What is Microcrystalline Cellulose/Cellulose Gel E460(i) in Food and Uses?
Microcrystalline cellulose, also known as cellulose gel, or its abbreviation MCC. It is a multi-functional ingredient commonly used as an anticaking agent, binder, thickener or stabilizer. The European food additive number for it is E460(i).
Let’s dip into the navigation to know more this ingredient:
What is Microcrystalline Cellulose?
Definition
MCC is a purified, partially depolymerised cellulose prepared by treating alpha-cellulose, obtained as a pulp from strains of fibrous plant material, with mineral acids. The degree of polymerisation (DP) is typically less than 400. (1)
Structure
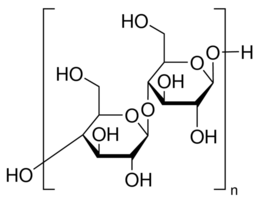
From EFSA
What is MCC Made of?
MCC is a linear polymer composed of repeating beta-D-glucopyranosyl units linked via (1,4) glycosidic bonds.
How is MCC made?
Generally, it is produced by the controlled hydrolysis of highly purified alpha-cellulose made from naturally occurring wood cellulose.
The following are the simple manufacturing process:
Step 1: Alpha-cellulose production
Alpha cellulose is the highest degree of polymerization and is the most stable among the three classes of cellulose: alpha, beta and gamma. It is the major component of wood and paper pulp. (2)
Three types of cellulose all have the same chemical structure but differ in DP: alpha-cellulose DP > 200; beta-cellulose DP 30-200; gamma-cellulose DP 10-30.
Alpha type can be separated from the other components by treating with 17.5% solution of sodium hydroxide as beta and gamma types are soluble while alpha is not.
Step 2: Hydrolysis
In plant fibers, microcrystalline cellulose accounts for about 70% (acid-insoluble), and the rest 30% is amorphous regions of cellulose (acid-soluble fraction).
When treated alpha-cellulose with a dilute mineral acid, e.g. hydrochloric acid to reduce the degree of polymerization, the acid-soluble fraction can be completely hydrolyzed and subsequently obtain the tiny, acid-resistant microcrystalline cellulose.
Properties
Appearance
Fine, white or almost white, odourless, free flowing crystalline powder.
Particle Size
Not less than 5 μm (not more than 10% of particles of less than 5 μm)
Solubility
In water
Insoluble in water, but can swell in water, dilute alkali and acids, and in most organic solvents. Practically insoluble or insoluble in sodium hydroxide solution (concentration: 50 g NaOH/L)
It forms colloidal solutions at the concentration below 1%, and generate thixotropic gels at the concentration above 1%.
In organic Solvents
Insoluble in ethanol, ether and dilute mineral acids.
| Other names | Cellulose, microcrystalline |
| CAS number | 9004-34-6 or 977005-28-9 |
| Chemical formula | (C6H10O5)n |
| Molecular weight | About 36,000 |
| Melting Point | 260–270 °C |
What’s the application of Microcrystalline Cellulose?
It is a naturally non-caloric indigestible dietary fiber that is widely used in food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries. Its primary purpose is as an anticaking agent in food and pharmaceutical processing.
Food
Food grade MCC is commonly used in combination with CMC, or methylcellulose. Also, it is together with starch to improve thickening.
Let’s see its benefits and functions in food categories.
Beverage
MCC stabilizes the liquid, adds viscosity, improves texture, and increases dietary fiber content in beverages, like fruit beverages, soft drinks, nutrition drinks and instant drinks. (3)
Bakery
MCC retains water longer, reduces oil absorption, and strengthens dough structure while softens the dough structure. And therefore prolong the shelf-life of donuts, bakery & pastries.
Also, it ensures the smoothness of the glaze by creating networks between liquid and sugar in glazings, icings, and fillings. (4)
Dairy
Generally, MCC stabilizes emulsions and foam, adds creaminess, replaces fats and oils, acts as an anti-caking agent and flavor carrier, improves flowability and prevents ice crystal growth in frozen desserts, whipped toppings, chocolate milk, cheese, ice cream and so on.
Culinary
MCC provides emulsion stability, forms gels, improves adhesion (icing), enables fat reduction, adds creaminess, modifies texture- thickens with favorable mouth feel in dressing, sauces, dips, soups.
Fried and Processed Food
It can reduce oil intake and fat absorption by adding it to fried food.
In meat, MCC enhances the mouth-feel and texture by providing a fat-like mouthfeel; also, it acts as an emulsifying, stabilizing and binding agent used together with hydrocolloids like sodium alginate and carrageenan.
Tablets
MCC can be used as a binder in tablet manufacturing to increase tablet hardness & also improves the flow properties, such as in vitamin supplement tablets.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, MCC acts as an absorbent, anticaking, bulking, emulsion stabilising, opacifying, stabilising, and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetics and personal care products. (5)
Pharmaceuticals
MCC is an excipient in the pharmaceutical industry as an adsorbent, suspending agent, diluent, disintegrating agent or binder in pills, tablets, capsules and etc. It can be used in both wet-granulation and direct-compression processes.
Is Microcrystalline Cellulose Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
The FDA has claimed that MCC can be used for anticaking agent or free-flow agent, drying agent, flavor enhancer, flavoring agent or adjuvant, formulation aid, humectant, stabilizer or thickener in food. (6)
However, it is not listed in 21CFR as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe). (7)
EFSA
MCC E 460(i) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (8)
Safety re-evaluation in 2017
After the studies of short and long-term toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity and other researches, in 2017, EFSA concluded that “there was no need for a numerical ADI and that there would be no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels for E460(i).” (9)
Authorised Uses and Use Levels
Its approved application is listed in Group I and separately by E460 and E 460(i). The uses in almost all authorised food categories are quantum satis (QS).
The application of Group I please see that of sodium CMC.
The following foods are separately by E460 and E 460(i) and may contain with it (10):
- Table-top sweeteners in tablets and liquid form
- Herbs and spices
- Unflavoured live fermented cream products and substitute products
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 460. (11)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, anticaking, emulsifier, stabilizer. (12)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set in 1997. (13)
What are the possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether microcrystalline cellulose is bad for our health and what are the side effects. There are almost no health risks but some people may be allergic to it and the large amount may cause problems.
Allergy
A case was documented from a woman allergic to MCC (as a binder) in pills in 2012.
Large amounts Side Effect
It was reported by the FDA in 2015, that “in man, consumption of large amounts appears to have no effect other than providing dietary bulk, reducing the nutritive value of such foodstuffs and possibly exerting a laxative effect.” (14)
Is it Safe for Pregnant?
Yes, it is safe but better consult with your doctor for the use condition.
Frequently asked questions
Is MCC Natural?
No, from the manufacturing process mentioned above, we can know it is a chemically modified form of naturally occurring cellulose.
The hydrolysis process breaks the beta -1,4 glycosidic bonds causing a complete structural and functional change from its native form. Therefore, it is classified as a synthetic additive.
Is MCC Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is MCC Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher or maybe kosher passover.
Is MCC Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as it complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is MCC Vegan?
Generally, it is vegan as it produced from cellulose, the plant-based fiber commonly from wood chips and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan as a food ingredient.
Is MCC A Polymer?
Yes, it is a polymer and the degree of polymerization is typically less than 400.
What is Silicified Microcrystalline Cellulose?
A high functionality and multifunctional excipient combined MCC with colloidal silicon dioxide (CSD) providing both optimum compaction and superior flow to formulations. (15)
Can MCC be Made from Corn?
Yes, MCC can be made from corn straw. Also, it can be manufactured from other fiber-rich plants like trees and cotton.
How to Use Microcrystalline Cellulose?
To take full advantage of the functionality of MCC, it is better to mix it well with the main ingredient of the product in the liquid media first to develop its weak gel. Disperse it in a high-speed mixer if in liquid products.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the multifunctional ingredient – microcrystalline cellulose (cellulose gel, E460(i)), from the following aspects:
- Manufacturing processes
- Uses
- Safety
- FAQs
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Feel free to let me know in the comments.



This Anti caking agent 460 causes diahorrea.
I found it in milkshake premix is it safe to consume for young children from age 3 of before and for all the other age groups . Cn we consume that milkshake premix for daily use?