What is Sodium Propionate (E281) in Food & Comparison with Potassium and Calcium Propionate?

Production | Three Propionates comparison | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Sodium propionate or sodium propionate, the sodium salt of propanoic acid that can be used as a preservative in food with the European food additive number E281. The common use for this ingredient is as a mold inhibitor in baked goods as they’re easily contaminated with the moisture in the air during cooling, slicing and packaging after the baking process.
How is Sodium Propionate made?
Sodium propionate can be produced by the reaction of propionic acid (E280) with sodium hydroxide in hydrogen peroxide and water. (1)
Comparison of three Propionates in bakery
There are three propionates that are approved as food additives, calcium propionate (E282) is the most used one, then sodium propionate, while potassium propionate (E283) is not common.
Calcium propionate
It is the most used propionate preservative for yeast-leavened baked products, also it enhances calcium nutrition in baked products.
But it is not a good choice for chemical leavened baked products since calcium ions will react with HCO3− from the chemical leavening agents – sodium bicarbonate.
Sodium propionate and Potassium propionate
Sodium propionate and potassium propionate are appropriate for non-yeast leavened baked products (e.g. cakes, tortillas, etc.).
Potassium propionate has the advantage as it doesn’t add sodium to bread and is therefore suitable for low-sodium products.
Chemical leavening agents or baking powder are mixtures that release carbon dioxide in the condition of moisture or with heat. Most of them are made of an acid (such as sodium aluminum phosphate, sodium acid pyrophosphate, monocalcium phosphate) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3).
Specification
| Other Names |
|
| CAS Number | 137-40-6 |
| Chemical formula | C3H5NaO2, CH3CH2COONa |
| Molar Mass | 96.060 g/mol |
Properties
Hygroscopic crystalline powder or granular with a little propionic acid odor, deliquescent in moist air.
Structure
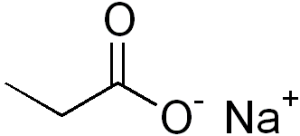
Image Source
Solubility
Water solubility is important since this property will influence its uses and function as a mold inhibitor.
In water
Freely soluble in water and with the solubility 100 g/100 mL at 15°C, which is better than that of calcium propionate.
Sodium propionate is a base and dissociates propionate ion after the reaction with H2O. And then propanoic acid generated as propionate ion combines with H2O (or exactly hydrogen ion in H2O).
In Organic solvent
Soluble in ethanol with the solubility 4.4 g/100 mL.
PH Range
PH value is another important role as preservatives need a suitable pH range for their antimicrobial activity.
The optimal pH range of propionates for inhibiting the growth of mold is from 2.5 to 5.5.
As mentioned above, propionates produce propionic acid after dissociation and combination with H2O. Propionic acid can penetrate the cell wall of microbes and lowers its intracellular pH. That results in inhibiting the growth of molds. This is how it works.
What’re the Uses of Sodium Propionate?
Sodium propanoate is primarily used in baked goods to extend the shelf life and can also be used in the following foods in to inhibit the growth of mold and other microbes (2):
- Nonalcoholic beverages
- Cheeses
- Confections and frostings
- Gelatins, puddings, and fillings
- Jams and jellies
- Meat products
- Soft candy
The common use of sodium propionate is in bread and the recommended usage is 0.2-0.5% of flour weight for standard bakery recipes (3).
How to Use Sodium Propionate in Bread?
Either of 3 ways is ok:
- Blending it with other dry ingredients
- Dissolving it first in water prior to use, due to its good solubility in water
- Added at the end of the dough making
Is Sodium Propionate Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Sodium propionate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used as an antimicrobial agent and a flavoring agent in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (4)
EFSA
Sodium propionate (E281) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (5).
Safety re-evaluation in 2014 and 2016
Its safety has been re-evaluated in 2014 (6) and there are also no safety concerns when sodium propionate is used in meat preparations, processed meat and fish with the maximum level 5,000 mg/kg (7).
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (8)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 281. (9)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, preservative. (10)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1973. (11)
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it Vegan?
Yes, sodium propionate is vegan as the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin so that it can be consumed by vegetarians.
What are the possible Side Effects of Sodium Propionate?
Studies in humans and mice from Harvard in 2019 found that the consumption of propionate may increase the health risk of obesity and diabetes. (12)
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the preservative – sodium propionate (E281), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Comparison with potassium and calcium propionate in bakery uses
- Safety
- FAQs
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Liquid soya letson kulam shilta
Hi Sanjay,
What do you mean?
Hi, thank you for the information!
I have a question, you said that propionates work at pH from 2.5-5.5. How is this pH achieved in a dough mixture? Thank you.
Hi Amab,
Low PH can be obtained by adding acidulents.
Hi, thanks for the information!
I’m currently assessing different preservatives and their efficiency on bread.
What factors must I consider to hypothesise which preservative is best?
I already have the pH of the food source as one but I can’t think of others.
Hi Cue,
Better to have a test yourself to find out which preservative suit your bread best.
Hi ,
How to use sodiam propinate in marsmellows. Plz reply All my massmellows is moldy after one week I added sodiam popainate but a week later it is moldy. Please help me.
My husband bought me a bag of sodium propionate so when i make bread it won’t get moldy as fast but it didn;t tell me how much to use in a recipe for one loaf can you help me?
Is there a reason as to why calcium propionate is the most commonly used in industry, like does it have greater microbe inhibiting qualities than sodium propionate or is it safer?
Hi! Is there any reason why potassium propionate (E283) is not so widely used? I await your response, thank you! Greetings from Argentina