What is Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (E463): Two types, Uses, Safety, Side effects

What is it | Property | Uses | Safety | Side effects | FAQs
Hydroxypropyl cellulose, or hydroxypropylcellulose, also referred to its abbreviation HPC. It is made from cellulose and used as a thickening agent in food. It has two types: HPC and L-HPC, the latter is the low-substituted form of HPC, which functions as a binder and disintegrant in the pharmaceutical field.
The European food additive number for both is E463 and E463a, respectively.
What is Hydroxypropyl Cellulose?
It can be divided into two grades, HPC (regular) and L-HPC (short of low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose), depending on the degree of substitution or the amount of hydroxypropoxy groups in the cellulose backbone.
As HPC has a large number of hydroxypropoxy groups than L-HPC, this making HPC soluble in water while L-HPC is not. Due to this characteristic, HPC can be used in aqueous solution whereas L-HPC cannot.
Let’s see the details.
HPC
It is cellulose obtained directly from strains of fibrous plant material and partially etherified with hydroxypropyl groups. HPC can be used as an emulsifier, film former, protective colloid, stabilizer, suspending agent, or thickener in food, may be also used as a binder in dietary supplements.
The following is hydroxypropoxyl groups specification of HPC:
| Assay | Not more than 80.5 % |
| Numbers | Not more than 4.6 per anhydroglucose unit |
| Average Numbers | 3.5 hydroxypropoxy groups per anhydroglucose unit |
| Molecular Weight | From about 30,000 to 1,000,000 |
L-HPC
It is a low-substituted poly (hydroxypropyl) ether of cellulose, manufactured by partial etherification of the anhydroglucose units of pure cellulose (wood pulp) with propylene oxide/hydroxypropyl groups. (1)
The full name is low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose within a small portion of the hydroxypropyl groups in the anhydroglucose unit. The E number E463a which was inserted since 2018. It is used as a binder and disintegrant in tablets or wafers containing dietary supplements of vitamins and/or minerals.
The following is hydroxypropoxyl groups specification of L-HPC (2):
| Other names | Cellulose, 2-hydroxypropyl ether (low substituted) |
| Assay | 5%-16% |
| Numbers | 0.1 to 0.4 per anhydroglucose unit |
| Average Numbers | 0.2 hydroxypropoxy groups per anhydroglucose unit |
| Molecular Weight | From about 30,000 to 1,000,000 |
What is Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Made from?
Cellulose is a polymer of glucose containing hydroxyl groups (-OH) which can be substituted with hydroxypropoxy groups (–OCH2CHOHCH3) to produce HPC. This mechanism is same with that of producing sodium CMC.
The manufacturing process can be furthered as the newly added hydroxyl groups in hydroxypropoxy groups can also be etherified. That’s resulted in the degree of substitute (DS) can be higher than 3.
Generally, the production can be achieved by two steps, alkalinization and etherification.
Step 1: Alkalinization
Disperse the raw material cellulose pulp in an alkali solution (generally sodium hydroxide, 5–50%) to form alkali cellulose.
Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2O
Step 2: Etherification
The reaction of alkali cellulose with propylene oxide is under strictly controlled conditions. In this reaction step, the hydroxyl groups (-OH) on the anhydroglucose monomers of the cellulose chain are partially replaced by hydroxypropoxy groups (–OCH2CHOHCH3) after etherification.
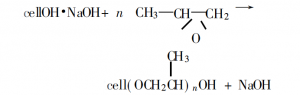
Properties
Appearance
Slightly hygroscopic white or slightly yellowish or greyish odourless and tasteless, granular or fibrous powder.
Solubility
In Water
- HPC: Soluble and swell in water, generate a clear to opalescent, viscous, colloidal solution.
- L-HPC: Insoluble in water; swelling in water. It dissolves in a solution of 10 % sodium hydroxide producing a viscous solution.
In Organic solvent
Soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether.
CAS Number
9004-64-2
Structure
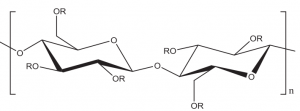
Image Source
Chemical Formula
The polymers contain substituted anhydroglucose units with the following general formula:
C6H7O2(OR1)(OR2)(OR3), where R1, R2, R3 each may be one of the following:
- — H
- — CH2CHOHCH3
- — CH2CHO(CH2CHOHCH3)CH3
- — CH2CHO[CH2CHO(CH2CHOHCH3)CH3]CH3
What are the Uses of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose?
As mentioned above, HPC can be used in food as a thickener, emulsifier and stabilizer in food and cosmetics; while L-HPC is commonly used in pharmaceuticals as a disintegrant and binder for tablets.
Food
Precooked Food
HPC preserves the freshness for hamburger, pizza, chicken and other foods by spraying it on the surface of these foods before cooking. And it can quickly disintegrate within 3 minutes during cooking.
Stabilizer
HPC functions as a stabilizer in ice cream and frozen milk to prolong the storage period and improve the overflow; It is used as a coating for chocolate and prevents the chocolate from softening, oxidation and mold when stored in a frozen temperature.
It is also used to stabilize loose food products. It is excellent in foaming and works well with vegetable oils.
Cosmetics
Per the “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, HPC can work as a binding, emulsifying, emulsion stabilising, film forming, and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (3)
Pharmaceuticals
L-HPC can be used as a disintegrant for its swelling action in water; also, it is good for both wet and dry blending in hard tablets due to its good compressibility and binding ability.
Let’s see the details.
Disintegration
L-HPC absorbs water and significantly expands in volume although it is not suitable in water. This swelling ability accelerates the disintegration and increases the fineness of a tablet dispersion.
L-HPC has better disintegration capability than other disintegrants such as sodium starch glycolate in both vitamin c tablets and aspirin tablets.
Compression
L-HPC can be used as a binder in both direct compression and wet granulation tablets. L-HPC increases the hardness of the tablet than other excipients such as croscarmellose sodium.
And as it is non-ionic it improves the bioavailability of the API. It is almost impossible to react with active ingredients in tablets compared with ionic excipients under the same moisture level.
Treating Dry Eyes
Hydroxypropyl cellulose is an ingredient in many prescriptions for treating dry eyes and other eye disorders, such as keratitis, decreased corneal sensitivity.
Is Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Safe to eat?
Yes, the safety of both HPC and L-HPC used as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), as well as other authorities.
FDA
HPC and L-HPC may be safely used in food (4) AND can be used for emulsifier or emulsifier salt, formulation aid, stabilizer or thickener and texturizer in food. (5)
EFSA
HPC (E463) and L-HPC (E 463a) are listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (6)
HPC Safety re-evaluation in 2017
After the study on genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity and others, EFSA concluded that “there was no need for a numerical ADI and that there would be no safety concern at the reported uses and use levels for E463.” (7)
L-HPC Safety evaluation in 2018
EFSA concluded there would be no safety concern as a food additive in food supplements in solid form (tablet), with a maximum use level of 20,000 mg/kg and a typical use level of 10,000 mg/kg. (8)
Uses
Its approved application is listed in Group I and separately by E463. The uses in all authorised food categories are quantum satis (QS).
The application of Group I please see that in sodium CMC.
The separated list by E463 is only in “Table-top sweeteners in tablets/powder form/in liquid form”. (9):
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 463. (10)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, emulsifier, glazing agent, stabilizer, thickener. (11)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set in 1989. (12)
What are the Possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether HPC is bad for our health and what are the side effects. We understand that consumers prefer natural food and have concerns about synthetic ingredients in the foods we eat. However, it is considered safe and there are rarely reported side effects.
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
No, from the production mentioned above we can know it is synthetical and the compound does not occur naturally.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal and we can find several manufacturers certificated with halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free according to FDA that HPC does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Generally, it is vegan as it comes from cellulose, the plant-based fiber commonly from wood chips and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is considered vegan and suitable for vegetarians.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge the cellulose derivative – Hydroxypropyl cellulose (E463), from the following aspects:
- Two types: HPC and L-HPC
- Manufacturing processes
- Uses in food, and pharmaceuticals
- Safety
- Side effects
- FAQs
Did I miss anything? Let me know in the comments.


