What is Calcium Propionate (E282) in Food: Uses, Safety, Side Effects

What is it | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Calcium propionate or calcium propanoate, the calcium salt of propionic acid, is a common bread and meat preservative which functions by inhibiting the growth of mold & other bacterial and therefore prolong food shelf life. It also provides nutritional value as a source of calcium. The European food additive number for it is E282.
What is Calcium Propionate?
It is a new type of food preservative developed in recent decades with its considered safety over sodium benzoate (E211), and price lower than potassium sorbate (E202). Calcium propionate is made from the reaction of propionic acid with calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan as made from the chemical reaction, the raw materials used are both manufactured without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is vegan and appropriate for vegetarians.
Does it Contain Dairy?
No. Calcium propionate is not derived from milk so it is dairy free. People who’re lactose intolerance or with milk allergy can eat the food with it.
Specification
Appearance
A white crystalline powder or granular, possessing not more than a faint odor of propionic acid, stable to heat and light.
Other Names
Calcium propanoate, Calcium dipropionate
CAS Number
4075-81-4
Chemical formula
Ca(OOCCH2CH3)2
Molar Mass
186.22
Structure
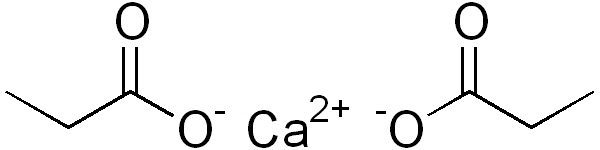
Image Source
Properties
Solubility
- In water: it is freely soluble in water with the solubility 49 g/100 mL (0 °C), and 55.8 g/100 mL (100 °C). It dissociates propanoic acid which has antimicrobial activity.
- In organic solvent: slightly soluble in methanol and ethanol, insoluble in acetone and benzene.
Water solubility is an important property as only dissolved preservatives can have antimicrobial action against microorganisms. That’s why another two preservatives, benzoic acid (E210) and sorbic acid (E200) are not commonly used in food due to their low solubility in water and made to their salts.
PH
PH value is another important role as preservatives need a suitable pH range for their antimicrobial activity. That’s to say, calcium propionate’s ability to inhibit the growth of mold and other microorganisms will be influenced if with an inappropriate PH value.
Studies show that its bacteriostatic and fungistatic activity is better in acid than in neutral or slightly alkaline solution because the antimicrobial action is due to the undissociated acid. It has good activity in the PH below 5.5.
Meanwhile, its addition to food will raise the pH value.
Antimicrobial activity
Calcium propionate is more active than sodium benzoate against molds, but have no activity against yeast, thus making it an ideal choice for bakery products (proper amount at the concentration 0.1-0.4%) that use yeast as an ingredient.
It can also be functioned as mold and rope inhibitors in cheese, non-alcoholic beverages, confections, fillings, frostings, fresh dough, pizza crust, puddings, gelatins, jams, jellies and some meat products.
Propionic acid (E280) will go into the cells of mold and then inhibits the enzyme metabolism; at the same time, it will inhibit microbial growth by competing with alanine or other essential amino acids which are needed for microbial growth. That is the mechanism of calcium propionate work to prevent mold and other microorganisms.
Propionic acid is also a preservative that can be found in natural foods. It has the best preservation activity when compared with calcium propionate and sodium propionate. Sodium propionate is also used as a mold inhibitor, but calcium form is better as it can help reduce sodium levels in food, also provide the nutritional value of calcium.
What are the Uses of Calcium Propionate?
It is used as a preservative in a wide variety of products that include bakery, cheese, meat, dairy products and etc. It is also used for the prevention of milk fever in cattle.
Food
Bread is easy to be contaminated with mold in a hot, humid environment and on the equipment although they were killed during the baking process. Calcium propionate is the mold inhibitor commonly used in bread and other yeast-based bakery goods without interfering with its fermentation as it has no activity against yeast.
In addition, it can enhance calcium nutrition.
Sodium propionate is not recommended to use in bread or rolls because it will delay fermentation of yeast, but it is suggested in the preservation of cakes while calcium (from calcium propionate) alters the action of chemical leavening agents in cakes.
How to Use it in Bread?
It is commonly added with the other ingredients during the dough-mixing process.
How Much to be Used?
Baked goods with low pH (higher acidity) such as bread (ph 5.3-5.8), cheese (Swiss Gruyere cheese PH 5.1 – 6.6), and cakes (angel cake, PH 5.2 – 5.6) require smaller quantities; higher pH products such as cake chocolate (ph 7.2-7.6) require more as the dissociated propionic acid is less.
During periods of high humidity and high temperature, a higher use amount is required.
Feed
Calcium propionate can also function as a mold inhibitor and treat milk fever for swine, ruminant (horses and cattles), poultry, fish, pet and other animal feed.
Metabolism
Calcium propionate will be hydrolyzed to propionic acid and calcium after entering into the feed body. Propionic acid is an important volatile fatty acid, a small amount of it will be converted to lactic acid, and the rest will turn to glucose or provide energy after oxidation. It can be seen that calcium propionate is an important energy substance.
Meanwhile, it is a supplement of calcium which benefits teeth, muscles, nerves, and cells work normally and also build and maintain strong bones.
Treat Milk Fever
Milk fever is a disorder that mainly occurs in dairy cows. The absorption of calcium will be reduced and excretion will be increased after calving, resulting in the calcium concentration below 5.0 mg/dl in the blood which will lead to milk fever and accompanies body function disorder.
Calcium propionate can effectively prevent and treat nutritional metabolic diseases such as ketosis and milk fever.
How to Use it in Feed?
Calcium propionate can be added directly to animal feed in the dry form or dissolved in water before the application due to its good solubility.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, calcium propionate acts as a preservative in cosmetic and personal care products. (1)
Is Calcium Propionate Safe to Eat?
Yes, its safety when used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
Calcium propionate is an antimicrobial agent used in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) as a direct human food ingredient in baked goods, cheeses, confections and frostings, gelatins, puddings, and fillings and jams and jellies. (2)
EFSA
Calcium propionate (E282) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (3)
Safety Re-evaluation in 2014
After the studies of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive & developmental toxicity and other researches, EFSA concluded that “it would not be a safety concern from the maximum concentrations of propionic acid and its salts at their currently authorised uses and use levels as food additives.” (4)
Authorised Uses And Use Levels
Its application is listed together with propionic acid (E280), sodium propionate (E281) and potassium propionate (E283). Its maximum permitted levels (MPLs) ranging from 1000 to 3000 mg/kg in foods. The following foods may contain with it (5):
- Ripened cheese
- Prepacked sliced bread and rye bread, energy-reduced bread; partially baked prepacked bread; prepacked rolls, tortilla and pitta
- prepacked fine bakery wares
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Preservatives” (6)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 282. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, preservative. (8)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1973. (9)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether calcium propionate is bad for our health and what are the possible health risks. We understand that consumers prefer natural preservatives and have concerns about the synthesized ones in the foods we eat. It is generally considered safe but it may have side effects on children and may link to diabetes & autism.
Health Concerns on Children
A study in 2002 found that calcium propionate may cause irritability, restlessness, inattention and sleep disturbance in some children in healthy foods consumed daily. And the adverse reactions can be reduced if lower its concentrations. (10)
Due to this study, an article posted in Forbs in 2018 said that McDonald might be getting rid of calcium propionate. (11)
May Linked to Diabetes and Autism
An article published in MERCOLA in 2019 found that the addition of calcium propionate in food may create an imbalance in gut microbiota, triggering altered neurobehavior and insulin resistance. (12)
Is it Safe for Pregnant?
Yes, it is generally safe but better consult with your doctor in the condition of use.
Frequently asked questions
Is it an Artificial Preservative?
Yes. It is obtained from the chemical synthesis, propionic acid and calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide as the main raw materials. So it is not natural.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, Calcium propionate is kosher. It meets all the “kashruth” requirements and has been certified as kosher. Kosher is a Hebrew word that means fit, proper or correct. Nowadays, it mostly describes food and drink that complies with Jewish religious dietary law.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is typically gluten-free and people with celiacs can eat it. It is an ingredient commonly found in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. The production complying with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the preservative – Calcium propionate (E282), from the following aspects:
- Manufacturing process
- How it works as a preservative, the similarity with sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate
- Uses in food and feed
- Comparison with sodium propionate
- Safety
- Side effects
- FAQs: is it vegan, does it contain dairy, and etc
Where have you seen this additive? Let me know in the comments.



Can calcium propionate be used in making meat pie.?
Whenever I eat anything that contains calcium propionate my skin around my mouth immediately goes dry and cracks .my skin goes dry and itchy. I have learnt that it is not good for people ( children in particular ) with eczema and or asthma. As soon as people with those conditions stop using food with calcium Propionate their condition improves
I began noticing blood blisters forming in my mouth when I ate some bread products. These were painful and appeared almost immediately as soon as I began to chew. After a process of elimination and checking food labels for ingredients, the likely suspect appeared to be calcium propionate. I have eliminated this from my diet, preferring freshly baked bread rather than the wrapped. Generally, I have had no further problems. However, I do occasionally get caught out when it crops up in a product that was not previously under suspicion or the ingredients had changed unnoticed.