What is Methylcellulose (E461) in Food: Uses, Safety, Side effects

What is it | Properties | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Methylcellulose, or methyl cellulose, also known as its abbreviation MC. It is made from cellulose and can be used as a thickener, emulsifier, binder, stabilizer and gelling agent in food with the European food additive number E461. It is also a fiber supplement.
What is MethylCellulose?
It is a water-soluble polymer chemically modified from natural cellulose by partially etherified it with methyl groups.
Structure
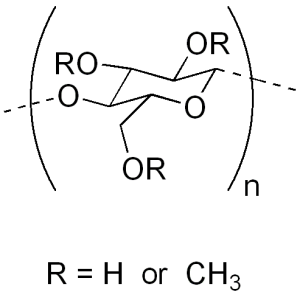
Image Source
How is MethylCellulose made?
Cellulose is a polymer of glucose-containing hydroxyl groups (-OH) which can be substituted with methoxide groups (-OCH3) to produce MC.
This mechanism is the same with that of producing sodium CMC.
Generally, the manufacturing process of MC can be divided into two steps, alkalinization and etherification.
Step 1: Alkalinization
Disperse the raw material cellulose pulp in an alkali solution (generally sodium hydroxide, 5–50%) to form alkali cellulose.
Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2O
Step 2: Etherification
The reaction of alkali cellulose with methyl chloride is under strictly controlled conditions. In this reaction step, the hydroxyl groups (-OH) on the anhydroglucose monomers of the cellulose chain are partially replaced by methoxide groups (-OCH3) after etherification.
Cell·O-Na+ +ClCH3 →Cell-OCH3 +NaCl
Different MC grades can be produced by controlling the degree of hydroxyl groups (-OH) substituted.
Properties
Appearance
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder.
Degree of Substitution (DS)
DS represents the average number of substituted hydroxyl groups per glucose. When all “R” are methoxy groups in the structure, the DS value is equal to 3.
Methylcellulose used as a food additive in Europe should have a methoxy content of 25% to 33% (while this percentage requested by FDA is 27.5% to 31.5%), and the corresponding DS value 1.7 to 2.2. (1)
Solubility
In water
MC dissolves and swells in cold water and will generate a clear to opalescent, viscous, colloidal solution.
Organic solvents
Insoluble in ethanol, ether and chloroform, soluble in glacial acetic acid.
The solubility is influenced by the DS value.
| DS Value | Soluble In |
| Less than 1.3 | Alkali |
| More than 2.6 | Organic solvents |
| Between 1.3 and 2.6 | Cold water, pyridine, aniline, trimethylformamide, benzyl alcohol and glacial acetic acid |
Gel & Viscosity
The aqueous solution of methylcellulose is neutral and stable at room temperature.
It produces gelation and precipitation at high temperatures. The gel temperature depends on the viscosity and concentration of the solution. The gel temperature would be lower at a higher viscosity and with a higher concentration.
The viscosity can be increased when an inorganic salt is present.
Reversible Thermal Gelation
The aqueous solution is surface active and forms a film after drying. It forms a thermoreversible gel, that is to say, it makes gel upon heating over a temperature, and goes back to viscosity solution after cooling down.
Specification
| Other Names | Cellulose methyl ether; Cellulose, methyl |
| CAS Number | 9004-67-5 |
| Chemical formula | The polymers contain substituted anhydroglucose units with the following general formula:
C6H7O2(OR1)(OR2)(OR3) where R1, R2, R3 each may be one of the following:
OR Written as C6H7O2(OH)x(OCH3)y, where
|
| Molecular Weight | 20,000 to 380,000 |
What’s the Uses of MethylCellulose?
As a polysaccharide and cellulose derivative, the uses of Methylcellulose is wide. MC is a non-caloric indigestible edible fiber in humans and can be used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceutical and other industries.
Food
Its food grade has wide uses for its thermal gelation, lubricity, stabilizing the emulsion, preventing syneresis and so on.
Let’s see its benefits and functions in some food categories.
Bakery
Gas retention during baking, provides freeze/thaw stability, improve emulsion stability, increases crumb softness, prolong shelf life.
Confectionary
It can be used as a lubricant for easy application, also provides creamier texture, improve spreadability and clean flavor release in glazes, icings and coatings. (2)
Frozen dessert
Controlling ice crystal formation, provide smooth texture as well as stabilize emulsification such as in ice cream.
Fried products
MC gels when fried (at high temperature) and therefore make the structure and reduces oil intake which benefits vegetarians.
Other food products
Methylcellulose can also be used in other products, such as in toppings, salad dressing, sauces to stabilize the emulsion and extend the shelf life. It can also function as a bulking agent in jellies, syrups and gums to provide fiber content without increasing available energy value.
Cosmetics
Per “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, methylcellulose can work as a binding, emulsion stabilising, stabilising, and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (3)
Pharmaceuticals
Excipient
Methylcellulose can be used as an excipient in most forms of pharmaceutical products such as powders, granules, inhalants, (film) tablets, dragées, ointments, creams, gels or liquids.
It functions as a dry binder in the tableting process to improve compressibility, also serves as a binder or a thickening and gelling agent in wet granulation. (4)
Laxative
It is a bulk fiber laxative to treat constipation by increasing stool frequency, water content, and fecal solids. (5)
Is MethylCellulose Safe?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Methylcellulose is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practice AND the methoxy content between 27.5% – 31.5% on a dry-weight basis. (6). It can be used as an emulsifier or emulsifier salt, flavor enhancer, and stabilizer or thickener in food. (7)
EFSA
Methylcellulose (E 461) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (8)
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
EFSA concluded that there was no need for a numerical ADI and that there would be no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels for E461. (9)
Authorised Uses And Use Levels
Its approved application is listed in Group I and separately by E461. The uses in authorised food categories are quantum satis (QS).
The following foods are separately by E461 and may contain with it (10):
- Table-top sweeteners in tablets and powder form.
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
MC is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 461. (11)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener. (12)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set since 1989. (13)
What are the possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether methylcellulose is bad for our health and what are the side effects. There are almost no health risks but some people may be allergic to it and the overdose may cause problems.
Allergy symptoms
Allergic reactions may occur like hives; breathing difficulty; swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat. (14)
Is it Safe for pregnant?
It is reported by the FDA that in pregnant mice, high doses (26-fold or more than daily dietary intake) of methyl cellulose caused a significant increase in maternal mortality and retardation of fetal maturation. (15)
Frequently asked questions about MethylCellulose
Is it Natural?
No, from the manufacturing process mentioned above we can know MC is synthetically produced and the compound does not occur naturally.
Is it Halal?
Yes, MC is recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, MC is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher or maybe further passover.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, MC is gluten free according to the FDA that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, MC is vegan as it derived from cellulose, the plant-based fiber commonly from wood chips and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan as a food ingredient.
Is it a Hydrocolloid?
Yes, MC is a hydrocolloid and often used as a thickening or gelling agent.
Is it a Soluble Fiber?
Yes.
Is it Anionic?
No, and polyvalent metal ions cannot combine with it to form insoluble precipitates as it is a non-ionic solution.
What is it Made Of?
MC is a mixture consisting of etherified methyl groups with the DS value 1-3.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the thickener – Methylcellulose (E461), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Safety
- FAQs
I’m probably forgetting some information, and if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



I had a Beyond Meat hamburger and got so sick. I developed cramps and the urgency to use the bathroom at least 15 times in the course of a few hours. I became dehydrated and had the shakes along with the chills. Terrible feeling and the hamburger was not that great. I will never eat methyl cellulose as long as I live.
Hi Josephone,
It is difficult to say it is methylcellulose that causes such problem, maybe other ingredients as you can see there are many ingredients in Meat hamburger.
Hi,
Is there somewhere online I can get it other than from Modernist Pantry?
You can search on amazon
i have tried both the burgers and the ground and i find they both taste the same there is a bitter after taste to both and an aroma that i find is not appetizing at all. Is there some kind of spice that could cause this? I tried the chicken strip and did not find this odor and after taste in them they was actually very good.
I am sick to my stomach from eating Dr. Prefers ground plant products! I drank a ton and I am having headache and stomach issues! I also can’t eat the impossible burger!
Hi James Han,
Thank you for the information on MC. we have been making plant-based burgers and the like for the past two years here in Thailand. However in an effort to combat the “Soft nature” of our burgers although our burgers have held up quite well to having a cohesive texture they are not as firm as I would like. I have been reluctant to use MC but I tried some from a company called Pure Methyl Cellulose on Amazon. That worked very well and If I can find this product at a sensible price I would buy it in bulk. 2 Lbs cost us approx $100 in Thailand . The average price from China is more like $2-4 per kilo something is wrong.
Firstly I can have no idea of the viscosity we should be using but from info across the net. I would guess it would be around 50-100,000 cps for this application we used 3% of the American product and it was all very good. Is HPMC the same as Methyl cellulose?
I did bring in some Food Grade HPMC from China and I think despite their advice it was suitable 4,500 CPS is not viscose enough. At this level it is no better than using Xanthan Gum. I am not a chemist and all I am trying to do is establish some guidance on this additive. Can you help please?
Thanking you in advance.
Does it contain Agar Agar?
how do you explain the laboratory studies of methyl cellulose and colerectal cancer in studies on rats.. and go on to say its safe.. just because the FDA says its permitted does not mean safe.. cancer possibilities and food .. for me at least .. are non negotiable.. any link to cancer.. and I do not want it.!!!
As a vegetarian I have been using meat alternative foods for years. I developed a skin rash and stopped eating cheese for a few weeks, that did nothing then I quit bread for as long, no avail. Stopped both, again nothing.
I have been taking Morning Star grillers prime which includes methylcellulose, their black bean burgers don’t. You guessed it, when I stopped grillers prime and a locally produced veg nuggets brand, both processed with methylcellulose, the rash subsided.
My idea of eating plant products is eating natural health giving plants – i.e. vegetables, fruit, beans, nuts, etc, as nature intended them, NOT eating something unnatural synthesized from saw dust / wood chips or the like. I’d rather eat real plants than fake meat made from methyl cellulose.