What is Sodium Cyclamate (E952) in food and Why Banned in the US?

Sodium cyclamate Vs Calcium cyclamate | Property | Uses | Safety
Sodium cyclamate, the second oldest artificial sweetener, which has the least sweetness – about 30 times sweeter than sucrose and with the European food additive number E952(ii). This non-caloric sweetener can be used as a sugar substitute to reduce calorie and sugar intake in table-top sweeteners, soft drinks, baked goods, confections, and preserves.
It has been banned for human consumption in the USA due to the potential side effects of cancer by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration since 1970.
Sodium cyclamate Vs Calcium cyclamate
Cyclamates refer to salts of cyclamic acid (cyclohexylsulfamic acid), usually related to its sodium and calcium salts.
Sodium cyclamate is the most used form, while calcium cyclamate can be used as its replacement in low-sodium or sodium-free products. The latter is not used widely as it will cause gelation and precipitation in some applications.
They can be produced by sulfonating cyclohexylamine with chlorosulfonic acid or sulfamate to cyclohexylsulfamate, then neutralization with NaOH or Ca(OH)2.
Property
| Other names | Sodium cyclohexylsulfamate, sodium cyclohexanesulfamate |
| CAS number | 139-05-9 |
| Chemical formula | C6H12NNaO3S (anhydrous), C6H12NNaO3S·2H2O (dihydrate) |
| Molecular weight | 201.22 (anhydrous)
237.22 (dihydrate) |
Two types
Its food grade can be divided into anhydrous and dihydrate forms according to the content of crystal water. The former (NF grade) is needle powder, while the latter (CP grade) with tablet appearance.
Structure
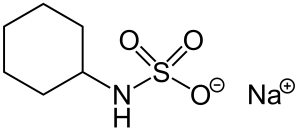
Image Source
Solubility
Soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol, and insoluble in most organic solvents.
Taste
30 times as sweet as sugar, so that only a little amount is needed to achieve the same sweet taste. Without bitter aftertaste which occurs in sodium saccharin.
Synergy
It is commonly blended with sodium saccharin in a 10-to-1 ratio to mask the bitter after taste and produce a synergistic sweetening effect. It can also be blended with aspartame and acesulfame potassium to improve product stability.
Other properties
- Heat stable, so can be used in cooking and baking.
- The lowest price among artificial sweeteners (sucralose, aspartame, acesulfame potassium, neotame, saccharin).
What’re the Uses of Sodium Cyclamate?
With the least sweetness, plus the US restriction, making sodium cyclamate not so popular among commercial artificial sweeteners.
This ingredient is used as a sugar alternative in sugar-free and low-calorie foods and beverages, also be used as a flavoring agent in pharmaceutical (as an excipient) and personal care products (e.g. toothpaste, mouthwash) to mask the unpleasant taste.
The following food may contain it:
- Table-top sweeteners in tablet, powder or liquid form
- Soft drinks
- Breakfast cereals
- Dairy products
- Cakes and baked products
- Dried fruits, preserved vegetables
- Nuts
- Jams, jellies and marmalades
- Chewing gum and candies
- Salad dressings
Benefits
- Zero glycemic index: suitable for diabetics without affecting blood sugar and insulin levels.
- Zero calories: as it is not metabolized for producing energy in the body.
- Teeth friendly: does not promote tooth decay.
Is Sodium Cyclamate Safe to Eat?
Yes, cyclamates has been approved for use as a safe food ingredient (including for tabletop sweeteners) in more than 50 countries, such as in the EU by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), UK by UK Food Standards Agency, Australia & New Zealand by Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
However, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) banned the use of cyclamate in foods in 1970 due to the association with bladder cancer. (1)
FDA
Calcium cyclamate, sodium cyclamate, magnesium cyclamate, and potassium cyclamate are currently prohibited from direct addition or use as human food in the United States. (2).
EFSA
Sodium cyclamate (E952ii) and calcium cyclamate (E952iii) are listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorised food additive and categorized in “ Sweeteners” (3).
EFSA set the ADI of 7 mg per kg of body weight. (4)
Canada
In Canada, sodium cyclamate is not a permitted food additive but can be used as a table-top sweetener, and also as a non-medicinal ingredient in natural health products and drugs. (5)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, sweetener. (6)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “0-11 mg/kg bw” expressed as cyclamic acid set in 1982. (7)
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the artificial sweetener – sodium cyclamate (E952ii), from the following aspects:
- Compare with calcium cyclamate (E952iii)
- Manufacturing process
- Uses
- Safety
- Possible side effects that make it banned in the US.
Did I forget to mention anything about sodium and calcium cyclamate? Do you have any questions or your own experience regarding the food containing it? Let me know in the comments.



Yes, you forgot to mention something about sodium cyclamate. Although bladder cancer in rats may have been the reason stated by the FDA for banning cyclamates (I believe South Korea is the only other country to prohibit it), it has been shown not to have that effect in humans due to different biochemistry between the spaces. Probably the real concern, which was not stated, is that other testing in animals over their lifetime showed a possible connection to irreversible testicular atrophy.
My second post of my comment was to correct some dictation typos.
Let’s be honest here, the only reason that Cyclamate was banned by the FDA was because its introduction to the US Food Market was having a disastrous affect on Sugar sales in the United States. Not really but that is what the Sugar Industry was deathly afraid of, and why they supported the research that found when you fed the human equivalent of 100,000 kg of Cyclamate to rats, they would contract Cancer. The FDA of course jumped on this research a reason to ban Cyclamate. An action by the way, which was only followed by South Korea. All of the rest of the World somehow came to the conclusion that Cyclamate was somehow perfectly safe for human consumption and that there was absolutely NO evidence that it caused Cancer. Funny how that works, isn’t it? Goes to show just how CORRUPT the Food and Drug Administration really is.