What Is Disodium Succinate In Food And Difference With Monosodium Succinate?

Source | Two types | Production | Uses | FAQs
Disodium succinate is the disodium salt of succinic acid that can be used as a flavor enhancer in food for its unique seafood flavor and synergy with other common flavor enhancers to boost the umami flavor, such as monosodium glutamate (MSG), disodium 5’-ribonucleotides (I+G) and hydrolyzed vegetable protein (HVP). Generally, this food additive is safe, natural or synthetic, vegan, halal, kosher and gluten-free.
Natural Source
Disodium succinate is commonly found in shellfish, shrimp, crab and other crustaceans seafood. It is an important ingredient that makes the umami taste of seafood, it also presents in mushrooms.
Two Types
Disodium succinate crystalline has two types, anhydrous (CAS number 150-90-3) and hexahydrate (CAS number 6106-21-4, contains six crystal water), the latter is the most used than the former in food. Disodium succinate hexahydrate can be converted to disodium succinate anhydrous after lose the water at 120 °C. The enhancing flavor powder of anhydrous is about 1.5 times that of hexahydrate.
How is Disodium Succinate Made?
Disodium succinate is synthesized between the reaction of succinic acid and sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. The following is a brief 4 steps manufacturing process (1):
- Heating the solution sodium carbonate solution or sodium hydroxide (with a concentration of 30%) to 65 °C.
- Adding succinic acid to the solution under stirring. The quantity of sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide should be excessive, otherwise, monosodium succinate would be obtained.
- Decolorization and filtering.
- Spray-dried into a powder.
This additive can also be divided into bio-based and chemical synthesized according to the manufacturing process of the raw material – succinic acid. It is bio-based if produced from fermentation or chemical synthesized from maleic anhydride.
Specification
Appearance
Odorless, crystalline powder or granular, with a special shellfish taste.
Other Names
- Sodium succinate hexahydrate
- Sodium succinate
- Butanedioic acid, disodium salt
- Disodium butanedioate
- Succinic acid, disodium salt
- Sodium succinate dibasic
Chemical formula and molecular weight
- Anhydrous: C4H4Na2O4, 162.06
- Hexahydrate: C4H4Na2O4·6H2O, 270.15
Structure
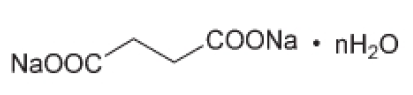
n=0 or 6
Properties
Solubility
Solubility in water, 35g/100ml at 65 °C, insoluble in ethanol.
PKa
Succinic acid is a weak diprotic acid that has two PKa, PKa1 4.2 and PKa2 5.6, respectively.
What are the Uses of Disodium Succinate?
Disodium succinate can be used as a flavor enhancer to improve the seafood taste in food and can boost the umami taste when combined with other common flavor enhancers, such as MSG, I+G or hydrolyzed vegetable protein. Its thermal stability also enables it to go through a high temperature process in food.
The following food may contain it:
- Seasoning
- Vinegar
- Sauce
- Instant noodles
- Ham & sausage
- Canned seafood (fish, shellfish, cuttlefish)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Disodium Succinate Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as animal products are not involved in the manufacturing process. So it is suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Disodium Succinate vs Succinic Acid?
The former is used as a flavor enhancer while the latter mainly functions as a PH regulator in food.
Disodium Succinate vs Monosodium Succinate?
Both can be used as flavor enhancers in Japan, but seldom used in Europe. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC) have approved disodium succinate as a flavor enhancer, while monosodium succinate is not included.
The former is made by two carboxyl groups in the molecule of succinic acid that reacts with sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide, while the latter is obtained only one carboxyl group reaction with NaOH or Na2CO3.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a good knowledge of the flavor enhancer – disodium succinate, from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Comparison with succinic acid and monosodium succinate
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Let me know in the comments.



Master Food Chinese Stir Fry Sauce containing “Disodium” appears to have caused me to come up in a rash. I have had similar rashes from products contain 212 and 250. Still looking for an answer.