, details please see that of methylcellulose, as both methods are very similar.
Step 1: Alkalinization
Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2O
Step 2: Etherification
Cell·O-Na+ +ClCH2CH3 →Cell-OCH2CH3 +NaCl
Different EC grade can be produced by controlling the substitution of ethoxyl groups.
Specification
Other Names
Cellulose ethyl ether; Ethyl cellulose polymer
CAS Number
9004-57-3
Melting Point
240-255 °C
Chemical formula
The polymers contain substituted anhydroglucose units with the following general formula:
C6H7O2(OR1)(OR2) where R1 and R2 may be any of the following:
— H
— CH2CH3
Properties
Appearance
Slightly hygroscopic white to off-white, odourless and tasteless powder.
Degree of Substitution (DS)
The average number of hydroxyl groups substituted per glucopyranose unit is known as the degree of substitution (DS). The DS would be 3 if with a complete substitution.
It is required by the EU and the FDA, that for the food grade ethyl cellulose, “the content of ethoxyl groups (-OC2H5) should not less than 44 % and not more than 50 % of on the dried basis, that’s equivalent to not more than 2.6 ethoxyl groups per anhydroglucose unit.” (1)
Solubility
In water
Practically insoluble in water and it is the only modified cellulose not soluble in water but soluble in ethanol.
In organic Solvents
Insoluble in glycerol and in propane-1,2-diol.
Its solubility in varying proportions in certain organic solvents depending upon the ethoxyl content:
- Less than 46–48%: freely soluble in tetrahydrofuran, in methyl acetate, in chloroform and in aromatic hydrocarbon ethanol mixtures.
- 46–48% or more: freely soluble in ethanol, in methanol, in toluene, in chloroform and in ethyl acetate.
Viscosity
Its viscosity depending on the concentration, temperature, degree of polymerization (DP), and the presence of salts or other additives.
Food
It is suggested by China manufacturer, Shandong Head, that the viscosity (5% toluene ethanol solution, 25˚C) varies from 4-100 (mPa.s) when used in food and feed. (2)
Pharma
The viscosity is advised from 4 to 300 (mPa.s) in pharmaceuticals applications such as for coating, release control, granulation, binding, micro-encapsulation. (3)
What’re the Application of EthylCellulose?
In food, it can be used for binding, emulsifying, film forming and flavor fixatives. Mostly it is used in pharmaceuticals as a coating in the formulations of tablets and capsules as it can help mask the non-desirable taste, protect the active ingredients and control the drug release.
Food
Some approved uses are listed by the FDA and EFSA as follows:
FDA
When evaluated the safety of EC from Dow Wolff Cellulosics (Dow) in food in 2013, the FDA approved the uses in viscosity modification, thickening, film-forming, stabilization, acting as a filler, and for thermal gelation in following foods at levels ranging from 0.0075 to 5% (4):
- Grain products
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Milk and milk products
- Legumes
- Nuts and seeds
- Fats and oils
- Sugars and sweets
- Beverages
EFSA
It can be used as a coating agent for solid dietary food supplements and as a micro-encapsulating agent for fixing colours and flavouring agents.
The following food may contain with it (5):
| Food Category | Function |
| (Solid) dietary supplements | As a thickener or binder, or a taste masking agent |
| Salad dressings | As an emulsion stabiliser |
| Pizza preparations | As a barrier layer controlling diffusion of ingredients |
Cosmetics
Per “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, ethyl cellulose can work as a binding, film forming, and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (6)
Pharmaceuticals
Ethylcellulose is a semi-synthetic polymer material which has good thermal stability, biocompatibility and biodegradability in vivo, and has good film-forming properties.
As a widely used drug carrier, EC plays a protective role in the prevention of pollution and destruction during the preservation, transportation and release rate of drugs.
1. Protection
It can be used to coat ingredients to prevent them from reacting with other materials. It can prevent discoloration of easily oxidizable substances such as ascorbic acid, allowing granulations for easily compressed tablets and other dosage forms. (7)
2. Sustained-release Dosage
Ethylcellulose is commonly used as a film coating in sustained-release dosage formulations as it does not swell and impedes drug release when in contact with water due to its water insoluble property.
It helps release the drug slowly, therefore it increases the duration of drug action and decreases dosing frequency of some water-soluble drugs, and maintain a more uniform drug level in the human body. In this way, it improves treatment efficacy and a lower incidence of adverse reactions caused by a more uniform drug level.
Water-soluble coating cannot be used in some applications because of the processing problems or water sensitivity of the active ingredient.
Is EthylCellulose Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
The FDA has claimed that it can be used for flavor enhancer, flavoring agent or adjuvant, formulation aid, solvent or vehicle, stabilizer or thickener in food. (8)
It may be safely used in food as a binder and filler in dry vitamin preparations; as a component of protective coatings for vitamin and mineral tablets; as a fixative in flavoring compounds. (9)
EFSA
Ethyl cellulose (E 462) is an authorised food additive in the EU according to Annex II and Annex III of Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 and it is listed as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (10)
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
EFSA concluded that there was no need for a numerical ADI and that there would be no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels for E462. (11)
Authorised uses and use levels
Its approved application is listed in Group I and uses in all authorised food categories is quantum satis (QS).
The application of Group I please see in sodium CMC.
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, adjuvant, bulking agent, carrier, tableting aid, thickener. (12)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set in 1989. (13)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether ethyl cellulose is bad for our health and what are the side effects. We understand that consumers prefer natural food and have concerns about synthetic ingredients in the foods we eat. There are almost no health risks but some people may be allergic to it.
Frequently asked questions About EthylCellulose
Is it Natural?
No, from the manufacturing process mentioned above we can know EC is synthetically produced and the compound does not occur naturally.
Is it Halal?
Yes, EC is recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, EC is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher or maybe further passover.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, EC is gluten free according to the FDA that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, it is vegan as it derived from cellulose, the plant-based fiber commonly from wood chips and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan as a food ingredient.
Conclusion
As the only water-insoluble modified cellulose, ethyl cellulose’s pharmaceutical application is unique among the cellulose derivatives.
What do you think of this ingredient? Let me know in the comments.


