What is Sodium Erythorbate (E316) in Food and Why it can Accelerate Curing in Meat Products?

If you have ever read the ingredients label of sausage, ham, hotdog, bacon and other cured meat products, you may have noticed an additive named sodium erythorbate or E316, which functions as an antioxidant, a preservative and a curing accelerator in food.
Let’s dip into the navigation to know more about this ingredient:
What is Sodium Erythorbate?
It is the sodium salt of erythorbic acid, a stereoisomer of sodium ascorbate. Likewise, it is used as an antioxidant, a preservative and a curing accelerator in meat and fish products. The European food additive number for it is E316.
Structure
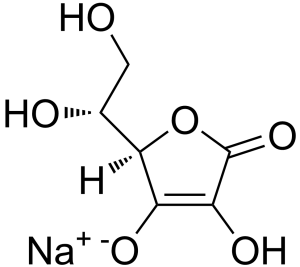
Image Source
What is Sodium Erythorbate Used for in Food?
It is used as an antioxidant, a preservative and a curing accelerator, let’s see each function:
- Antioxidant: it keeps the food fresh (color, flavor and etc) as sodium erythorbate itself can be oxidized by scavenging oxygen and then inhibiting the oxidation of fruits and vegetables.
- Preservative: it prevents microbial growth and therefore extends the shelf life of food.
- Curing accelerator: it accelerates the curing process of meat and fish products by speed up the development of the pink color.
How does Sodium Erythorbate Work in Processed Meat?
The stable pink color, unique flavor, aroma as well as microbial control and antioxidant activity are developed by reactions of nitric oxide with meat. The whole process is associated with curing agents & added ingredients and the oxidation-reduction reactions among them.
1. Where does Nitric Oxide come from?
Potassium or sodium salts of nitrate and nitrite are used as a curing agent which is a must ingredient in curing meat as it can be reduced to nitric oxide (NO).
2. What Reacts with Nitric Oxide to Produce Color?
Myoglobin (a meat pigment) can combine with nitric oxide to form nitrosomyoglobin to produce a bright red color.
During heat processing and cooking, nitrosomyoglobin is converted to a stable pigment, nitrosohemochrome, which has a pink color.
3. What does Sodium Erythorbate do?
It is an antioxidant that can converts nitrite to nitric oxide, thereby speeding up this conversion and increasing the color of meat products.
Meanwhile, it can reduce the amount of nitrites used in meat products and the amount of residues, and therefore effectively reduce the formation of nitrosamines which is a carcinogen.
How is it Made?
Sodium erythorbate is synthesized using the same procedure as for the production of erythorbic acid. Generally, it is also produced by fermentation of food grade starch hydrolysate but the manufacturing process is finished in the 4th step of producing erythorbic acid.
Specification
| Appearance | White crystalline solid, available in two forms, powder and granular |
| Other names | Sodium isoascorbate, Sodium D-isoascorbic acid, Sodium salt of 2,3-didehydro-D-erythro-hexono-1,4-lactone, 3-keto-D-gulofurano-lactone, sodium enolate monohydrate |
| CAS number | 6381-77-7 |
| Chemical formula | C6H7O6Na·H2O (monohydrate) |
| Molecular weight | 216.13 |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol |
| PH | 5,5 to 8,0 (10 % aqueous solution) |
What’re the Application of Sodium Erythorbate?
Food
Processed Meat
The cured meats in the human diet have a history of thousands of years.
Sodium erythorbate is used primarily to bring out a nice red color in sausage, ham, bacon and other cured meat products or fish products as it can accelerate the reduction of nitrite & nitrate to nitric oxide which generates the pink colour in meat.
It is always be added together with curing salt (nitrites/nitrates). Potassium or sodium salts of nitrate and nitrite act as a curing agent while sodium erythorbate accelerates the rate of curing by cutting down the processing time.
Fruit & Vegetables
It functions as an antioxidant to keep the freshness and flavor by inhibiting the browning by scavenging oxygen and by reducing quinones back to polyphenol compounds.
It is used by spraying or dipping fruit and vegetables in an aqueous solution of sodium erythorbate.
Fresh Meat
It can prolong color stability and extend its shelf life.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, it functions as an antioxidant in cosmetic and personal care products. (1)
Is Sodium Erythorbate Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
It can be used as an antimicrobial agent, antioxidant, color or coloring adjunct, dough strengthener, flour treating agent, oxidizing or reducing agent, processing aid, surface-finishing agent. (2)
EFSA
Sodium erythorbate (E 316) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive in the EU as “Additives other than colours and sweeteners”. (3)
Safety Re-evaluation in 2016
After the studies of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity and others, EFSA claimed “there is no reason to revise the current ADI of 6 mg/kg bw/day and the use of erythorbic acid (E 315) and sodium erythorbate (E 316) as food additives at the permitted or reported use and use levels would not be of safety concern.” (4)
Authorised Uses
The following are the approved uses and max usage, which are the same with that of erythorbic acid. (5):
| Food Categories | Maximum permitted levels (mg/L or mg/kg as appropriate) |
| Cured and preserved meat products | 500 |
| Frozen and deep-frozen fish with red skin | 1500 |
| Preserved and semi-preserved fish products | 1500 |
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 316. (6)
JECFA
Food grade Specification, function class: Antioxidant. (7)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1990. (8)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether sodium erythorbate is bad for our health and what are the side effects in the food we eat. However, it is generally considered safe and almost no reported health risks. Maybe some people are allergic or sensitive to it.
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, we can know it is synthetic from the manufacturing process mentioned above.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher or maybe kosher passover.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free according to FDA that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, it is vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan and vegetarians can eat the food with it.
What does it Made Of?
From the chemical formula C6H7O6Na·H2O, we can know it is composed of water and sodium erythorbate anhydrous.
Does Heat Destroy it?
The decomposition temperature of erythorbic acid is 164–172°C, so it is stable during the heat process.
What are its Alternatives in Processed Meats?
Another antioxidant – Sodium Ascorbate, can replace it.
How Much is it Used in Bacon?
According to USDA, 0.055% of either sodium ascorbate or sodium erythorbate is required to add in pumped bacon. This addition greatly reduces the amount of free nitrite and, thus, minimizes the formation of nitrosamines. (9)
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the antioxidant – Sodium erythorbate (E316), from the following aspects:
- Main purposes and applications in food, particularly used widely in processed meat
- Brief manufacturing process
- Safety
- Possible side effects
- FAQs: substitute, use levels in bacon, is it vegan and etc.
What kind of meat have you found it in? Let me know in the comment.



Hi! I would like to ask how much should E316/sodium erythorbate be added to a 1kg of meat?
Is it known whether or not Sodium Erythorbate uptakes into the body? It might be useful as a nutrient/prebiotic if it does NOT. If it uptakes, then it likely demonstrates the same effects vitamin c: proclivity to kidney stones… and perhaps escalation of the body’s vitamin C concentration. If it is not absorbed through the gut lining into the body, then it would remain in the gut and inhibit the production of nitrosamines by meat-digesting gut bacteria resident therein — a useful effect. Are you aware of any studies that examine uptake behavior of Sodium Erythorbate?
Hi Lim,
You can see the max usage in the article.
What is the permitted or recommended application for still drinks and soft drinks?
How to apply to the meat? Directly or with water?
in a usda plant can I use soduim erythorate in raw sausage products?