What Is Carrageenan (E407) In Food? Types, Uses, Safety, Side Effects

Sources | 3 Types | Production | Uses | Health benefits | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Carrageenan, a multifunctional ingredient extracted from red algae that are harvested in the sea, commonly used as a gelling agent, thickener, stabilizer in food categories, like meat, jellies, ice creams, and puddings. The European food additive number for it is E407 and E407a (with cellulose content). Generally, it is safe, natural, vegan, halal, kosher and gluten free.
Sources
Carrageenan is located in the cell wall and intercellular matrix of the seaweed plant tissue.
It is a family of linear sulfated polysaccharide present in certain species of red seaweed. It is made of repeating units of sulfated D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-D-galactose.
The following are approved sources of the red seaweed by the FDA (1) :
- Chondrus crispus
- Chondrus ocellatus
- Gigartina acicularis
- Gigartina pistillata
- Gigartina radula
- Gigartina stellata
- Eucheuma cottonii
- Eucheuma spinosum
3 Types of Carrageenan
There are 3 major types of carrageenan, named kappa, iota and lambda.
Their thickening and gelling properties are quite different due to the degrees of sulfation (between 15% and 40%), all types are soluble in hot water and higher of ester sulfate groups mean lower solubility in cold water and lower gel strength.
Kappa is commonly extracted from Eucheuma Cottonii seaweeds (90% harvested from South East Asia), Iota made from Eucheuma Spinosum seaweeds, and Lambda is derived from the seaweeds in South America. Kappa is mostly used in food compared with another two types.
Kappa Carrageenan
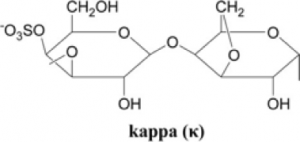
Kappa structure
Also called K carrageenan, produces firm and brittle gel.
- Ester sulfate: only one, the fewest among three types.
- Solubility: at 80⁰C water.
- Gel: gel with syneresis, gelation can be enhanced by the reaction with potassium ions.
- Uses: in meat, canned pet food (dog and cat food), beer production.
Following are the appearance of semi refined and refined kappa.

Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) kappa Powder
Below are the water gel of semi refined and refined kappa.
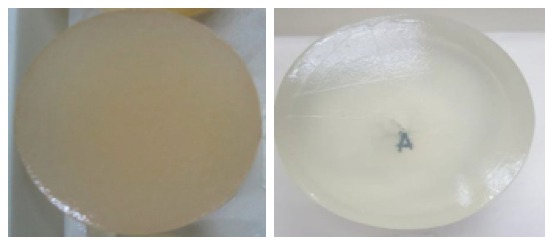
Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) kappa Gel
Iota Carrageenan
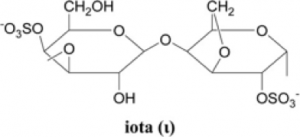
Iota structure
Also called I carrageenan, with two ester sulfates in the structure, it can react with calcium ions to increase the gel strength to form a soft and elastic gel with syneresis free, good freeze-thaw and re-healing properties.
It is partially soluble in cold water and can be used in soft gel capsules and jelly production.
Following are the appearance of semi refined and refined Iota.

Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) Iota Powder
Below are the water gel of semi refined and refined kappa.
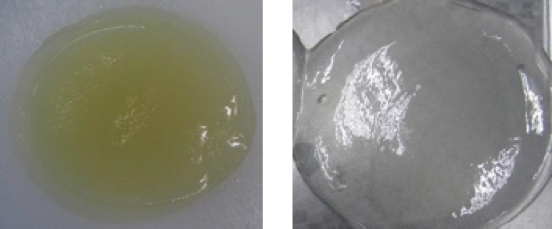
Semi Refined (left) and Refined (right) Iota Gel
Kappa + iota are commonly used together in applications like in ice cream, air freshener gels.
lambda Carrageenan
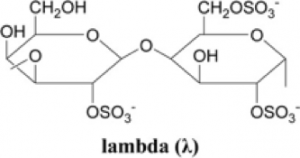
lambda structure
Lambda, with three ester sulfates in the structure, cold water soluble, cannot react with salts to form the gel and only works as a thickening agent to provide viscosity & give texture or body to food. It is used less than K and I type in food application.
The common use is in chocolate milk as it can react with milk.
How is Carrageenan Made?
Every type of carrageenan also can be divided into semi refined and refined forms according to the different manufacturing processes and raw materials.
- Manufacturing processes: During refined carrageenan production the carrageenan is solubilized to remove the cell wall of the seaweed, while the semi refined is made by simple alkaline treatment, without extraction and filtration processes and therefore contains cellulosic structural matrix.
- Raw material: the only approved source for semi refined is Eucheuma Seaweed.
Both are mainly composed of the potassium, sodium, magnesium and calcium sulphate esters of galactose and 3,6-anhydrogalactose polysaccharide, while semi refined contains up to 15 % cellulose of its total weight. (2)
The production of semi refined or refined kappa and iota are similar, the following are the brief kappa carrageenan manufacturing process.
Semi Refined Flow Chart
Semi refined carrageenan is also known as processed eucheuma seaweed with the E number E407a. It is obtained through the following process:
- Seaweeds
- Washing to remove sand, salts and other foreign substances
- Cooking in hot water in saturated brine (potassium chloride) for a short time at the temperature of 70–80°C. Carrageenan cannot be dissolved or extracted in this temperature but low-molecular-mass impurities can be removed.
- Decoloration
- Rinsing in water
- Chopping
- Drying
- Grinding
- Packaging
Refined Extraction Process
- Seaweeds
- Washing to remove sand, salts and other foreign substances
- Cooking in hot water (90 °C) to Paste (seaweed is dissolved)
- Filtration, to remove the insoluble cellulose and other impurities
- Syrup
- Jelification
- Pressing
- Washing in potassium chloride to make the solution to gels and syneresis to remove water
- Pressing
- Drying
- Grinding
- Packaging
What’re the Uses of Carrageenan?
With the advantage of naturally derived, compatible with other food ingredients, easy to use and economical, carrageenan has been used in a lot of food applications, such as in meat, dessert, candy, chocolate milk, beer, ice cream, pet food and so on.
Food grade carrageenan sold in the market are usually diluted with sugars and mixed with other food grade hydrocolloids and salts for obtaining different gelling or thickening characteristics.
Sometimes, carrageenan products consist of both refined and semi-refined types.
Meat
Carrageenan is primarily used in the meat, like ham, sausages, corned beef and luncheon meat. The market share is around 60%-70% of its total consumption.
Kappa carrageenan is mainly used in meat which has high brine gel strength and fine particle size, and is suitable for tumbling or injection processes of meat.
Meat application commonly can be divided into three parts: injected/tumbled meat, emulsified meat can canned meat.
Injected Meat
Brine solution containing water and salt is distributed to whole meat products, such as chicken meat.
Semi-refined kappa carrageenan or the mixture of semi-refined and refined kappa carrageenan are often used as a thickener, binder and stabilizer to improve texture, retain moisture and increase weight yield of meat and make good sliceability.
The common use amount is 0.5 – 1.5% of total ham weight.
Tumbled Meat
Semi-refined Kappa and Iota carrageenan can be used to provide excellent water-holding property; soft texture and uniform consistency.
The common use amount is 1.0 – 2.0% of total sausage weight.
Emulsified Meat
The mix of semi-refined kappa and Iota carrageenan can be used to stabilizes fat-protein emulsion; improve sliceability and mouth feel; enhance water holding capacity (increase yield), freeze-thaw stability and soft texture (tenderness and juiciness); also provide high gel strength and good sliceability.
The common use amount of 0.5 – 1.5% of total sausage weight.
Water Dessert
Refine kappa, iota or the combination carrageenan can produce a transparent, adhesive and highly/moderately elastic water dessert with minimum syneresis and quick-setting.
Jelly
A clear, bright gel made from fruit juice, sugar, carrageenan or other gelling agents to form a gel. The property of viscosity, gel strength, texture, clarity and syneresis are important in the jelly product.
The gelling agent: carrageenan, agar agar and gelatin are commonly involved in the production of jellies or puddings.
How to Make Water Dessert Jelly with Carrageenan?
- Step 1: Weighting ingredients: Sugar (20%), Carrageenan (1%), Citric acid (0.15%), Sodium benzoate (0.1%), Sodium citrate (0.1%), and water (make 100%).
- Step 2: Premix carrageenan with other dry ingredients
- Step 3: Disperse the premix at the vortex of the rapidly agitated water.
- Step 4: Heat to 80°C – 85°C with continuous stirring.
- Step 5: Remove from heat and add Citric Acid at 70°C. Stir then pour into cups and cool to set.
Gummy Candy
Gummy candy is a type of chewable product containing a high sugar content. The content of total soluble solids, gel strength, texture, syneresis are important in the gummy candy. Common ingredients includes water, sweeteners, gelling agent, color, and flavors.
Carrageenan provides desirable elasticity of chewy candies, minimal syneresis, and suitable for people of vegan.
It can be a substitute for gelatin which is commonly used as a gelling and texturizing agent. Or in combination with other hydrocolloids, such as konjac gum and gum arabic.
How to Make Gummy Candy with Carrageenan?
- Step 1: Weighting ingredients: Glucose (40%), Sugar (25%), carrageenan (1.5%), Trisodium citrate (0.3%), citric Acid (0.5%), Flavor (appropriate), Color (appropriate) and Water (make 100%).
- Step 2: Premix half of sugar with Carrageenan and trisodium citrate.
- Step 3: Dissolve glucose and half of sugar in water and heat until 60 oC with continuous stirring.
- Step 4: Gradually add sugar-Carrageenan premix and cook until boiling with continuous stirring.
- Step 5: Add color
- Step 6: Cook solution until it reaches 76 to 80 ºC.
- Step 7: Add citric acid and flavor.
- Step 8: Mix thoroughly and immediately pour into mold while hot.
- Step 9: Cool and solidify.
Chocolate Milk
Carrageenan can be used in chocolate milk as it can keep the cocoa and milk in suspension by interaction with milk proteins. It also imparts homogeneous appearance, provides excellent mouthfeel, and therefore can be used in a wide variety of cocoa and milk types.
How to Make Chocolate Milk with Carrageenan?
- Step 1: Weight ingredients: Sugar (8%), Skimmed Milk (5%), Full-Creamed (5%), Cocoa Powder (1%) , Chocolate Flavor (suitable), Color (suitable), Carrageenan (0.03%) and Water (make 100%).
- Step 2: Dissolve milk powder in water
- Step 3: Mix dry ingredients
- Step 4: Disperse dry ingredients in milk solution
- Step 5: Pasteurization
- Step 6: Cooling and agitation
Beer
Carrageenan can be used in beer to improve wort recovery, yeast vitality and beer clarity; decreases production cost and time by minimizing the use of filter aids.
Dairy Beverage
Blends for dairy applications are mostly composed of kappa and/or iota carrageenan with high milk protein reactivity and system stability. Such as in yogurt, cottage cheese, almond milk, coconut milk and soy milk.
These specially-formulated products provide excellent textural properties with a creamy mouthfeel and good flavor release.
Ice Cream
Carrageenan provides smooth and homogenous meltdown. It increases the viscosity of the ice cream and functions as a stabilizer which imparts ice cream chewiness and smoothness and ensures very fine ice crystals formation.
It also inhibits the precipitation of casein by binding with the casein globules. Sometimes it is used in combination with locust bean gum, guar gum, and sodium alginate.
How to Use Carrageenan Powder to Make Ice Cream?
- Step 1: Weigh ingredients: sugar (15%), milk (10%), butter (8%), carrageenan (0.6%), glucose (4%), water (make 100%)
- Step 2: Premix sugar, carrageenan, and milk (Premix 1).
- Step 3: Dissolve glucose and butter in lukewarm water (Premix 2).
- Step 4: Disperse Premix 1 in Premix 2 with rapid agitation.
- Step 5: Pasteurize in a hot water bath at 70-80 ºC for 15 mins with occasional stirring.
- Step 6: Homogenize using a hand-held homogenizer for 15 sec.
- Step 7: Cool in an ice bath until the solution reaches 15.5 ºC.
- Step 8: Measure ice cream viscosity (before aging) at 15.5ºC using the appropriate spindle.
- Step 9: Age solution overnight at 4 ºC.
- Step 10: Measure ice cream viscosity (after aging) at 15.5ºC using the appropriate spindle.
- Step 11: Feed the solution in an ice cream maker until it forms into a thick and creamy texture.
- Step 12: Collect ice cream into a clean container and store in the freezer.
Pet Foods
Pet foods include dry, canned, semi-moist types, snacks such as biscuits, kibbles and treats. Mainly for dog and cat food.
Carrageenan can bind meat particles, allow homogeneity during pet food processing, provide uniform moisture, contribute easy unmolding and excellent sheen to the finished canned product.
The usage quantity of Carrageenan around 1-2% of the total weight in canned pet food (contains 70 to 80% moisture).
Ingredients in Pet foods
- Liquid: Water, meat broth
- Main components: By-product of meat, poultry, seafood, grains, soybean meal.
- Stabilizer and Gelling Agent: Carrageenan, bean and guar gum, cellulose, starches
- Others: Salt, flavors, vitamins and minerals.
Toothpaste
Carrageenan is used as an emulsifier and thickener to prevent the separation of oil/water mixture and make the toothpaste smooth.
What’re the Health Benefits?
It has 3 of the health benefits as follows:
1. Prebiotic effects
A study in 2015 showed that the red seaweed Chondrus crispusrats has prebiotic benefits on rats. The rats’ gut health and immune modulation are improved by supplementing with this alga which contains 50-65 % carrageenan and is rich in dietary fiber and oligosaccharides. (3)
2. Antioxidant
A study on rats in 2006 suggested that Kappa carrageenan oligosaccharides and their derivatives can increase antioxidant activity in vitro and in a cell system. Its benefits such as work against H(2)O(2) and UVA (long-wave ultraviolet radiation). (4)
3. H1N1 Inhibitor
A study in 2009 found that kappa Carrageenan may inhibit Swine Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus by interfering its life cycles replication. (5)
Is Carrageenan Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved safe by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), and is being used in more than 50 countries.
FDA
Carrageenan may be safely used under 21CFR172.620 and may be found in following food used as a fat replacer, stabilizer, thickener, binders, and texturizer (6):
- Baked goods
- Dressings
- Frozen desserts
- Confections
- Cake and dessert mixes
- Dairy products
- Pudding and gelatin mixes
- Jams and jellies
- Sauces
EFSA
Carrageenan (E407) and processed eucheuma seaweed (E407) are listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (7).
Safety re-evaluation in 2018
No adverse effects of carrageenan were found in the studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive, developmental toxicity and others, but due to the insufficient data, e.g. its different food-grade molecular weight distribution and stability in food, EFSA concluded that the existing group acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 75 mg/kg bw per day is temporary, and would be set again within 5 fives (by 2023). (8)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents” (9)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
Like in Europe, it is listed as the code number 407 and 407a in Australia and New Zealand. (10)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier, gelling agent, stabilizer thickener. (11) (12)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 2007 and in 2014 JECFA concluded the maximum uses level 1000 mg/L of refined carrageenan in infant formula for special medical purposes was safe. (13) (14)
What’re the Possible Side Effects of Carrageenan?
It is common that sometimes consumers have health concerns about whether carrageenan is bad for our health and what are the side effects. Although Carrageenan is a safe ingredient, there may be some possible side effects as follows:
- Intestinal inflammation
- Bloating
- Irritable bowel syndrome and IBD (inflammatory bowel disease )
- Glucose intolerance
Development of Intestinal Inflammation
A study in 2017 found that carrageenan and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) may increase the development of intestine inflammation. (15)
A report in 2018 indicated that more researches needed to be conducted to know the levels of public exposure in our foods, the link between carrageenan with the colon microbiome and inflammation, and the controversies. (16)
Does Carrageenan Cause Cancer?
No. Degraded carrageenan or poligeenan, a carcinogen found to cause cancer in animals in the research in 1982 (17).
Different with carrageenan, the degraded form is not a food additive and not used in any food application (18). Although they’re different, the carcinogenicity of degraded carrageenan is always mistaken link to carrageenan.
Is Carrageenan safe for pregnant?
Yes, it is generally safe, better consult your doctor for the uses under conditions.
Allergy
Carrageenan may cause allergy and intolerance symptoms in sensitive people. A case found that carrageenan is a potential cause of IgE-mediated reactions in unexplained food allergy presentations. (19)
Questions and Answers about Carrageenan
Is Carrageenan Halal?
Yes, it is permissible according to Islamic law and it is certificated with halal.
Is Carrageenan Kosher?
Yes, E407 is kosher as complies with Jewish religious dietary law and meets all the “kashruth” requirements.
Is Carrageenan Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free and can be used in gluten free food and drink. It comes from red algae that complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Is Carrageenan Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as it is a naturally occurring indigestible polysaccharide extracted from red algae, and animal matter or animal-derived products are not involved in the manufacturing processes of both semi refined and refined carrageenan. Therefore, it is suitable to add in the diet of vegetarians.
Is Carrageenan the Same as MSG?
Obviously not, MSG is derived from corn.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a good knowledge of the thickener – carrageenan (E407) from the following aspects:
- Three types and the sources: kappa, iota and lambda
- Two grades and their different production process: refined and semi refined grades
- Food uses: as a gelling agent, thickener and emulsifier
- Approved safety
- Possible side effects
- Some FAQs
What kinds of food packaging have you found this ingredient in? Let me know in the comments.
Featured image Source



My gosh, you are so very thorough and make all this easy to understand, sort of. I just wanted to see what one thing was and went on to read and read! I am saving this site to return to in future. My compliments to you!
Carrageenan itself is safe. However, when it comes into contact with an acid, such as stomach acid, it degrades and goes through a chemical change. It then becomes Poligeenan, which is the equivalent of drinking battery acid or drain cleaner. It degrades linings and encourages bad growth, leading to stomach cancer, IBS, Crohn’s, Colon polyps and cancer, rectal prolapse, and a whole other slew of preventable gastrointestinal issues. Doctors and scientists agree, it is simply too dangerous to test on humans to prove it is in fact harmful to ANY mammal or animal that produces stomach acid. What does the FDA say? “Well, you can’t prove it’s bad, so we consider it ‘generally safe for consumption'”. When I cut it out of my diet, I CURED the IBSD that I’d had for over 20 years. I never even had it! It was carra/poligeenan the entire time causing my intestines to degrade and leak. Too many people blindly trust the FDA, it’s just how we were raised. I can trust them as far as I can throw a 200lb Atlas ball.
Thankyou Kim Tanner I too am have had to cut out carrageenan….I became seriously in I’ll with inflammation from mouth to anus. Burning mouth, lips, stomach, intestines, uretha, arms, feet…I didn’t know what to do until I discovered carrageenan can cause all of the above. Now, if I daily check everything I eat & avoid carrageenan I stay well.
Interesting, I always liked Swiss Gruyère cream until I read the pack and saw this additive. Why they have to contaminate a natural product I do not know.
My wife, 89 years old with dementia has a problem swallowing water or any liquid. She delays swallowing it and chokes on it. I thought that the problem would be solved by feeding her jelly. I chose a jelly, “Simply delish”, which uses carrageenan as setting agent. I am now worried that this particular jelly which sets at room temperature will not liquefy systemically at body temperature and will therefore not become available as a hydrating agent. Am I correct in my assumption? Am I dehydrating my wife?
Hi, Take it easy, that’s would be okay most probably
As above comments say, Carrageenan can cause Intestinal inflammation and Irritable bowel syndrome and IBD.
It did with me and took years to find out it was the cause. I was close to death as developed septicemia from the inflammation.
Thank you for sharing.
I have read several articles about CARRAGEENAN. Industry tends to say it is safe and GRAS,
and the manufacturers of it defend it constantly against criticism. I do not believe that just
because something is considered “safe”, that is always is. There are 79 pages of FDA GRAS
substances, and not all of them are innocuous.
One issue is, HOW is it ‘extracted”. Perhaps that is part of the problem here.
However, several articles/studies say it causes health problems, as stated by other commentors.
I took a gel supplement made with it for 2 years, and I believe it has caused some type of digestive
inflammation. I am stopping the supplement for 2-4 weeks to see if I notice a difference. I
do consume seaweeds from non-toxic oceans, but they never cause any problems.
Carrageenan created alpha gal syndrome
Carrageenan is an ingredient in Costco’s famous rotisserie chicken! Is it safe, and can it cause any intestinal problems or any other medical disorders? Can it cause cancer?