What is Stearic acid (E570): Sources, Types, Uses, Safety and More

Composition | Source | Production | Types | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Stearic acid or octadecanoic acid, a most common saturated fatty acid (without double bonds) with the chemical formula C₁₇H₃₅COOH. It occurs naturally as a glyceride in both animal fats & oils and vegetable oils. When used in food, it has the European food additives number E570.
Stearic acid and/or its derivatives can be used as a surfactant, emulsifier, and lubricant in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, candles, rubbers, plastics and etc.
What is it Made of?
The main compositions in commercial stearic acid are stearic acid and palmitic acid, although pure stearic acid is also available. Their assays differ based on the purity or grade of stearic acid.
Similar with its food grade, per the USP definition, its USP-NF grades can be divided into three types according to the content of stearic acid as follows (1):
- Type 50: stearic acid (40.0%–60.0%), stearic acid + palmitic acids: NLT 90.0%.
- Type 70: stearic acid (60.0%–80.0%), stearic acid + palmitic acids: NLT 90.0%.
- Type 95: stearic acid (NLT 90.0%), stearic acid + palmitic acids: NLT 96.0%.
Foods Rich in Stearic acid?
According to the data of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in 2005-2006, the following foods are high in stearic acid (2):
- Grain-based desserts
- Regular cheese
- Sausage, franks, bacon, and ribs
- Chicken, beef, pork
- Pizza
- Candy
- Pasta
- Eggs
- Butter
- Milk products
- Nuts/seeds
- Potato/corn/other chips
- Quickbreads, crackers
- Soups
Cocoa butter is also high with it.
How is it Made?
Stearic acid is commercially made from hydrolyzing tallow or hydrogenated vegetable oil from edible sources. And follows the process of acid distillation, steaming and pressing.
Here is the general hydrolysis manufacturing process of the triglycerides (stearic acid naturally exist in this form )
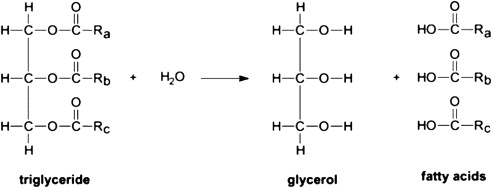
Image Source
The following are the common sources of animal fats & oils, and vegetable oils.
Animal fats & oils
- Mutton tallow
- Beef tallow
- Lard
- Butter
Vegetable oils
- Palm oil
- Soybean oil
- Coconut oil
- Olive oil
- Corn oil
Commonly the content of stearic acid derived from animal fat (up to 30%) is higher than that from vegetable oils (typically <5%) (3). Commercial vegetable stearic acid is mainly produced from palm oil.
Hydrogenation is a chemical process converting liquid vegetable oils into solid or semi-solid stable fats. The unsaturated double bonds in fatty acids are turned into saturated bonds after hydrogenation.
Types of Stearic Acid and their Difference
It can be classified into two types if based on the sources: animal and vegetable-based types. Meanwhile, per the purity degree or manufacturing process, it can also be divided into three types, that is one, double and triple pressed stearic acid.
The purity of various grades are defined with different C18 content. The common assay of C18 (stearic acid) content is 40%-60%.
Triple pressed stearic acid is the purest one, commonly sourced from vegetable oils and used in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical. The refined degree of double pressed stearic acid is between one and three pressed one.
Double and triple pressed stearic acid are both white waxy solids, while the one pressed stearic acid is a pale yellow waxy solid.
The one pressed stearic acid is mainly derived from animal fats & oils, and primarily used in industrial applications, including:
- as a vulcanization active agent in the rubber
- a stabilizer in plastics
- as a water repellent and brightener in paper
- as a softener, waterproofing agent in textile
Properties
| Other names | Octadecanoic acid, Mixture of stearic acid and palmitic acid |
| CAS number | 57-11-4 |
| Chemical formula | C₁₇H₃₅CO₂H |
| Molecular weight | 284.484 |
| Melting point | 69.3 °C |
| Boiling point | 361 °C |
| Acid value | 194–212 (4) |
| Viscosity (mPa·s) | 7.79 (80°C), 6.29 (90°C) (5) |
Appearance
The pure product is a white gloss soft flakes or powder at room temperature, and it will turn to liquid around 70°. It has an odor of pungent and oily.
Solubility
Insoluble in water (solubility 0.00034 g/100 g at 30 °C, will float on the water) while soluble in oils & alcohols, e.g. solubility in ethanol 5.42 g/100 g (30 °C)
Why is it insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol?
Although stearic acid has a carboxyl group which is polar, a long chain C18 hydrocarbon chain makes it non polar. So it is insoluble in water but soluble in non polar solvents. And it is covalent instead of ionic in water.
It can be dissolved in organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, chloroform, ether, hexane, ethyl acetate, and petroleum ether due to its non polarity property.
How to dissolve it in water?
Add strong base, such as NaOH to improve the water solubility.
Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB)
Its HLB value is 6.5 (6), which means it is hydrophobic and soluble in oil.
Structure
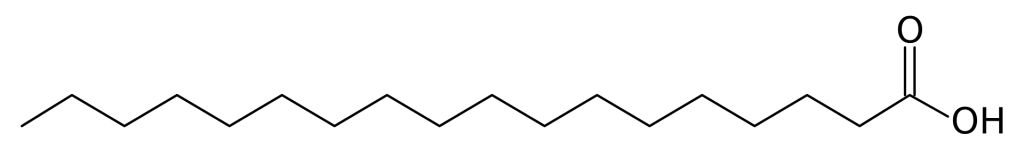
Image Source
Stearic acid is a typical fatty acid, which contains a carboxyl group at one end and a methyl group at the other. Totally there are 18 carbons in length of molecule structure, and with the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)16COOH.
What’re the Health Benefits of Stearic Acid?
It may have the following health benefits:
- Inhibit tumour development. A study in 1987 found that stearic acid can inhibit tumour development in rats. (7)
- Benefits breast cancer. A 2010 research showed that dietary stearate may be helpful in preventing or treating breast cancer. (8)
- Decrease Cardiovascular Risks. A study in 2018 said that C16:0 increased cardiovascular and cancer risk while C18:0 (stearic acid) can decrease both. (9)
What’re the Uses of Stearic Acid?
Stearic acid has a wide use in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and other industries mainly due to the carboxyl group in the molecule, also both the hydrophilicity and lipophilicity it has.
Food
The direct use of stearic acid in food is not common. It can be used for its lubricity, emulsification and soft properties in gum and candy. Also, it can be used as a coating agent, and to produce stearates and emulsifiers.
The following food list may contain it:
- Bakery
- Dairy
- Sauces, seasonings, snacks
- Desserts & ice cream
- Cocoa products
- Chewing gum
- Vitamins & dietary supplements
Stearates
Stearic acid is primarily used for the manufacturing of stearates. It can be made into sodium stearate, potassium stearate, calcium stearate and magnesium stearate to be used in food.
Emulsifiers
Another main purpose of stearic acid in food is to produce the following emulsifiers:
- DATEM
- Mono and Diglycerides
- Glycerol monostearate
- Sorbitan monostearate
- Sodium stearoyl lactylate
- Calcium stearoyl lactylate
- Polysorbates (20, 40, 60, 80)
- Sorbitan tristearate
- Sucrose esters of fatty acids
Coating agent
Stearic acid can be used as a coating agent to be applied to the surface of food to polish, preserve freshness, and prevent water evaporation.
You may find such applications in cocoa products, e.g. chocolate and chocolate products and candies.
Cosmetics
Like other fatty acids, stearic acid functions mainly as a cleansing, emulsion stabilising, fragrance, refatting, surfactant – cleansing and surfactant – emulsifying when added to cosmetics and skin care products. (10)
The application fields such as detergents, soaps, lotions, face cream, moisturizers, deodorants, shampoos, shaving cream products and so on.
Is stearic acid an emulsifier?
There is no simple answer “yes or no” to this question. If precisely, it is not an emulsifier although it can stabilize and thicken an emulsion.
However, it can be considered as an emulsifier if used together with sodium hydroxide (or in alkaline conditions) as it produces sodium stearate, which works as an emulsifier and helps oil and water phases mix well.
Benefits for skin
Stearic acid is often combined with emulsifiers to thicken and stabilize ointments, lotions, and emollients. It washes the oil, dirt, and other impurities that have accumulated on your skin away and retains moisture on the skin’s surface. Finally, it creates a cooling feel on the skin.
Pharmaceuticals
Its derivative magnesium stearate, an excipient commonly used as a lubricant in pharmaceutical tablets & capsules and supplements.
Wax
Stearic acid can be used as a wax hardener in candle production. It can not only help pillars or freestanding candles maintain their shape in a warm temperature for a long time, but also increase the whiteness of wax and help demoulding. Plus, it stabilizes the perfume and aromas for a longer time.
Soap
Stearic acid hardens the soap bar, and creates a soft & creamy lather.
Rubber
This ingredient is used as a dispersing agent and accelerate the vulcanization process in rubber.
Plastics
In the plastics industry, stearate (lead, zinc, calcium, barium, magnesium, etc.) can be used as a heat stabilizer, which can interact with HCl degraded from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to prevent PVC decomposition.
Is Stearic Acid Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects when used as a food additive.
FDA
Stearic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) as a direct human food ingredient by the FDA. It can be used as a flavoring agent and adjuvant in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (11)
Fatty acids that are permitted for direct use in food that can be used as a lubricant, binder, a defoaming agent, and as a component in the manufacture of other food-grade additives. (12)
Other fatty acids include palmitic acid, oleic acid, myristic acid, lauric acid, capric acid and caprylic acid.
EFSA
Stearic acid is a fatty acid approved by the European Food Safety Authority for use as a food additive with the E number E570.
The EFSA concluded that fatty acids (E 570) was of no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels in the safety re-evaluation in 2017. (13)
Fatty acids (E 570) are listed in the Group I of food additives authorised at quantum satis (QS), which means it can be used in a lot of food and with no specific quantity restriction. It is also used as a glazing agent for fruit and as a carrier in nutrients except nutrients containing unsaturated fatty acids.
Other Authorities
JECFA approved it as a flavoring agent with no safety concern at current levels of intake. (14)
It is also approved in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 570. (15)
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, although stearic acid is a natural ingredient present in the form of glycerides both in fats & oils of animal and vegetable, the commercial stearic acid is obtained by chemical method as mentioned above.
Is it Halal and Kosher?
Yes, stearic acid would be halal and kosher if it is vegetable-based, as that can comply with the policy of Muslims and Jewish dietary regulations.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free that complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, stearic acid originated from vegetable oils is considered vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. However, some manufacturers may produce it from animal fats. Therefore, vegetarians should avoid it.
Now the vegetable stearic acid is required in many uses and the palm oil is the most common plant source.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the fatty acid – Stearic acid (E570), from
- Components
- Production
- Types
- Properties
- Uses in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, candle, soap, rubber, and plastics
- Health benefits
- Safety
What do you think of this fatty acid? Let me know in the comments.

Wonderfully captured the entire essence of Stearic Acid. How ever one query? what is the method/test to determine whether the stearic acid is from Vegetable source or Tallow source?
I’m in desperate need to know if I’m getting a serious rush reaction from cream containing stearic acid if I should avoid it if they use it in tablets I’m using? I never realized they use it in medication an now have serious doubts about some of my medications and I have been struggling with crazy fatigue for quite some time could it be the stearic acid in the tablets causing the heyhoc in my body? Doctor keep saying it’s just because I had covid but I’m starting to wonder if this isn’t a huge factor? Please help?
Hi Tina,
I know your concerns. Take it easy, please. Maybe your doctor is right, as the stearic acid in tablets is very limited. As you know, recovering from covid is the first place, so you need to take tablets, do you think so? Hope you can recover soon.