What is Guar Gum (E412) in Ice Cream: Food Uses, Health benefits, Safety, Side Effects

What is it | Property | Uses | Safety | Health benefits | Side effects | FAQs
Guar gum or guaran, a natural food additive derived from the endosperm of seeds from the guar bean which mainly grows in India and Pakistan. It is commonly used as a thickener, emulsifier and stabilizer in ice cream with the European food additive number E412.
This ingredient is keto friendly, vegan, gluten-free and commonly used as a substitute of xanthan gum in food.
What is Guar gum?
Source
According to the FDA’s 21CFR184.1339 definition, that guar gum is a natural substance made from the maceration of the seed of Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (Linne) Taub., or Cyamopsis psoraloides (Lam.) D.C. (1)
Structure
Like in locust bean gum and tara gum, galactomannans also contribute to a large percentage in guar gum, that’s why it can also be chemically described as galactomannans.
Galactomannans are a polymer polysaccharide consists of mannose and galactose with an approximate ratio 2:1 in guar gum, while this ratio is 3:1 in tara gum and 4:1 in LBG.
Following is its structure of galactomannans from EFSA.
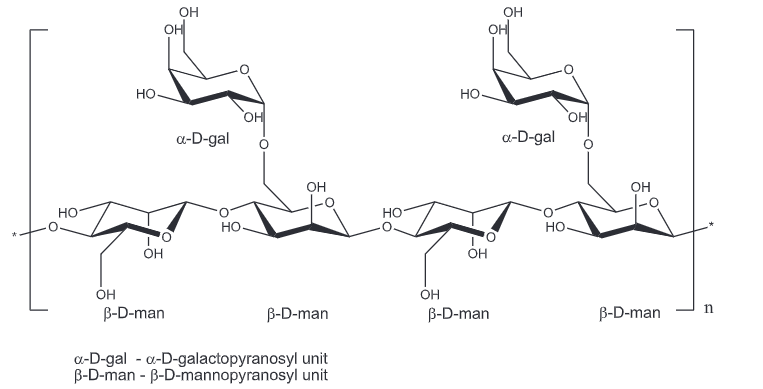
Image Source
What is Guar gum made of?
The food grade of this edible gum is generally composed of:
- Galactomannan guaran not less than 75%
- Protein 5–6%
- Fiber 2.5%
- Moisture 8–15%
- Ash 0.5–0.8%
- Small amounts of lipids
How is Guar gum made?
It is produced in a similar method to other vegetable gums that by milling the endosperm of the seeds.
The manufacturing process is mainly using heat treating to separate endosperm from the husk and the germ. Then milled endosperm to obtain guar gum as the mesh size needed.
The composition of the seed:
- husk (16-18%) on the outside
- germ (43-46%)
- endosperm (34-40%)
It may be further purified by dissolution in water, precipitation and recovery with ethanol or isopropanol. It is called as clarified (purified, extracted) guar gum. Clarified guar gum does not contain cell wall materials and is normally standardised with sugars in the market. (2)
3 types of Guar gum
It can be classified into three types based on the different production methods.
Apart from two types, the common type and clarified guar gum mentioned above, there is another one called partially hydrolyzed guar gum, which is partially hydrolysed by either heat treatment, mild acid or alcaline oxidative treatment for viscosity adjustment.
Specification
Appearance
A white to yellowish-white, nearly odourless powder.
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 9000-30-0 |
| Molecular weight | 50,000 -8,000,000 |
Properties
Solubility
- In water: soluble in cold and hot water.
- In organic solvent: insoluble in ethanol, practically insoluble in organic solvents like oils, greases, hydrocarbons, ketones and esters.
Viscosity
Guar gum can be dispersed in cold or hot water to form a highly viscous solution for its ability to hydrate rapidly in cold water. It exhibits a strong viscosity after dispersed in cold water for about two hours, and the viscosity increases gradually and will reach the highest level in about 24 hours.
Its thickening ability is 5 to 8 times that of the cornstarch, and the highest viscosity is quickly reached by heating.
Like other hydrocolloids, the viscosity of guar gum depends on time, temperature, concentration, the particle size of powder, pH, ionic strength and also the agitation.
Temperature
Generally, the lower the temperature, the higher the viscosity.
In most cases, a lower viscosity was observed by preparing guar gum solutions through heating than the same solutions prepared with cold water. The viscosity of 0.5% (w/w) guar solution at 25°C is significantly higher than that of 37°C. (3)
Concentration
Its solution has the highest viscosity among natural gums and shows very high viscosity even at very low concentration, the viscosity of a 1% aqueous solution is around 4 to 5 Pa.s. It is recommended to use at below 1% concentration in most food.
PH
Due to its non-ionic property, its solution is stable over a wide pH range of about 1.0–10.5.
Its solution is neutral. The following is the viscosity varies with PH values:
| PH Value | Viscosity |
| 3.5 or less | Increase |
| 3.5 to 6 | Decrease following with the pH goes down |
| 6 to 8 | Reach the highest |
| 10 or more | Go down quickly |
Synergy
Guar gum shows viscosity synergy with xanthan gum, gum tragacanth and karaya gum.
Gelling agent
It is not self-gelling but a gel can be formed with small amounts of sodium borate added to its aqueous solution.
What are the uses of Guar gum?
Its powder form is used widely in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and other industries for its thickening, emulsifying, binding and gelling functions.
The application fields are similar to that of LBG and Tara gum, as they’re all galactomannans.
Food
Guar gum is one of the cheapest hydrocolloids used in food like in ice cream, frozen desserts, baked products, dairy products, beverage and so on. It is a multi-functional ingredient with advantages like water retention ability, source of dietary fiber, calories reduction, improvement in ice crystal formation and regulation of rheological properties.
Ice cream
Guar gum acts as a binder and stabilizer in ice cream manufacturing.
Its property of rapid hydration in cold water makes it outstanding as an ice cream stabilizer, especially in a high temperature, short-time processes, for example, under the condition of 80°C for 20–30 seconds. The good quality ice cream can be produced with 0.2% of guar gum.
1. Combination
When used together with calcium sulfate, it gives a dry and stiff ice cream with a retarded meltdown. It is also combined with sodium hexametaphosphate and sodium citrate as a stabilizer in ice cream mixes.
2. What does guar gum do in ice cream?
- Prevent crystal growth and contribute to body, texture and creaminess
- Add fiber and reduce fat
- Increase stiffness
- Reduces crystal formation, Provide a slower and more uniform meltdown
- Prevent lactose crystallization and shrinkage during storage
Bakery
It increases the dough yield and gives baked products a softer texture and a longer shelf life, as well as a fiber supplement. Such as in bread.
Sauces & Salad
It functions as a thickener due to the high viscosity, acid stability & cold water solubility.
Dairy Products
It thickens dairy products such as milk, yogurt and pudding. It improves texture, maintain uniform viscosity and color. Such as in coconut milk to stabilize coconut milk and provides smooth and creamy.
Beverages
Acting as a viscosity controlling agent and reduce calories for low calories beverages.
Pet food
Commonly we can see it in the labels of dog and cat foods. Mainly it acts as a stabilizer and the safety of its uses in animals has been approved by the FDA.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, guar gum can function as a binding, emulsion stabilising, film forming, masking and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (4)
The following products may contain it:
- Hair gel
- Shampoo
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used as an excipient for its disintegrating, binding agent, viscosity-enhancing or thickening properties. For example, it is used to enhance the cohesiveness in the drug powder for forming tablets.
Clinical nutrition
Partially hydrolyzed guar gum ( a low viscosity form, maybe 10-fold lower) is a water-soluble dietary fiber with a wide range of uses in clinical nutrition. It may reduce the incidence of diarrhea in symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. (5)
Laxative
A main ingredient in some bulk-forming laxatives.
Others
Industries uses may include oil drilling & mining, textiles, explosives and paper industry.
Is Guar gum Safe to eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
The FDA claimed guar gum added directly to human food affirmed as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) (6). And it is also safely used as a stabilizer in animal feeding. (7)
It can be used as an anticaking agent, emulsifier, stabilizer or thickener and with other functions in food. (8)
The following food may contain guar gum and with the maximum use levels (9):
- Processed vegetables and vegetable juices: 2.0%
- Fats and oils: 2.0%
- Breakfast cereals: 1.2%
- Gravies and sauces: 1.2%
- Sweet sauces, toppings and syrups: 1.0%
- Dairy products analogs: 1.0%
- Jams and jellies: 1.0%
- Soups and soup mixes: 0.8%
- Cheese: 0.8%
- Milk products: 0.6%
- All other food categories: 0.5%
- Baked goods and baking mixes: 0.35%
EFSA
Guar gum (E 412) is authorised as a food additive in the EU according to Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/20083 and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (10)
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
After the study on genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity and others, EFSA concluded that “there is no need for a numerical ADI for guar gum (E 412), and there is no safety concern for the general population at the refined exposure assessment of guar gum (E 412) as a food additive.” (11)
Uses
Its approved applications are listed separately E412 and in Group I where the uses is quantum satis (QS).
The following foods may contain it (12):
- Fermented cream products
- Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables
- Jams, jellies and marmalades
- Table-top sweeteners in powder and liquid form
- Infant formulae
- Processed cereal-based foods and baby foods
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 412. (13)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickener. (14)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI not specified set since in 1975. (15)
What are the health benefits of Guar gum?
It is a natural fiber meeting the dietary fiber definition of the FDA. And following is its beneficial effects to our body (16):
- Lowering blood glucose and cholesterol levels
- Lowering blood pressure
- Reducing calorie intake
- Increasing the frequency of bowel movements
- Increased mineral absorption in the intestinal tract
What are the possible side effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether guar gum is bad for our health and what are the side effects. We understand that consumers have concerns about ingredients in the foods we eat.
Nowadays there are few reported dangers but some allergic symptoms were observed in the early years. Let’s see it.
Allergy
May cause asthma
It is reported in 1990 that three people whose work was exposed to guar gum had the allergic symptoms like rhinitis and asthma. (17)
May cause flatulence
It is reported to cause flatulence while used for lowering serum total cholesterol levels. Guar gum. (18)
Other possible side effects
In 1992, the diet pill, Cal-Ban 3000 was reported to have serious health problems like esophageal obstruction, small bowel obstruction or even death. Maybe these symptoms were triggered due to guar gum’s water-holding capacity and gel-forming tendency to swell in size 10- to 20-fold. (19)
Pregnant
It is generally safe for pregnant from the EFSA’s study of reproductive and developmental toxicity on animals.
Frequently asked questions
Is it natural?
Yes, from the raw material and the manufacturing process mentioned above we can know it is a natural polysaccharide that comes from the endosperm of seeds of the guar bean.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is halal and we can find several manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free according to the FDA’s definition as guar gum does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan. Guar gum is a vegetable gum which is sourced from the seeds and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is appropriate for vegetarian diets recipes.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the natural, plant-based thickening agent – Guar gum (E412), from the following aspects:
- Properties similar to locust bean gum and tara gum
- Manufacturing process
- Composition
- Three types and their differences: common, clarified and partially hydrolyzed guar gum
- The important characteristics of viscosity
- Details function in ice cream and other food uses
- Health benefits as dietary fiber
- Safety
- Possible side effects caused by its water-absorption ability.
- FAQs: is it vegan, natural, halal, gluten free and etc.
Maybe we’ll witness its market demand rise as one of the 7 authorized dietary fiber by the FDA. What do you think of this ingredient? Let me know in the comments.


