What is Propionic Acid (E280) in Food and its Uses?

Source | Production | Mechanism | Uses | Safety | Side effects
Propionic acid, also known as propanoic acid, is a naturally occurring three-carbon carboxylic acid that can be used as a preservative in food with the European food additive number E280. This ingredient is used to inhibit the growth of mold in baked goods and cheeses.
Natural source
It can be found naturally in dairy products such as butter and cheese (1). In our body, it is produced from the breakdown of amino acids and the oxidation of fatty acids. Propionic acid also presents in sweat and brings a vinegar-like smell in certain people. (2)
How is Propionic Acid made?
Propionic acid can be produced by chemical synthesis or bacterial fermentation. The following are the main five manufacturing processes, where the mainstream industrial synthesis is almost dominated by petrochemical processes 1. (3)
- Synthesis from ethylene (petroleum-based), carbon monoxide and steam. The following is the flow chart:
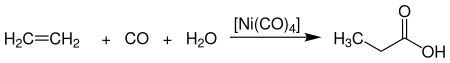
Image Source
- Ethylene is reacted with the mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen to obtain propionaldehyde, and further oxidation of propionaldehyde. Here is the reaction equation:
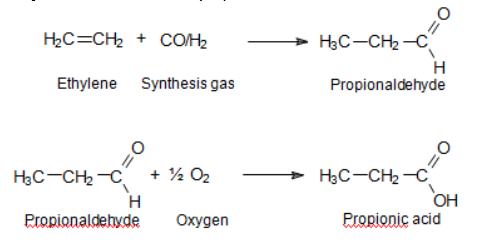
Image Source
- Reaction ethanol with carbon monoxide using boron trifluoride as a catalyst.
- Microbial fermentation with propionibacterium, but there is a way to go before this biosynthesis method is large-scaled used in commercial. (4)
- A byproduct in the pyrolysis of wood.
How Propionic Acid works as a Preservative?
Propionic acid’s mechanism of preservation is similar with that of benzoic acid and sorbic acid. The optimal pH range for its antimicrobial effectiveness is from 2.5 to 5.5.
It is the undissociated form of propionic acid that has antimicrobial activity. The undissociated propionic acid penetrates into the microbial cell membrane and enters into cytoplasm.
And then, propionic acid accumulates and dissociates prone which decreases the internal pH of the microbial and finally prevents the growth of the microbial or even kills them. (5)
Specification
| Other names |
|
| Chemical formula | CH3CH2COOH, C2H5COOH, C3O2H6 |
| CAS Number | 79-09-4 |
| Molecular weight | 74.08 |
| Boiling Point | 141 °C |
| Melting point | -22.4 ºC |
Properties
It is a volatile acid. And unlike with its salts, potassium, sodium propionate and calcium propionate in powder or granular form, it is an oily liquid with a slightly pungent and rancid odor.
Structure
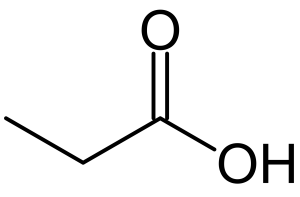
Image Source
Functional group
- Carboxylic acid is active to produce the derivatives of ester, anhydride, amide, and chloride by the reaction of esterification, internal esterification, amine reaction, and substitution reaction respectively.
- Alpha-c of carboxylic acid: halogenation can happen with bromine.
Solubility
- In water: miscible with water.
- In organic solvents: miscible with ethanol and soluble in most organic solvents.
PH
Propanoic acid is a weak acid that dissociates H3O+ and CH3CH2COO- (conjugate base) when it reacts with water. Its PKa value is 4.88, less acidity than benzoic acid and sorbic acid.
The following is the dissociation equation in water.
H3CCH2CO2H(aq) +H2O(l)⇌H3CCH2CO−2+H3O+
Its PH value 3.96 at the concentration of 1nmol/L. (6)
What’re the Uses of Propionic Acid?
Propionic acid is primarily used as a mold inhibitor in food and feed. And due to the activity of carboxylic acid and alpha-c of carboxylic acid in the molecule, it can be made to various derivatives that have a wide application in dyes, textiles, plastics, pesticides, perfumes, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. China exported around 7,200 MT in 2019, with the amounts 9 million USD.
Food
Propionic acid is primarily used as a mold inhibitor which is fungistatic rather than fungicidal. It is effective against molds with concentration ranging from 0.05 to 0.25%. However, less effective in inhibiting the growth of bacterial and no effect on the growth of yeast.
Food-grade propionic acid can be used to produce its salts, calcium propionate and sodium propionate which are commonly used as a preservative in the following food:
- Bread
- Tortillas
- Cheeses
- Cakes
It is also a raw material in the manufacturing of vitamin E.
Animal Feed
Propionic acid in the market is mainly made into ammonium propionate which is used as a preservative in animal feed and grain due to its less corrosive to farm equipment than propionic acid.
The following feed may contain it or ammonium propionate (7):
- High moisture grains such as oats, corn, barley
- Hay
- Drinking water for livestock and poultry
Ammonium propionate is not a food additive, it can be produced by partial neutralization of propionic acid with ammonia or ammonium hydroxide.
Is Propionic Acid Safe to Eat?
Yes, it has been approved as a safe ingredient by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). as well as Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
FDA
Propionic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used as an antimicrobial agent and flavoring agent in food and with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice (8). Meanwhile, it is also GRAS when functioned as a chemical preservative in the feed. (9)
EFSA
Propionic acid (E280) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “Additives other than colours and sweeteners” (10).
Approved uses
Its application is listed together with sodium propionate (E281), calcium propionate (E282) and potassium propionate (E283) with the maximum permitted levels (MPLs) from 1000 to 3000 mg/kg in foods. (11)
Safety re-evaluation in 2014
EFSA stated there was no concern with respect to genotoxicity and carcinogenicity when propionic acid used as a food additive. And no safety concern from the authorised maximum usage. However, an ADI was not allocated due to the available toxicity database. (12)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Others” (13)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 280. (14)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, flavoring agent, preservative. (15)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not limited” set in 1973. (16)
What are the possible Side Effects of Propionic Acid?
Propionic acid is a general safe ingredient, but there may be some side effects as follows:
- Irritation of eyes, nose, and throat or even skin and eye burns. (17)
- Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) (18)
- Other possible health risks: headache, nause, vomit, diarrhea and abdominal pain. (19)
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the preservative – Propionic acid (E280), from the following aspects:
- Five production process
- Uses in food and feed
- Safety
- Possible side effects
If you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



Hi, I am a late diagnosed autistic health professional. I wonder if you know if propionic acid or its salts are used in organic produce in the uk?