What is Neotame (E961) in Food and Uses? Neotame vs Aspartame

Production | Uses | Benefits | Safety | Side effects
Neotame, a derivative of aspartame, is a new generation artificial sweetener with the European food additive number E961. It is approximately 6000 times sweeter than sugar, commonly used as a sugar replacement in food and drink with the advantage of heat stability, no-calorie, zero glycemic index, and safe to people with PKU.
How is it made?
Generally, neotame is produced by the reaction between aspartame and 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde under hydrogen pressure. Other raw materials involved in the reactions are methanol (solvent), palladium/carbon (catalyst), and diatomaceous earth (food grade may be used as a filtering aid). (1)
Here is the synthesis reaction:
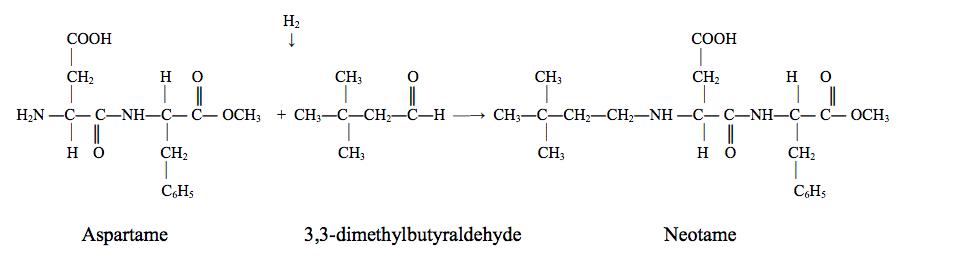
Image Source
Specification
| Other names | N-(N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L-alpha-aspartyl)-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester |
| CAS number | 165450-17-9 |
| Chemical formula | C20H30N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 378.47 |
Properties
Appearance
A white, crystalline powder or granular with a clean, sweet taste.
Structure
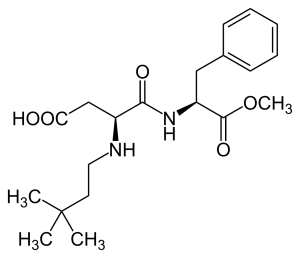
Image Source
Its name comes from its molecular structure, a 6-carbon neohexyl group attached to the amine nitrogen of aspartame.
Solubility
Sparingly soluble in water (solubility in water, 12.6g/L at 25℃, aspartame is 10g/L) and very soluble in alcohol.
Stable than aspartame
Heat stable in 100℃, and can be used at high temperatures for cooking and baking while aspartame cannot. This advantage also enables it to be used in the process of pasteurization and high temperature sterilization, but it would be decomposed if exposed for a long time at 120℃.
Sweetness
It is the sweetest among the category of artificial sweeteners. The following are the sweetness comparison among artificial sweeteners:
- Table sugar 1 (as the base)
- Sodium cyclamate 50
- Aspartame 200
- Acesulfame k 200
- Sodium saccharin 300
- Sucralose 600
- Neotame 6000
Tastes and aftertaste
Taste like sugar, without a bitter, or metallic aftertaste, making it the optimal sugar replacement to use in food and drink products.
What’re the Uses of Neotame?
Since it is 6,000 sweet than sugar, only a very low amount is needed to sweeten the low/reduced-calorie food and drink. Meanwhile, it has better heat stability over aspartame, and thus can be used in cooking and baking products where aspartame cannot.
Neotame is also used to strengthen the sweetness in the blends with other high-intensity sweeteners.
The following food list may contain neotame:
- Chewing gum
- Carbonated soft drinks
- Tabletop sweeteners
- Frozen desserts, yogurt
- Baked goods
- Preserved fruits
- Salad dressings
Bakery
The property of heat-tolerant makes it ideal for baking applications, such as in cookies, cakes and muffins.
Beverages
Stable in carbonated drinks and can be used in powdered drinks and juices to lower the sugar content and reduce the calorie intake while maintaining the sweet taste.
Table top sweeteners
Without hygroscopicity makes it suitable as a sweetener in table-top sweeteners.
Confectionery
This ingredient can be used together with sugar alcohols in confectionery products, such as chocolates, gums, and candies.
Dairy
The stability in high temperature short time can be utilized to produce dairy products, such as yogurts, desserts, and ice creams.
What are the Benefits of Neotame?
Likewise other sugar substitutes, there are main three benefits for neotame:
- Zero calories
- Zero glycemic index
- Safer for people with PKU, compared with aspartame
Zero calories
This property can be applied in food applications to replace sugar to control daily calorie intake.
Zero glycemic index
Its intake will not raise the blood sugar level and insulin response, which can help diabetic keep their blood sugar and thus suitable as a sweetener in their diet.
Safe for Phenylketonurics (PKU)
It is safer for people who suffer from phenylketonuria (PKU) as it doesn’t produce l-phenylalanine (or very little) during the process of metabolism, while aspartame does.
Is Neotame Safe to Eat?
Yes, this non-nutritive sweetener has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Neotame may be safely used as a sweetener and flavor enhancer in food (2). The ADI is 0.3mg/kg bw/d. (3)
EFSA
Neotame (E961) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Sweeteners” (4).
Safety re-evaluation in 2007
After the studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity, along with the degradation products researches, EFSA concluded it was not of safety concern when neotame is intended to be used as a sweetener and flavour enhancer and an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of 0-2 mg/kg bw/day was established. (5)
Approved uses
- When used as a sweetener, neotame is commonly used in energy-reduced or no-added-sugar products with the maximum usage ranges from 2-200mg/kg; or the use levels are “quantum satis” in table-top sweeteners in liquid/powder/tablets.
- When used as a flavour enhancer, its maximum usage is 2mg/kg. (6)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Sweeteners” (7)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 961. (8)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, sweetener, flavor enhancer. (9)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-2mg/kg bw” set in 2003. (10)
What are the possible Side Effects of Neotame?
Is neotame has some health concerns as aspartame? The fact is that it almost has no reported side effects due to the very few phenylalanine it generated, compared with aspartame.
Considering the major metabolic pathway of neotame in humans is de-esterification to NC-00751 and methanol (11), and the low use levels in food, that make the content of the metabolite – l-phenylalanine very little in our body, which is safer for people with PKU.
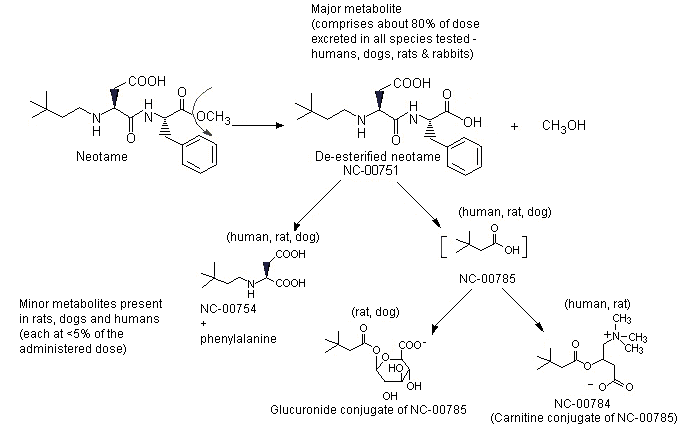
Metabolism of neotame, Image source
Neotame vs Aspartame
Generally, there are mainly four points about their difference:
- Heat stability: defines some applications
- Price: neotame’s price around 1/3 of aspartame
- PKU: mentioned above
- Possible side effects: there are many possible adverse effects around aspartame
The top USA manufacturer – Nutrasweet closed its aspartame factory in 2014, due to the fierce price competition from China, plus the possible dangers (12). Now Nutrasweet is the top neotame brand.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the artificial sweetener – neotame (E961), from the following aspects:
- Production process
- Uses
- Safety
- Benefits
- Comparison with aspartame in uses, metabolism and safety
I’m probably forgetting some information, and if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Guardian Uk article. A sweetener used in cakes, soft drinks and chewing gum can seriously damage people’s health by weakening the gut, a new study has found.
Consumption of even a small amount of the sweetener neotame can lead to someone starting to suffer irritable bowel syndrome, insulin resistance, and even sepsis, a condition that kills about 40,000 in Britain a year.
The findings underlined that some of a new generation of sweeteners that give food products a super-sweet taste can have a “toxic effect” on health, the researchers said.
Dr Havovi Chichger , the senior author of the study, said that while sweeteners could be a healthier alternative to sugar, some could harm consumers.
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/apr/24/cakes-and-drinks-sweetener-neotame-e961-can-damage-gut-wall-scientists-find