What is Erythritol (E968) in Food? Uses, Safety, Side Effects

What is Erythritol? | Health benefits | Uses | Safety | Side Effects | FAQs
Erythritol, a sugar alcohol (or polyol) commonly used as an ingredient in reduced-sugar and low-calorie foods, such as in bakery, beverage, dairy products, chewing gum, chocolate and candies. It is a natural sweetener with 60-80% sweet as sugar, made from carbohydrate fermentation and with the European food additive number E968.
What is Erythritol?
A four-carbon carbohydrate with low carbs and zero calorie, also known as a sugar substitute and bulk sweetener. Like with other sugar alcohols, erythritol will not influence the blood sugar level and so suitable for diabetics, and it can prevent the occurrence of dental caries.
The difference with other sugar alcohols is that erythritol has no calories, a higher amount tolerance (no diarrhea symptoms), and produced by fermentation while other sugar alcohols, such as maltitol, mannitol, xylitol, and sorbitol are made by chemical hydrogenation.
Two types in the market
The pure product is available in powdered and granulated forms.
Natural sources
Erythritol naturally comes from the following sources:
- Fungi: mushrooms, seaweed
- fruits and vegetables: cucumber, pears, grapes
- fermented foods: beer, soy sauce
- human and animal body fluids and tissues: urine, blood
What is it made of?
It is mainly (not less than 99.0%) composed of erythritol, also along with very small compositions of (1) :
- Reducing sugars: not more than 0.3 % expressed as D-glucose
- Ribitol and glycerol: not more than 0.1%
What is it made from?
Mainly sourced from corn starch to produce glucose, may also be obtained from other starch sources (such as tapioca, potato and wheat) and sugar cane.
How is it made?
At present, erythritol is commercially produced by microbial fermentation instead of chemical synthesis, and the microorganisms used are mostly food-grade osmophilic yeasts, such as Moniliella (pollinis and megachilensis), Candida, Pichia, Trigonopsis, Moniliella, Torulopsis, Trichospornides, Hansenula and Yarrowia.
1. Fermentation
In Cargill, erythritol is fermented by feeding food-grade osmophilic yeasts such as Moniliella pollinis with carbohydrate sources, e.g. glucose or sucrose, followed by purification, crystallization and drying. (2)
2. Chemical synthesis
There are also chemical synthesis manufacturing processes available but not used in commercial production for the disadvantages, such as high requirements of the production, severe pollution and safety issues. The brief manufacturing flow is to convert starch into dialdehyde starch, and then hydrogenated to obtain erythritol.
What are the health benefits?
Generally, erythritol has the following six health benefits which will do good for our body when compared with table sugar.
- Zero glycermic index
- Does not raise blood glucose and insulin
- Antioxidant
- Oral health
- Zero calorie
- High tolerance
Zero glycemic index
With glycemic index 0. That’s to say, it does not change blood sugar levels and is safe for diabetics. (3)
Does not spike blood glucose and insulin
Erythritol is a small molecule that can be easily absorbed by the small intestine through passive diffusion. It cannot be digested and broken down in our body as there is no enzyme available in the human body that can metabolize it.
Meanwhile, it does not participate in sugar metabolism and mostly excreted from the urine through the kidney, so erythritol does not raise the body’s blood glucose and insulin levels after entering the human body.
Therefore, erythritol can be used in foods for obesity and people with diabetes.
Antioxidant
Erythritol has antioxidant activity that can effectively remove free radicals in the body, and also has a good inhibitory effect on the generation of free radicals, so it helps prevent vascular damage induced by hyperglycemia. (4)
Oral health
Like other sugar alcohols, erythritol is a noncariogenic carbohydrate sweetener that will not cause dental caries. (5)
In addition, it has anti-caries properties that make it cannot be utilized by pathogenic bacteria such as Streptococcus mutans.
As a result, it is more suitable and safe in children’s food to replace sugar to avoid or reduce the occurrence of dental caries and dental plaque. Such application includes candy, chewing gum and beverage.
Zero calorie
It has a caloric value of 0 and is the lowest energy value among all sugar alcohols. Therefore, it can be used alone or in combination with other sweeteners to replace sucrose (4 kcal/g calories) to make low-calorie foods.
Caloric value of other sugar alcohols (kcal/g) (6):
- Isomalt: 2.0
- Lactitol: 2.0
- Xylitol: 2.4
- Maltitol: 2.1
- Sorbitol: 2.6
- Mannitol: 1.6
High tolerance
The human body is highly resistant to erythritol, so eating foods containing erythritol normally will not cause side effects such as flatulence or mild diarrhea.
Specification
| Other names |
|
| Appearance | White, non-hygroscopic crystalline powder or granular. |
| CAS number | 149-32-6 |
| Chemical formula | C4H10O4 |
| Molecular weight | 122.12 |
| Melting point | 119-123 °C |
Properties
Easy to crystallize, easily soluble in water, high stability to acid and heat. Compared with other sugar alcohols such as xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, and maltitol, erythritol has lower molecular weight and low hygroscopicity.
Solubility
Freely soluble in water (37%, 25ºC) and forms a colorless and very low viscosity solution after dissolving in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in diethyl ether.
Structure
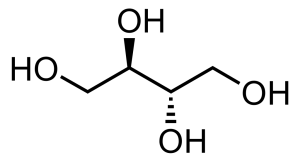
From Wikipedia
Sweetness
Approximately 60%-80% sweetness of sucrose, with a cooling taste.
What Are The Uses?
Erythritol is a multifunctional ingredient that is primarily used in sugar-free or low-sugar food. It is a sweetener with a clear sweet taste similar with that of sucrose but without calories. It not only has excellent processing characteristics, but also has good functional characteristics.
Therefore, it has been applied in many industries such as food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Commonly we may find the following foods contain it:
- Bakery fillings, cakes and cookies, pastries
- Chewing gum, soft and hard candies
- Ice cream, frozen dairy desserts, puddings, yogurt
- Reduced and low-calorie beverages, dairy drinks
- Fat-based cream
- Chocolate
- Desserts
- Fruit canning
Baked goods
It is widely used in bakery products, such as cakes, cookies, and biscuits. Erythritol is used to replace part of sucrose while maintaining good taste, it can also prevent moisture and prolong the shelf life.
Beverage
Erythritol can be used in the production of low-calorie beverages as it reduces the amount of sucrose, e.g. in fruit juice and it has a certain protective effect on vitamin C in fruit drinks.
Meanwhile, it is stable in acidic solution, and provides a clean, sugar-like taste and can mask offensive odors and improve the flavor of the soda. Also, it works well with high intensity sweeteners.
Other drinks:
- Cool beverage: it can be used to make cool drinks as erythritol generates a large endothermic when dissolved.
- Dairy products: the heat-stable properties make it suitable for beverages that require pasteurization and ultra-high temperature sterilization.
Candy
The advantages of erythritol in confectionery are: clean and sugar-like taste, sugar-free, natural, no calories, anti-caries, high tolerance, a cooling taste, non-hygroscopic, and no brown or caramelize (Maillard reactions).
Chocolate
Erythritol has extremely low or no hygroscopicity so the problem of frost caused by moisture absorption will not occur in the production of chocolate. Also, erythritol is easy to pulverize to produce a very fine powder which is required by chocolate.
Ice cream
The addition of erythritol to ice cream can reduce the amount of sugar in ice cream and prevent potential health risks caused by excessive sugar and calories. Erythritol-added ice cream meets the market consumer demand for delicious and healthy ice cream, especially for children and diabetic consumers.
Table-top sweeteners
Erythritol can make the table-top sweeteners free-flowing better due to its non-hygroscopicity. It is usually combined with high intensity sweeteners (e.g. sucralose, sodium saccharin, aspartame, acesulfame k, and stevia) to produce a synergistic effect in sweetness and mask the unpleasant metal aftertaste from high intensity sweeteners.
Toothpaste
Erythritol has been used in toothpaste and mouthwash for its anti-caries properties, promotes plaque breakdown, and helps maintain oral health.
The toothpaste manufacturer, KAO discovered that erythritol can break up bacterial biofilms easily and developed a high concentration of erythritol toothpaste.
Pharmaceutical
Erythritol is a good flavoring agent and excipient for pharmaceuticals and healthcare products. With no hygroscopicity, good flowability, dispersibility and compatibility with various active ingredients, it can be made into tablet, powder, granular, capsule and other dosage forms with other ingredients.
Is erythritol safe to eat?
Yes, its safety used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
FDA has not published that all erythritol in the market are GENERALLY RECOGNIZED AS SAFE (GRAS) so far but it claimed “no question” that Cargill’s erythritol is GRAS when responded to Cargill’s claim for GRAS in 2019. It mainly based on two conditions (7):
- Uses: as a flavor enhancer, humectant, nutritive sweetener, sequestrant, stabilizer and thickener, texturizer, and formulation aid in a certain food.
- Production: through fermentation by Moniliella pollinis
EFSA
Erythritol (E968) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized as “sweeteners” (8).
Authorised uses and levels
Most of its application is listed in Group I with the usage of “quantum satis” for purposes other than sweetening. It can also be used as a carrier in all food additives, flavourings and nutrients. (9)
UK Food Standards Agency
Categorized in “Sweeteners” (10)
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
In Australia and New Zealand are all with the code number 968. (11)
JECFA
Functional Class: food additives, flavor enhancer, humectant, sweetener. (12)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set in 1999. (13)
What are the possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have concerns whether Erythritol is bad for our health and what are the possible side effects. It is generally considered safe but some people may be allergic to it, and it may cause weight gain and large amounts may cause some problems.
Allergy
It may trigger some sensitive symptoms such as headaches and stomach upset. A case of allergic urticaria was reported in 2000, caused by erythritol in canned milk-tea (14).
Weight gain
A study among 264 university freshmen found that erythritol may be associated with obesity. (15)
Large amount
Too much consumption of sugar alcohols may cause gastrointestinal intolerance, e.g. gas, bloating and diarrhea in some people (16). However, our body is more quite acceptable with erythritol than other sugar alcohols, e.g sorbitol. (17)
Is Erythritol safe for Dogs and Cats?
Yes, it is safe and not toxic to pets. A study showed that dogs are well tolerated with erythritol at the daily consumption up to 3.5 g/kg body wt. (18)
Is it safe for Pregnant?
Yes, it is generally safe as polyols naturally present in both maternal and fetal from normal pregnancy (19). But better consult your doctor in the condition of use.
Frequently asked questions
Is erythritol natural?
Yes, it is found naturally and the production process is also natural, similar to the fermentation process of yogurt.
Is it an artificial sweetener?
No, artificial sweeteners commonly refer to aspartame, sucralose, neotame, saccharin, and acesulfame k.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal as it is permitted under the Islamic Law and fulfill the conditions of Halal. And we can find some manufacturers certificated with MUI halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. E968 meets all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is It Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan-friendly as derived from starch and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is suitable to add it to the diet of vegetarians.
Is it Gluten Free?
Yes, it is a common ingredient in both gluten-free and gluten-containing food labels. Erythritol complies with the FDA’s definition of gluten free, that it does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains. And it is generally considered safe for people with celiac disease.
What is the cooling effect of erythritol?
We feel refreshing when it is in our tongue as it has the endothermic effect when dissolving in our mouth with water.
Is it non GMO?
Yes, commonly it is derived from non GMO plants, and the importers always need GMO free documents.
Conclusion
Now I think you may have a knowledge of the natural sweetener- erythritol (E968), from natural sources, production process, six health benefits, uses, approved safety and possible side effects. Also you may be clear with some common FAQs such as is it gluten free, vegan and natural.
What kinds of food packaging have you found this ingredient in? Let me know in the comments.



See Witkowski M, Nemet I, Alamri H, Wilcox J, Gupta N, Nimer N, Haghikia A, Li XS, Wu Y, Saha PP, Demuth I. The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk. Nature Medicine. 2023 Feb 27:1-9.
University paper by UNC and NC State scientists: Erythritol causes blood clots. Should would be outlawed, but ultra wealthy psychos controlling markets stole all the power. Caveat emptor on everything.