What is Pectin (E440)? Sources, Types, Uses, and Benefits

Source | Components | Types | Production | Uses | Safety | FAQs
Pectin, a natural polysaccharide commonly used as a gelling agent, thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer in food with the European food additive number E440. This ingredient is mainly made from citrus peel and apple pomace, and commonly used to gel jams and jellies.
Sources
Pectin occurs naturally in plants and can be found in the cell walls and in the middle layer of the cell of most vegetables and fruits. The sources for commercial production of pectin mainly come from apple pomace and citrus peel. Both derived pectin are high methoxyl pectin.
1. Apple pomace
Apple pomace is the main by-product of apple juice manufacturing. Apples are first processed into juice, and the remaining pomace is used to make pectin. Dry pomace contains around 10% to 20% pectin.
Apple pectin can be used as a thickener in dairy products, a gelling agent for jams and jellies, a blending agent in fruit drinks and a stabilizer in various food processing.
2. Citrus peel
Citrus peel is the most common raw material used to produce pectin than apple pomace as high in pectin. Citrus pectin refers to pectin extracted from the peels of citrus fruits such as lime, lemon, orange and grapefruit.
Citrus peel is the main by-product of citrus fruit processing. Its pectin content accounts for about 20-30% of the dry weight. Compared with other types of pectin, it has strong gelation, high esterification degree, and large molecular weight.
3. Other sources
Pectin content varies according to the types, origin, maturity, storage period and manufacturing processing of plants. The following fruits also contain pectin but with lower content compared with the above two main sources:
- Apricot
- Blackberry
- Cherry
- Peach
- Pineapple
What is pectin made of?
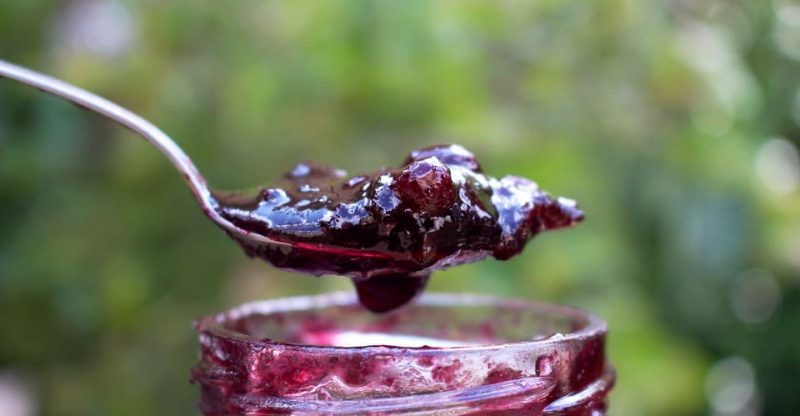
Food grade pectin is a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide, which is made of two parts: more than 65% galacturonic acid, and 35% of other polysaccharides and some little monosaccharides.
D-galacturonic acid
The basic structure of pectin is primarily composed of D-galacturonic acid units, which are polymerized by α-1,4 glycosidic linkages and partially of the carboxyl groups on the galacturonic acid residues occur as methyl esters (methylated).
The rest carboxyl groups on galacturonic acid exist as free acid or in the salt of potassium, sodium, ammonium, calcium and so on.
The percentage of total galacturonic acid reflects the purity of pectin, the content of which should not be less than 65% for its food grade.
Other polysaccharides
Other types of neutral saccharides are connected to the basic structure as side chains. Such saccharides mainly refer to galactose, rhamnose, arabinose, fucose, xylose, mannose and etc.
Degree of esterification or degree of methoxylation
Galacturonic acid is usually estered with methoxy group, amide group and the like. Degree of esterification (DE) is the sum of methylation, acetylation and amidation of polygalacturonic acid on the main chain of pectin.
DM refers to the degree of methylation of polygalacturonic acid on the long chain of pectin. DE has almost the same meaning as DM in pectin.
DE is the main item to distinguish the type of pectin, and it is also an important factor that reflects the physical and chemical properties of pectin, such as solubility, gel properties, and emulsion stability.
DE usually differs due to various raw materials origins and the manufacturing process. It generally ranges from 30% (e.g. sunflower pectin) to 70% (e.g. citrus, apple pectin).
Three types of pectin
There are three types pectin if classified by the degree of esterification (DE):
- High methoxyl pectin (HMP): DE>50% (typically 55–75%)
- Low methoxyl pectin (LMP): DE<50% (typically 20% – 40%)
- Low methoxyl amidated pectin (LMAP): the degree of amidation<25%, 25%<DE<50%
HMP and LMP share the same E number of E450i, while the E number of LMAP is E450ii.
1. High methoxyl pectin
Also called HM pectin, with the DE >50%. It is mainly used to produce high-sugar and high-calorie foods, commonly for making traditional (high sugar) jams and jellies, not suitable for diabetics.
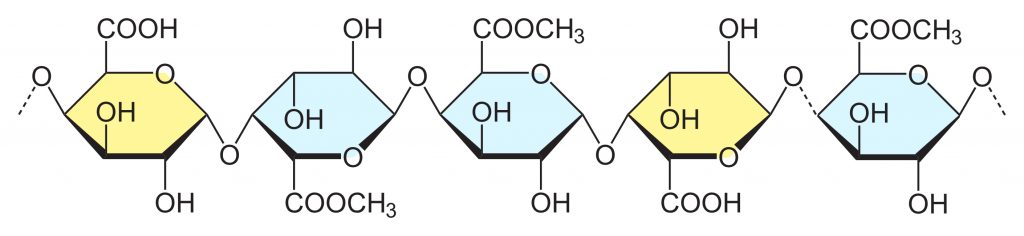
Structure Source
Gel
Gel strength is one of the main properties to measure the quality of pectin. It is the capability to form a gel with the solids (usually sucrose and glucose) under certain conditions.
HM pectin can form heat irreversible gel after cooling in the presence of high content of soluble solids and a low pH. And a high temperature is needed to cook pectin to form a gel, while LM pectin can set at a lower temperature. (e.g. 50 to 70°C)
By the way, pectin forms thermo-reversible gels when a sodium alginate solution is added after cooking.
Gel strength
DE is closely related to the gel strength and speed of gelation (the higher the DE, the faster the gel formation). HM pectin sets quickly at higher temperatures and forms more elastic and brittle gel than LM pectin.
Gel mechanism
HM pectin and LM pectin share different gel formation mechanisms due to different DE values. The gel mechanism of HM pectin is the hydrophobic bond interaction between hydrogen bonds and the methyl ester groups. Such gelling-mechanism is also called sugar-acid-pectin gelation.
DE
The lower the DE value, the longer the setting time and the lower the set temperature needed. HM pectin can be further divided into three types according to the setting time and temperature: rapid set, medium rapid set and slow set.
Rapid & slow set
Rapid set pectin sets quickly at a higher temperature than the nexts. It is suitable for the production of any jams and jellies requiring suspension of fruits, and appropriate for homemaking at small quantities.
Slow set pectin forms gels slowly. It is usually to make large scale jams and clear jellies that don’t require suspension.
PH
The optimal pH for gels is 2.0 – 3.8. It is difficult for high ester pectin to form a gel if the pH value is higher than 3.8; at the same time, gelation degree will be reduced and pectin will be decomposed under the over-acid environment.
Soluble solids content
The gelation of high-ester pectin requires a large amount of soluble solids, generally, the soluble solids content should be higher than 55%. Sugar is usually as the soluble solids and added to promote the gelation.
Pectin content
Gels can be formed when the pectin content is 0.3-0.5%.
2. Low methoxyl pectin
Also called LM pectin, with the DE <50%, which is used to make foods with low sugar and low calories. It is produced by acidification/alkalization/enzymatic de-esterification of HM pectin. It can be applied in low sugar or savory jams and jellies.
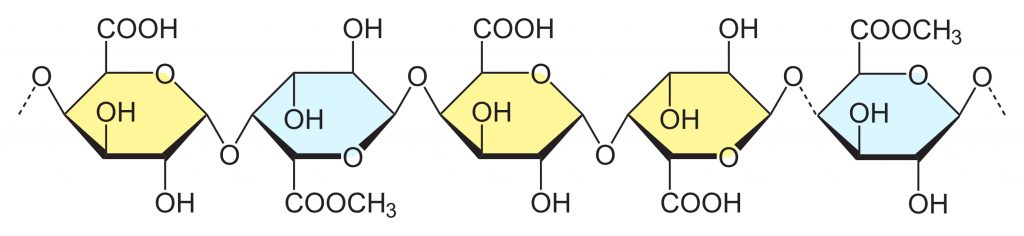
Structure Source
Gel
The gelation of LM pectin has lower requirements for the soluble solid content but the presence of divalent cations is must needed, such as calcium ions (commonly added in the form of calcium lactate instead of calcium chloride, which cannot be used to make delicious jams and jellies because of its bitter flavor).
It can be gelled with low content of soluble solids, and the formed gel is thermally reversible. The higher the degree of esterification, the lower the gel temperature.
Generally, it gels at the following conditions:
- PH: a wide range of pH, from 2.6 to 7.0.
- Soluble solid content: from 10-80%.
Mechanism
The carboxyl groups in pectin can react with calcium ions, which links two carboxyl groups with negative charges. Calcium ions can combine with pectin molecules to form a gel without needing too much sugar compared with HM pectin. This is how LM pectin gel forms.
High methoxyl pectin VS Low methoxyl pectin
Apart from the above comparisons, here are some other differences between them:
- Solubility: the higher the DE of pectin, the less hydrophilic, so HM pectin is less soluble than LM pectin in water or even agglomerate. Solving such problems is to raise the temperature of dissolution.
- Acidic stability: HM pectin can be stable in a pH value ranges from 2.5 to 4.5, while LM pectin can only be stable in a solution with a lower acidity. HM pectin will be converted to LM pectin if too acidic.
3. Low methoxyl amidated pectin
Low methoxyl amidated pectin (LMAP), another kind of LM pectin, is usually obtained by the reaction of HM pectin with ammonia. It cannot be considered as a natural additive.
The carboxyl groups on the galacturonic acid residues of LMAP occur partially as methyl esters and amide esters. The amidation degree (DA) of LMAP refers to amidated galacturonic acid in total galacturonic acid, the food grade of which is usually not more than 25%.
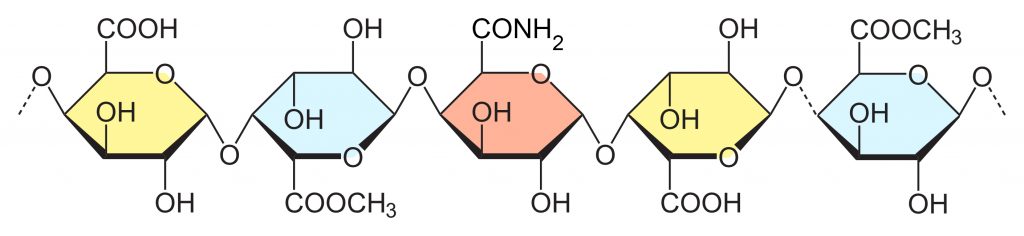
Structure Source
Gel
Compared with common LM pectin with the same DE, the temperature required for gelation of LMAP is lower.
LMAP forms a thermally reversible gel after being heated, melted and cooled. It requires a smaller percentage of Ca2+ concentration (0.1 – 0.3%) to form gels, compared with common LM pectin, which needs 0.3 – 0.5%.
Modified citrus pectin
Also called MCP, a more digestible form of pectin, and therefore can be easily absorbed by the body. It is a low-molecular-weight citrus pectin obtained by hydrolyzing natural pectin to a low degree of esterification and thus a low molecular weight. MCP may have the benefits of suppressing cancer cell growth. (1)
How is Pectin made?
The basic principle used to extract pectin is to decompose the original pectin (in the form of protopectin, pectinic acids, and pectinates) into water-soluble pectin and then separate it from the cellulose, starch, protein, colors, and other components.
Acid extraction
Acidic, enzymatic, and microbiological manufacturing processes are used to extract pectin. The acid extraction method is the commonly used method.
Mineral acids (such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid) or organic acids (e.g. citric acid) are employed to hydrolyze the original pectin into water-soluble pectin, and then obtain crude pectin by ethanol precipitation or metal salt precipitation.
Ethanol precipitation
Ethanol precipitation is occupied as pectin is insoluble in isopropyl alcohol, ethanol and other organic solvents. And follows drying, milling and standardization (usually with sugar).
Enzymatic processing
Enzymes such as esterases, polygalacturonases, and pectin lyases are often used to facilitate the hydrolysis of pectin to different degrees of esterification or polymerization.
Properties
Solubility
Pectin is soluble in hot water. Its solubility is related to the degree of polymerization and the content & distribution of methoxy groups.
Similar to other hydrocolloids, pectin particles are first swell and then dissolved. If the particles are not separated evenly when dispersed in water, the lumps happen. So, it is recommended to pre-blended it with sugar and other ingredients, then dissolved in hot water (85 – 90°C) slowly with a suitable high-speed stirrer.
Viscosity
Pectin can be used as a thickener in food applications, but it exhibits a lower viscosity compared with other thickening agents. Its viscosity is associated with the composition, structure, molecular weight, and DE.
What’re the Uses of Pectin?
Pectin is used widely as a gelling agent in canning jams and jellies; also functions as a thickener, stabilizer and emulsifier in fruit juices, baking, candy, and dairy products. Meanwhile, it is a source of dietary fiber. The global annual output reaches 60,000 tons, but still in short supply.
Pectins can also work with other thickeners in food, such as gelatine, locust bean gum, modified food starch, agar agar, guar gum and gum arabic.
Jams
The use of pectin is primarily in jams, jellies, and marmalades, which are the various types of fruit preserves.
Fruit jam products are the traditional application of pectin where it improves the delicateness, reduces cooking time, provides good fluidity, improves texture & color, and increases the shelf life. The recommended use amount is around 0.2-0.3%.
There are many fruit jam products that can be made with pectin, such as the following list:
- Plum jam
- Raspberry jam
- Peach jam
- Strawberry jam
- Orange marmalade
- Blackberry jam
- Apricot jam
- Blueberry jam
- Rhubarb jam
- Apricot jam
- Tomato jam
- Grape jam
- Mango jam
- Cranberry jam
Jelly
It improves texture, adds flavor, reduces syneresis, enables jelly taste soft and smooth.
Fruit juice and drink
Pectin improves the mouthfeel, helps flavour release, stabilizes other ingredients and provides viscosity for fruit juice or fruit beverages. Also, it is as a soluble fiber in the drink.
Ice cream
With an emulsifying and stabilizing effect, make the finished product have a delicate and smooth taste. The recommended use level: 0.1%-0.2%.
Candy & Gummies
Pectin is an ideal gelling agent to produce high-grade candy and gummies. It imparts a transparent appearance, giving an elastic texture, presents an excellent flavor, and non-stick to teeth, along with a low calorie. The recommended use level: 1.5%-2.5%.
Also, its synergy with gelatine to avoid a low-melting temperature which occurs if only gelatine is used, thus improving the stability of confectionery.
Yogurt
Its purpose is to improve the taste and prolong the shelf life by providing a creamy and thick taste, and stabilize the emulsion.
Health Benefits
Together with cellulose, guar gum, locust bean gum and other three ingredients, pectin is defined as dietary fiber by the FDA, which is good for our health and with the benefits as follows (2):
- Lowering blood glucose/blood pressure
- Maintain blood cholesterol
- Relieve constipation
- Increase in satiety and result in reducing energy intake
Is Pectin Safe to Eat?
Yes, it almost has no side effects and the safety has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), as well as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
EFSA
After the studies of genotoxicity, chronic toxicity, reproductive toxicity, and others, EFSA concluded no need to establish an ADI and no safety concern for the use of pectin (E 440i) and amidated pectin (E 440ii) as food additives. (3)
FDA
Pectin is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and can be used as an emulsifier, stabilizer and thickener in food with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice. (4)
JECFA
Function Class: Gelling agent, thickener, stabilizer, emulsifier. (5)
Acceptable daily intake: ADI “not specific” set since 1981. (6)
Frequently asked questions
Is it Halal?
Yes, pectin is halal and complies with Muslim policy.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free as without wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, pectin is vegan as it naturally exists in fruits and the manufacturing process without using animal-derived products are, so it is suitable to the diet of vegetarians.
How to make jam with liquid and dry pectin?
Commercial pectin is available both in dry powder (white, or light yellow) and liquid. They have the same function to gel a jam or jelly, but not interchangeable and the cooking method for forming gel is different, especially the order of adding sugar.
Liquid pectin can be added after the boiling of sugar and fruit or juice, while sugar is not added until powdered pectin is dissolved and cooked with fruit or juice for some minutes.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the thickener & gelling agent – pectin (E440), from the following aspects:
- Two main fruit sources: apple pomace and citrus peel.
- Three types pectin: HMP, LMP and LAMP categorized by the degree of esterification (DE)
- Manufacturing processes: acid extract, follows ethanol precipitation.
- Food uses: jams, jellies, ice cream, confectionery and yogurt.
- Heath benefits as dietary fiber
- Safety
- FAQs: is it vegan, gluten free, liquid vs dry pectin.
What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in? Or if you have any questions or remarks about this additive, feel free to let me know in the comments.



What kind of pectin should i use for non-alcoholic bevarages ?
I want to add pectin in yogurt.please give me to some information to which pectin use to yogurt for best results.
how to make passion fruit jam with preservative?
It’s a long answer…as you know