What is Tara Gum (E417) in ice cream: Common Uses, Safety, Side Effects

What is it | Property | Uses | Safety | Health benefits | FAQs
Tara gum, a natural ingredient derived from the endosperm of seeds from the tara tree – caesalpinia spinosa plant, which mainly grows in Peru. It is commonly used as a thickener and stabilizer in food and with the European food additive number E417.
What is Tara gum?
Like guar gum and locust bean gum, tara gum is also a galactomannan, which is a high molecular weight polysaccharide made of mannose and galactose approximately in a ratio of 3:1. This ratio is 4:1 in locust bean gum and 2:1 in guar gum.
The difference and similarity of the ratio of mannose and galactose provide tara gum likeness properties to both.
What is Tara gum made of?
This edible gum is generally composed as follows (Tara‐Kern‐Mehl, Benk, 1977):
- Galactomannan 77–78%
- Moisture 14–15%
- Fibers 2.5%
- Nitrogen compounds 3–4%
- Minerals (ash) 1.5%
- Fatty compounds 1%
Structure
The structure of galactomannan (the assay about 75%-80% in common specifications) in tara gum composed mainly of a linear chain of (1-4)-beta-D-mannopyranose units with alpha-D-galactopyranose units attached by (1-6) linkages.
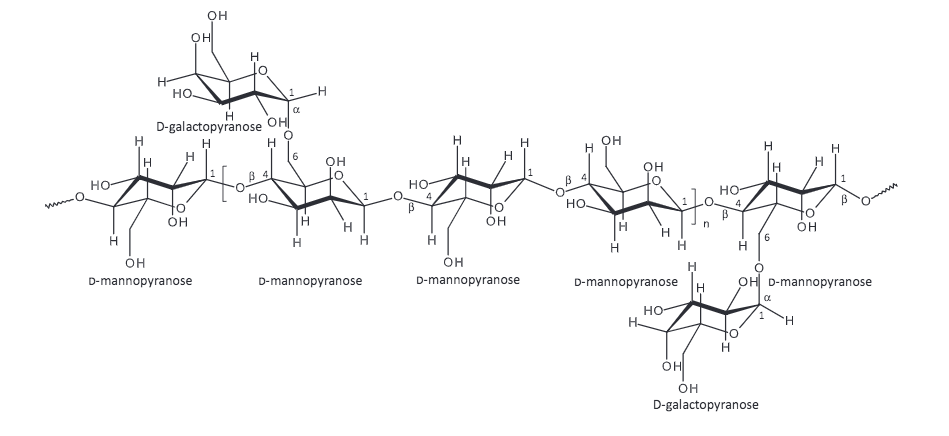
Image Source
How is Tara gum made?
It is a seed gum similar to guar gum and locust bean gum (LBG).
The manufacturing process is similar to that of produce LBG, using acid process or roasting process.
- Acid process: the seeds are treated with sulfuric acid at elevated temperature, and the hull can be removed after washing and brushing operations. Germs and endosperm can be separated in a drying process afterwards.
- Roasting process: the seeds are roasted in a rotating furnace to remove the seed coat and separate germ and endosperm.
Specification
Appearance
White to yellowish-white odourless powder.
| Other names |
|
| CAS number | 39300-88-4 |
| Chemical formula | NA |
| Molecular weight | Between 1,000,000 and 2,330,000 |
Properties
Solubility
- In water: Soluble in hot water and partially soluble in cold water.
- In organic solvent: Insoluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol.
Viscosity
Temperature
Its 1% aqueous dispersion has a viscosity of 2000–3600 cps while the 1% solution has the viscosity around 5,500 cps as tara gum will only produce about 50% viscosity when dispersed in water at room temperature.
Its viscosity can be completely achieved after heating to 85°C for 10 minutes and then cool down.
The viscosity value similar to guar gum and almost three times higher than LBG.
PH
It has a stable viscosity over a wide pH range (pH 3-11). (1)
Synergy
Synergistic effects when combined with carrageenan, xanthan gum or agar to increase viscosity & gel strength and to reduce syneresis.
Gelling agent
A gel can be formed if small amounts of sodium borate are added to its aqueous solution.
What are the applications of Tara gum?
Its food grade provides food manufacturers with many advantages in many different applications. It functions as a stabilizer, thickening agent, and emulsifier in processed foods as well as a wide range of nonfat and low-fat food applications.
Food
Tara gum is a unique hydrocolloid that bridges the gap between the cold soluble, highly galactose guar gum and hot soluble, lower galactose locust bean gum.
Commonly we can find the following food with it: ice cream, frozen products, bakery, jellies, meat and sauce & dressing.
Let’s see the uses and functions.
Ice Cream
Control ice crystal growth and meltdown, provide good mouthfeel.
Dairy Products
Provide cream texture, increase free/thaw stability in frozen desserts, liquid dairy products, puddings, custards, etc.
Bakery Food
Make it soft, moisture retention and prolong shelf life.
Beverage
Add viscosity and clarify the solution.
Jams, jellies, fillings
Reduce syneresis, suspend fruits, improve mouthfeel
Meat
Improved structure, moisture retention and texture.
Also, it can be used as an alternative to locust bean gum and guar gum in some applications for its similarly to guar and LBG.
Cosmetics
Per “European Commission database for information on cosmetic substances and ingredients”, tara gum can function as a film forming, skin conditioning and viscosity controlling agent in cosmetic and personal care products. (2)
Is Tara gum safe to eat?
The safety as a food additive has been approved in Europe. Such information cannot be found (seems has not approved? Please let me know if anyone finds it) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) but has approved in Canada.
Canada Government
Safety
The Government Of Canada claimed the safety of tara gum and listed it in the emulsifying, gelling, stabilizing or thickening Agents from 14th, May. 2018. (3)
Uses
Its approved uses including bread, cream, milk, cheese, ice cream and others with the maximum uses levels not exceed 0.75%. (4)
European Food Safety Authority
Tara gum (E 417) is authorised as a food additive in the EU according to Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/20083 and categorized as “additives other than colours and sweeteners” (5)
Safety Re-evaluation In 2017
After the study on genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive and developmental toxicity and others, EFSA concluded that “there is no need for a numerical ADI for tara gum (E 417) and that there is no safety concern for the general population at the refined exposure assessment of tara gum (E 417) as a food additive at the reported uses and use levels. ” (6)
Uses
Its approved application is listed in Group I and the uses in all authorised food categories are quantum satis (QS).
Food Standards Australia New Zealand
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand with the code number 417. (7)
JECFA
Function Class: food additives, stabilizer, thickener. (8)
Acceptable Daily Intake: ADI “not specified” set since in 1986. (9)
What are the health benefits of Tara gum?
Soluble fiber
Tara Gum is a soluble dietary fiber, which means it has positive effects on the human metabolism. Soluble fibers help regulate the digestive process and the absorption of nutrients into the body.
Low calories
Tara Gum is low in calories and can be used as a fat replacer in many food applications. This is why it is currently being used in many low-fat desserts and frozen food applications.
What are the possible Side Effects?
It is common that sometimes consumers have questions whether tara gum is bad for our health and what are the side effects. We understand that consumers have concerns about ingredients in the foods we eat. However, there were few side effects reported.
Allergy
No reports on the allergic symptoms were found.
Is it safe For pregnant?
Yes, it is generally safe. Tara gum did not induce parental, reproductive or developmental toxicity up to the highest dose tested, 2,500 mg tara gum/kg bw per day from the EFSA’s study of dietary three-generation toxicity and a developmental study in rats.
Frequently asked questions
Is it Natural?
Yes, from the production method mentioned above, we can know it naturally comes from caesalpinia spinosa seeds.
Is it Halal?
Yes, it is generally recognised as halal.
Is it Kosher?
Yes, it is kosher pareve. It has met all the “kashruth” requirements and can be certified as kosher.
Is it Gluten free?
Yes, it is gluten free according to the FDA’s definition as tara gum does not contain wheat, rye, barley, or crossbreeds of these grains.
Is it Vegan?
Yes, it is vegan. Tara gum is a vegetable gum which is sourced from the tara tree seeds and the manufacturing process without the use of animal matter or products derived from animal origin. So it is appropriate for vegetarian diets.
Tara gum VS Locust bean gum?
Tara gum (E417) has the following advantages than LBG:
- A better solubility in cold water.
- A higher galactose content (25%) than LBG (20%), guar gum has 34%.
- Providing a higher solution viscosity than LBG with the same concentration.
- More stable.
- At a lower price.
Tara gum VS Guar gum?
Its advantages as follows:
- Freeze/thaw stability: Tara Gum exhibits high stability than Guar Gum.
- Color: Tara Gum is white while Guar Gum is white to brown.
- Gel: Tara Gum forms a gel when combined with xanthan gum but guar gum with xanthan gum does not form any gel. Tara gum with kappa carrageenan forms a strong gel without syneresis while guar gum does not develop a strong gel with carrageenan and increase syneresis.
Conclusion
Now you may have a knowledge of the natural, plant-based thickening agent – Tara gum (E417), from the following aspects:
- Made of
- Manufacturing processes
- Uses in ice cream, frozen dairy products and so on
- Comparison with another two galactomannans: guar gum and locust bean gum
- Safety
- FAQs: is it vegan, natural and etc.
The increasing demand for low fat and low calorie food may drive the demand for tara gum. Meanwhile, it is a substitute of guar gum due to its similar properties but with a lower price compared. What kinds of food labels have you found this ingredient in or What do you think of this ingredient? Let me know in the comments.



From consuming an ice cream product manufactured by Tropical Foods, Ontario, CA, I suspect a food alergy reaction to tara gum. Eating their ice cream I have blood in my urine. When I urinate during the day my urine is typically a light red. When I urinate first thing in the morning after sleeping on my back my urine is a dark red and I often pass a clot of blood that I’m imagining has coagulated in my urethra or settled in my bladder. I have stopped eating their ice cream and no longer have blood in my urine. This has been a real cause of alarm because last year I underwent a Green Light Laser procedure to trim the size of my prostate and I’m am very cognisant and concerned about any changes, especially blood, in my urine. Another ingredient in this ice cream is guar gum. Should I be equally concerned in consuming guar gum?