What Is Acesulfame Potassium (E950)? Uses, Safety, Side Effects

Production | Health Benefits | Uses | Safety | Side Effects | Conclusion
Acesulfame potassium, 200 times sweeter than sugar, is an artificial sweetener used in food and beverage to replace sugar by providing a sweet taste with no calories and zero glycemic index, which may be helpful in controlling weight & obesity and benefit to diabetes. The European food additive number is E950. You might also see this ingredient listed as Ace-K or Acesulfame K in the food label.
Ace-K is one of eight approved high intensity sweeteners in the United States by the FDA. The other seven are saccharin (E954), aspartame (E951), sucralose (E955), neotame (E961), advantame (E969), steviol glycosides (E960) and luo han guo fruit extracts.
How is it made?
Ace-K is commercially made from the chemical reactions among sulfamic acid, diketene, triethylamine, acetic acid, sulfur trioxide and potassium hydroxide.
The following is the 5 steps brief manufacturing processes (1):
- Step 1: the reaction among sulfamic acid, triethylamine and acetic acid to synthesize amidosulfamic acid salt.
- Step 2: acetoacetamide salt formed by reacting amidosulfamic acid salt with diketene.
- Step 3: reacting the acetoacetamide salt with a cyclizing agent sulfur trioxide to form a cyclic sulfur trioxide adduct.
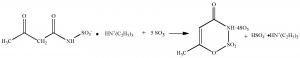
- Step 4: obtaining acesulfame -H by hydrolyzing the cyclic sulfur trioxide adduct.
- Step 5: neutralizing acesulfame-H with potassium hydroxide to obtain the final product.
What are the health benefits?
Ace-k is quickly excreted via the urine unchanged after absorption and no accumulation in our body. It contributes zero calorie, without raising insulin levels, and does not promote dental caries.
Zero Glycemic Index
Acesulfame k cannot be metabolized in the human body so it has a glycemic index with 0. That’s to say, it does not raise blood sugar and insulin levels and therefore it is safe for diabetics.
Tooth friendly
It will not cause tooth decay so it is a suitable ingredient to be added in food for children.
Specification
| Other Names | 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt |
| CAS Number | 55589-62-3 |
| Chemical formula | C4H4KNO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 201.24 |
Properties
Appearance
White crystalline powder.
Sweetness
The sweetness of its 3% solution is approximately 200 times than table sugar, but like sodium saccharin, it has a slightly bitter aftertaste at high concentrations. It shares the same sweetness with aspartame, 2/3 sweet as sodium saccharin and 1/3 sweet as sucralose.
Solubility
Very soluble in water (30g/100ml, 20℃) and slightly soluble ethanol.
Structure
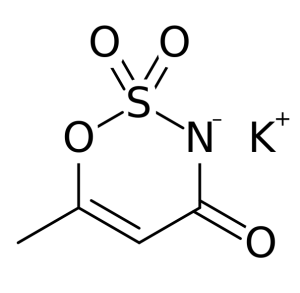
Image Source
What are the uses?
Acesulfame K is commonly used in reduced sugar/calorie food, e.g. soft drinks, table top sweeteners, baked goods, confectionery and dairy products.
It has a bitter aftertaste when used alone so it is usually combined with aspartame to mask its metallic taste and exhibits a synergistic sweet effect, for example, in Pepsi’s zero sugar soda (2).
In Europe, there is an ingredient called “salt of aspartame-acesulfame”, which is made of two molecule aspartame with one molecule acesulfame K, with the E number E962. Ace k can also be blended with sucralose or sugar alcohols to generate a more sugar-like taste.
Ace k is widely used in carbonated drinks for its purpose of good sweet taste and zero calorie, and we can find this ingredient in the label of diet coke feisty cherry and coca-cola zero sugar of Coca-Cola’s products. (3)
Also, ace k functions as a non-caloric and sugar free sweetener in energy drink, such as in Redbull (4) and coffemate of Nestle (5).
Is acesulfame potassium safe?
Yes, the safety used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
May be safely used as a general-purpose sweetener and flavor enhancer in foods. (6)
EFSA
Acesulfame potassium E950 is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “sweeteners” (7).
Authorised Uses And Use Levels
It is listed in a lot of food applications with the maximum usage ranges from 25mg/kg (in beer) to “quantum satis” (in table-top sweeteners). The following energy-reduced or no sugar products may contain it(8):
- Jams jellies and marmalades
- Sauces
- Spreads
- Cocoa and Chocolate products
- Chewing gum
- Ice cream
- Table-top sweeteners
- Dietary foods for weight control diets
- Flavoured drinks
- Desserts
- Fine bakery wares
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Sweeteners” (9)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
In Australia and New Zealand are all with the code number 950. (10)
JECFA
Functional Class: food additives, flavour enhancer, sweetener. (11)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “15 mg/kg bw” set in 1990. (12)
What are the possible side effects?
As a synthesized ingredient, it is common that sometimes consumers have health concerns whether acesulfame potassium is bad for our health and what are the possible side effects. It is generally considered safe as a sugar substitute and with few controversies compared with aspartame. The concerns are focus on the possibility of cancer, headache, allergy, weight gain and so on.
Does acesulfame k cause cancer?
In 2006, controversies say that it may cause cancer and more studies should be performed if it is safe. (13)
Does acesulfame k cause headaches?
Methylene chloride may be used as an organic solvent in the production which is a potential occupational carcinogen that may lead to mental confusion, lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, and headache. (14)
Does acesulfame k upset stomachs?
There is no such solid proof documents so far.
Does acesulfame k cause allergy?
It is seldom associated with allergy and only a case reported in 2014 that a person with sulfite and sulfonamide allergies was also found with hypersensitivities to taurine and acesulfame potassium, all containing a SO3 moiety. (15)
Does acesulfame k cause weight gain?
We always think that it will not lead to weight gain as it is calorie free and no GI response. However, a study in mice in 2017 found that acek influenced gut microbiome and body weight gain was observed in males but not in females. (16)
Is acesulfame k safe during pregnancy?
Yes, it is generally safe but better consult your doctor in the condition of use.
Frequently asked questions
Is it natural?
No, it is chemical synthetic and cannot be naturally found.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. E950 meets all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan friendly as derived from the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is suitable to add it to the diet of vegetarians.
Is it gluten free?
Yes, it is a common ingredient in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. Ace k complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
Acesulfame potassium vs aspartame?
Acesulfame K and aspartame are both artificial sweeteners but with different properties. The following are the major six difference between them:
- Taste: aspartame with no bitter after-taste while ace k has.
- Metabolism in our human body: aspartame will be digested and metabolized whereas ace k does not.
- Calorie: ace k is a non-nutritive high-intensity sweetener without calorie while aspartame contains more than 2% the calories of table sugar.
- Uses: ace k is heat stable to the high temperature of 225℃ and can be used in baking and cooking while aspartame will be decomposed below 100℃ and therefore cannot be applied in bakery.
- Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI): aspartame has a higher ADI 50 mg/kg bw/d, the number for ace k is 15 mg/kg bw/d. (17)
- Safety: aspartame seems less safe than ace k as it produces phenylalanine which is dangerous to people with phenylketonuria (PKU) after digestion. Therefore, some people should be cautious with aspartame and avoid it.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a good knowledge of artificial sweetener – acesulfame potassium (E950), from the production, health benefits in controlling blood glucose and insulin, uses, approved safety and possible side effects. Also with some common FAQs such as is it gluten free, vegan and the comparison with aspartame.
What kinds of food packaging have you found this additive in? Let me know in the comments.


